
Radius of the largest circle which passes through the focus of the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4x$ and contained in it is:
(a) $16$
(b) \[5\]
(c) $8$
(d) \[4\]
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: The equation of circle to be considered is ${{\left( x-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-b \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$. Since the given parabola lies along the y-axis, the largest possible circle passing through the focus of the parabola would have its centre on the x-axis. So, we can take the centre as \[\left( b,0 \right)\].
Complete step-by-step solution -
The equation of the parabola given in the question is ${{y}^{2}}=4x$.
We know that the general equation of the parabola is given by ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$. On comparing the parabola in the question with the general form, we get \[a=1\].
We also know that the focus of the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ is $\left( a,0 \right)$. Therefore, the focus for the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4x$ can be obtained as \[\left( 1,0 \right)\]. Let us denote the focus by point $B$ such that we get \[AB=1\], as in the figure below.
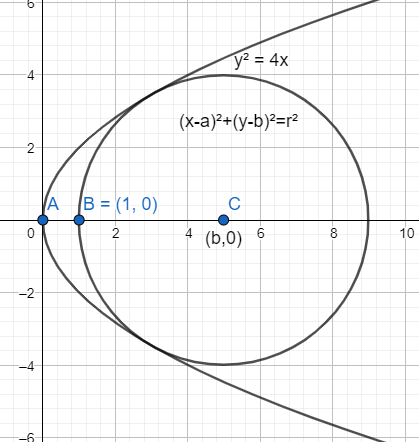
We know that the general equation of a circle is given by ${{\left( x-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-b \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$. Let us consider a circle with center \[\left( b,0 \right)\]. As it is contained in the parabola, by referring to the figure, we can write the radius as \[BC=AC-AB\]. Therefore, we get the radius as $r=b-1$.
Now, we can write the equation of the required circle as
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-0 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( b-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( x-b \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{\left( b-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We also know that the circle touches the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4x$. So, we can substitute ${{y}^{2}}=4x$ in the equation above. So, we get
\[{{\left( x-b \right)}^{2}}+4x={{\left( b-1 \right)}^{2}}\]
We know that $r=b-1$, so we get $b=r+1$. Now substituting this in the equation above, we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-\left( r+1 \right) \right)}^{2}}+4x={{\left( \left( r+1 \right)-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( x-\left( r+1 \right) \right)}^{2}}+4x={{\left( r \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Since we know that \[{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}\], we get
\[{{x}^{2}}-2x\left( r+1 \right)+{{\left( r+1 \right)}^{2}}+4x={{r}^{2}}\]
Since we know that \[{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}\], we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-2xr-2x+{{r}^{2}}+2r+1+4x={{r}^{2}} \\
& {{x}^{2}}-2xr+2x+2r+1=0 \\
& {{x}^{2}}+x\left( 2-2r \right)+2r+1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
In the obtained quadratic equation, we have to put discriminant $=0$ as it will have equal roots because the circle is contained in the parabola.
\[\begin{align}
& {{b}^{2}}-4ac=0 \\
& {{\left( 2-2r \right)}^{2}}-4\times 1\times \left( 2r+1 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Since we know that \[{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}\], we get
\[\begin{align}
& 4-8r+4{{r}^{2}}-8r-4=0 \\
& 4{{r}^{2}}-16r=0 \\
& 4r\left( r-4 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we can get two values as \[r=0,r=4\]. Since the radius can’t be zero, we get the radius of the circle as \[4\].
Therefore, we get option (d) as the correct answer.
Note: In this question, we have to find the radius of the largest circle contained in the parabola. For that, we have to equate the discriminant = 0 as it is the condition for equal roots. If we consider the value of the radius as zero, it becomes a point circle.
Complete step-by-step solution -
The equation of the parabola given in the question is ${{y}^{2}}=4x$.
We know that the general equation of the parabola is given by ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$. On comparing the parabola in the question with the general form, we get \[a=1\].
We also know that the focus of the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ is $\left( a,0 \right)$. Therefore, the focus for the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4x$ can be obtained as \[\left( 1,0 \right)\]. Let us denote the focus by point $B$ such that we get \[AB=1\], as in the figure below.

We know that the general equation of a circle is given by ${{\left( x-a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-b \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$. Let us consider a circle with center \[\left( b,0 \right)\]. As it is contained in the parabola, by referring to the figure, we can write the radius as \[BC=AC-AB\]. Therefore, we get the radius as $r=b-1$.
Now, we can write the equation of the required circle as
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-b \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-0 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( b-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( x-b \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{\left( b-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We also know that the circle touches the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4x$. So, we can substitute ${{y}^{2}}=4x$ in the equation above. So, we get
\[{{\left( x-b \right)}^{2}}+4x={{\left( b-1 \right)}^{2}}\]
We know that $r=b-1$, so we get $b=r+1$. Now substituting this in the equation above, we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-\left( r+1 \right) \right)}^{2}}+4x={{\left( \left( r+1 \right)-1 \right)}^{2}} \\
& {{\left( x-\left( r+1 \right) \right)}^{2}}+4x={{\left( r \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Since we know that \[{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}\], we get
\[{{x}^{2}}-2x\left( r+1 \right)+{{\left( r+1 \right)}^{2}}+4x={{r}^{2}}\]
Since we know that \[{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}\], we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}-2xr-2x+{{r}^{2}}+2r+1+4x={{r}^{2}} \\
& {{x}^{2}}-2xr+2x+2r+1=0 \\
& {{x}^{2}}+x\left( 2-2r \right)+2r+1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
In the obtained quadratic equation, we have to put discriminant $=0$ as it will have equal roots because the circle is contained in the parabola.
\[\begin{align}
& {{b}^{2}}-4ac=0 \\
& {{\left( 2-2r \right)}^{2}}-4\times 1\times \left( 2r+1 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Since we know that \[{{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}\], we get
\[\begin{align}
& 4-8r+4{{r}^{2}}-8r-4=0 \\
& 4{{r}^{2}}-16r=0 \\
& 4r\left( r-4 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we can get two values as \[r=0,r=4\]. Since the radius can’t be zero, we get the radius of the circle as \[4\].
Therefore, we get option (d) as the correct answer.
Note: In this question, we have to find the radius of the largest circle contained in the parabola. For that, we have to equate the discriminant = 0 as it is the condition for equal roots. If we consider the value of the radius as zero, it becomes a point circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




