
Rain is falling down vertically, to a man walking on road, velocity of rain appears to be 1.5 times his velocity. To protect himself from rain he should hold the umbrella at an angle $\theta $ to vertical. Then $\tan \theta $ is equal to
A. $\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}$
B. $\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}$
C. $\dfrac{2}{3}$
D. $\dfrac{3}{2}$
Answer
556.2k+ views
Hint: Read the given information and draw a vector diagram for the situation to get a better and easy understanding. Then by using trigonometric identities and some geometry calculate the value of $\tan \theta $.
Formula used:
${{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1$
Complete step by step answer:
Let the man be walking on the road with a velocity v. It is given that the rain is falling down vertically. Since the man is moving, the direction of the coming rain will be different with respect to the man. Let the velocity of the rain be ${{v}_{r}}$ in the downward direction.
And let the man move in the direction of the positive x-axis. It is also given that the man has to hold his umbrella at an angle $\theta $ to vertical. This means that the direction of the rain, for the man, is making an angle $\theta $ with the vertical, as shown in the figure.
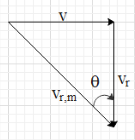
It is said that the speed of the rain with respect to the man is 1.5 times his speed. Then this means that the speed of the rain with respect to the man is equal to ${{v}_{r,m}}=1.5v$
Now, from the figure we get that $\sin \theta =\dfrac{v}{1.5v}=\dfrac{2}{3}$.
Let use the identity ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)}^{2}}+{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1$
$\Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-\dfrac{4}{9}=\dfrac{5}{9}$
$\Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}$, (we shall only consider the positive value since our angle is acute)
Now, we know that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$.
Then,
$\therefore \tan \theta =\dfrac{\dfrac{2}{3}}{\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:We can also directly calculate the value of $\tan \theta $ by first find the value of ${{v}_{r}}$ in terms of v with the help of Pythagoras theorem.
From Pythagoras theorem we get that $v_{r,m}^{2}=v_{r}^{2}+{{v}^{2}}$.
Substitute ${{v}_{r,m}}=1.5v$.
Then,
$\Rightarrow {{(1.5v)}^{2}}=v_{r}^{2}+{{v}^{2}}$`
$\Rightarrow v_{r}^{2}=\dfrac{9}{4}{{v}^{2}}-{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{5}{4}{{v}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{r}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}v$.
Then,
$\therefore\tan \theta =\dfrac{v}{{{v}_{r}}}=\dfrac{v}{\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}v}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}$
Formula used:
${{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1$
Complete step by step answer:
Let the man be walking on the road with a velocity v. It is given that the rain is falling down vertically. Since the man is moving, the direction of the coming rain will be different with respect to the man. Let the velocity of the rain be ${{v}_{r}}$ in the downward direction.
And let the man move in the direction of the positive x-axis. It is also given that the man has to hold his umbrella at an angle $\theta $ to vertical. This means that the direction of the rain, for the man, is making an angle $\theta $ with the vertical, as shown in the figure.

It is said that the speed of the rain with respect to the man is 1.5 times his speed. Then this means that the speed of the rain with respect to the man is equal to ${{v}_{r,m}}=1.5v$
Now, from the figure we get that $\sin \theta =\dfrac{v}{1.5v}=\dfrac{2}{3}$.
Let use the identity ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{2}{3} \right)}^{2}}+{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1$
$\Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-\dfrac{4}{9}=\dfrac{5}{9}$
$\Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}$, (we shall only consider the positive value since our angle is acute)
Now, we know that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$.
Then,
$\therefore \tan \theta =\dfrac{\dfrac{2}{3}}{\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:We can also directly calculate the value of $\tan \theta $ by first find the value of ${{v}_{r}}$ in terms of v with the help of Pythagoras theorem.
From Pythagoras theorem we get that $v_{r,m}^{2}=v_{r}^{2}+{{v}^{2}}$.
Substitute ${{v}_{r,m}}=1.5v$.
Then,
$\Rightarrow {{(1.5v)}^{2}}=v_{r}^{2}+{{v}^{2}}$`
$\Rightarrow v_{r}^{2}=\dfrac{9}{4}{{v}^{2}}-{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{5}{4}{{v}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{r}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}v$.
Then,
$\therefore\tan \theta =\dfrac{v}{{{v}_{r}}}=\dfrac{v}{\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}v}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




