
: \[P\xrightarrow{{KMn{O_4}/KOH}}Q\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{Soda\lime}}R\xrightarrow[{anhy.AlC{l_3}}]{{C{H_3}Cl}}S\]
If $P$ and $S$ are toluene, $Q$ and $R$ ________ and ________ respectively.
A. Benzaldehyde, Benzoic acid
B. Benzaldehyde, Sodium benzoate
C.Benzoic acid, Benzene
D. Benzene, Benzoic acid
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: The potassium permanganate acts as a strong oxidizing agent and oxidizes the methyl group of toluene into carboxylic acid. The benzoic acid formed would undergo decarboxylation to give benzene. The benzene will react with methyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride to yield toluene.
Complete step by step answer: The series of conversions can be explained one by one.
As we have been already notified that $P$ is toluene, the reaction with alkaline potassium permanganate will yield the product as:
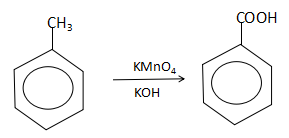
Thus, we can see that the alkaline potassium permanganate acts as a strong oxidizing agent and converts toluene into benzoic acid ($Q$).
Moving to the next step, we can find that the benzoic acid on the reaction with soda lime gets decarboxylated and releases carbon dioxide as the by-product. The reaction can be understood as follows:
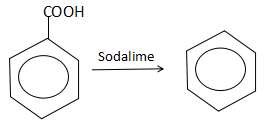
Thus, we observe that a decarboxylation of benzoic acid yields benzene ($R$).
The final step is the reaction of benzene with methyl chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride to yield toluene. The reaction is as follows:
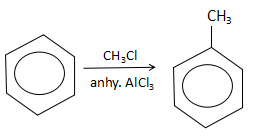
The aluminium chloride extracts a chloride ion to form $AlCl_4^ - $ ion. Due to this, the methyl electrophile is free in the solution. As benzene is a electron rich species and will act as a nucleophile, it will attack on the $CH_3^ + $ ion to yield toluene ($S$).
Thus, the complete reaction sequence is:
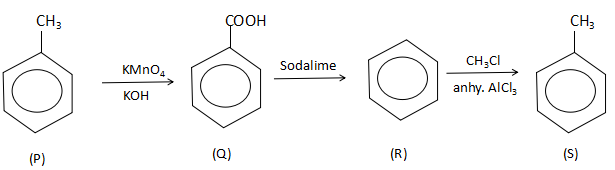
Thus, the correct option is C. Benzoic acid, Benzene.
Note: The conversion of $R$ to $S$ is known as Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction. The anhydrous aluminium chloride acts as a greedy electrophile and attracts the electrons of the chlorine atom from the methyl chloride. But it cannot retain the chloride ion for long and releases it soon to gain back stable$AlC{l_3}$. But this duration is enough for the benzene to attack on the free methyl carbocation and forms toluene. Thus the reagent is retained back after the reaction.
Complete step by step answer: The series of conversions can be explained one by one.
As we have been already notified that $P$ is toluene, the reaction with alkaline potassium permanganate will yield the product as:

Thus, we can see that the alkaline potassium permanganate acts as a strong oxidizing agent and converts toluene into benzoic acid ($Q$).
Moving to the next step, we can find that the benzoic acid on the reaction with soda lime gets decarboxylated and releases carbon dioxide as the by-product. The reaction can be understood as follows:

Thus, we observe that a decarboxylation of benzoic acid yields benzene ($R$).
The final step is the reaction of benzene with methyl chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride to yield toluene. The reaction is as follows:

The aluminium chloride extracts a chloride ion to form $AlCl_4^ - $ ion. Due to this, the methyl electrophile is free in the solution. As benzene is a electron rich species and will act as a nucleophile, it will attack on the $CH_3^ + $ ion to yield toluene ($S$).
Thus, the complete reaction sequence is:

Thus, the correct option is C. Benzoic acid, Benzene.
Note: The conversion of $R$ to $S$ is known as Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction. The anhydrous aluminium chloride acts as a greedy electrophile and attracts the electrons of the chlorine atom from the methyl chloride. But it cannot retain the chloride ion for long and releases it soon to gain back stable$AlC{l_3}$. But this duration is enough for the benzene to attack on the free methyl carbocation and forms toluene. Thus the reagent is retained back after the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




