
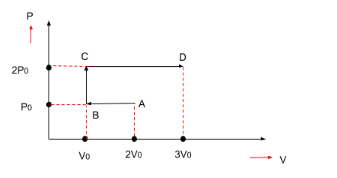
P-V diagram of an ideal gas is shown in figure. Work done by the gas in the process ABCD is-
A.)$2{P_0}{V_0}$
B.)$3{P_0}{V_0}$
C.)${P_0}{V_0}$
D.)$4{P_0}{V_0}$

Answer
600k+ views
Hint: We will find out the work done from point A to point B. from point B to point C, from point C to point D respectively. Then we will add the values of each work done in order to find out the total work done. Refer to the solution below.
Formula used: ${W_{AB}} = P \times \Delta V = area$
Complete answer:
As we know that the work done for the P-V curve is the area under the P-V curve.
First, we will find out the work done from point A to point B.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = P \times \Delta V = area$ (as shown in the figure)
Pressure = ${P_0}$
Volume-
Initial volume is $2{V_0}$
Final volume is ${V_0}$
$ \Rightarrow {V_0} - 2{V_0} = - {V_0}$
Substituting these values in the formula for work done-
$
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = P \times \Delta V \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = - {P_0}\left( {{V_0}} \right) \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = - {P_0}{V_0} \\
$
Now, we will find out the work done from point B to point C.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{BC}} = P \times \Delta V = area$ (as shown in the figure)
Volume in this case will be as zero as can be seen from the figure. Hence, the work done will also be zero.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{BC}} = 0$
Now, we will find out the work done from point C to point D.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{CD}} = P \times \Delta V = area$ (as shown in the figure)
Pressure = $2{P_0}$
Volume-
Initial volume is ${V_0}$
Final volume is $3{V_0}$
$ \Rightarrow 3{V_0} - {V_0} = 2{V_0}$
Substituting these values in the formula for work done-
$
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = P \times \Delta V \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = 2{P_0}\left( {2{V_0}} \right) \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = 4{P_0}{V_0} \\
$
Now, work done in total will be the sum of all the above values-
$
\Rightarrow {W_T} = - {P_0}{V_0} + 0 + 4{P_0}{V_0} \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_T} = 3{P_0}{V_0} \\
$
Hence, it is clear that option B is the correct option.
Note: Gas can work against excessive ambient pressure by extending or compressing it. Work done is often referred to as the amount of pressure-volume or PV. The volume of a gas increases
Formula used: ${W_{AB}} = P \times \Delta V = area$
Complete answer:
As we know that the work done for the P-V curve is the area under the P-V curve.
First, we will find out the work done from point A to point B.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = P \times \Delta V = area$ (as shown in the figure)
Pressure = ${P_0}$
Volume-
Initial volume is $2{V_0}$
Final volume is ${V_0}$
$ \Rightarrow {V_0} - 2{V_0} = - {V_0}$
Substituting these values in the formula for work done-
$
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = P \times \Delta V \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = - {P_0}\left( {{V_0}} \right) \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = - {P_0}{V_0} \\
$
Now, we will find out the work done from point B to point C.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{BC}} = P \times \Delta V = area$ (as shown in the figure)
Volume in this case will be as zero as can be seen from the figure. Hence, the work done will also be zero.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{BC}} = 0$
Now, we will find out the work done from point C to point D.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{CD}} = P \times \Delta V = area$ (as shown in the figure)
Pressure = $2{P_0}$
Volume-
Initial volume is ${V_0}$
Final volume is $3{V_0}$
$ \Rightarrow 3{V_0} - {V_0} = 2{V_0}$
Substituting these values in the formula for work done-
$
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = P \times \Delta V \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = 2{P_0}\left( {2{V_0}} \right) \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = 4{P_0}{V_0} \\
$
Now, work done in total will be the sum of all the above values-
$
\Rightarrow {W_T} = - {P_0}{V_0} + 0 + 4{P_0}{V_0} \\
\\
\Rightarrow {W_T} = 3{P_0}{V_0} \\
$
Hence, it is clear that option B is the correct option.
Note: Gas can work against excessive ambient pressure by extending or compressing it. Work done is often referred to as the amount of pressure-volume or PV. The volume of a gas increases
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




