
Prove that, the normal to ${{y}^{2}}=12x$ at $\left( 3,6 \right)$ meets the parabola again in $\left( 27,-18 \right)$ and circle on this normal chord as diameter is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-30x+12y-27=0$.
Answer
532.2k+ views
Hint: From the question given that we have to prove that, the normal to ${{y}^{2}}=12x$ at $\left( 3,6 \right)$ meets the parabola again in $\left( 27,-18 \right)$ and circle on this normal chord as diameter is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-30x+12y-27=0$. As we know that the general equation of a parabola is ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ and the general point is $\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$, and the general equation of the normal for this parabola is $y+tx=2at+a{{t}^{3}}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
From the above question the given parabola is
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=12x$
Now we will rearrange the given parabola as
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=4\times 3\times x$
As we know that the general equation of a parabola is
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=4ax$
Now compare this with the given parabola equation, we will get,
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=4\times 3\times x=4ax$
$\Rightarrow a=3$
and the general point is
$\Rightarrow \left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$
Now we will compare $\left( 3,6 \right)$ with the general point of parabola,
$\Rightarrow \left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)=\left( 3,6 \right)$
From this we will get,
$\Rightarrow 2at=6$
$\Rightarrow 2\times 3\times t=6$
$\Rightarrow t=1$
As we know that the general equation of normal to the parabola is
$\Rightarrow y+tx=2at+a{{t}^{3}}$
Now we have to substitute the values in their respective position we will get,
$\Rightarrow y+x=6+3$
$\Rightarrow y+x=9$
$\Rightarrow y=9-x$
From the question given that the parabola intersects again with this normal,
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=12x$
In place of y, we will substitute the intersection point $y=9-x$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 9-x \right)}^{2}}=12x$
$\Rightarrow 81-18x+{{x}^{2}}=12x$
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-30x+81=0$
By further simplification we will get,
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-27x-3x+81=0$
$\Rightarrow x\left( x-27 \right)-3\left( x-27 \right)=0$
$\Rightarrow \left( x-27 \right)\left( x-3 \right)=0$
$\Rightarrow x=3,27$
$x=3$is already taken as point of normal and general point of parabola,
So,$x=27$ then
$\Rightarrow y=9-x$
$\Rightarrow y=9-27$
$\Rightarrow y=-18$
Hence the parabola meets normal at $\left( 27,-18 \right)$
Given that this normal chord as diameter then centre of the circle will be the midpoint of these two intersection of normal points with the parabola,
Therefore, the centre is
$\Rightarrow centre=\left( \dfrac{3+27}{2},\dfrac{6-18}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow centre=\left( 15,-6 \right)$
Now the radius of the circle will be the distance from the centre to any of the intersection points, we will find the distance between the centre and the point $\left( 3,6 \right)$ this distance will be the radius.
$\Rightarrow radius=\sqrt{{{\left( 15-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -6-6 \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow radius=\sqrt{{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow radius=12\sqrt{2}$
As we know that the general equation of circle having centre $\left( h,k \right)$ and radius r is
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
From this the required circle equation is
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x-15 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-\left( -6 \right) \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 12\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}$
By further simplification we will get,
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-30x+225+{{y}^{2}}+12y+36=288$
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-30x+12y-27=0$
Therefore, hence proved.
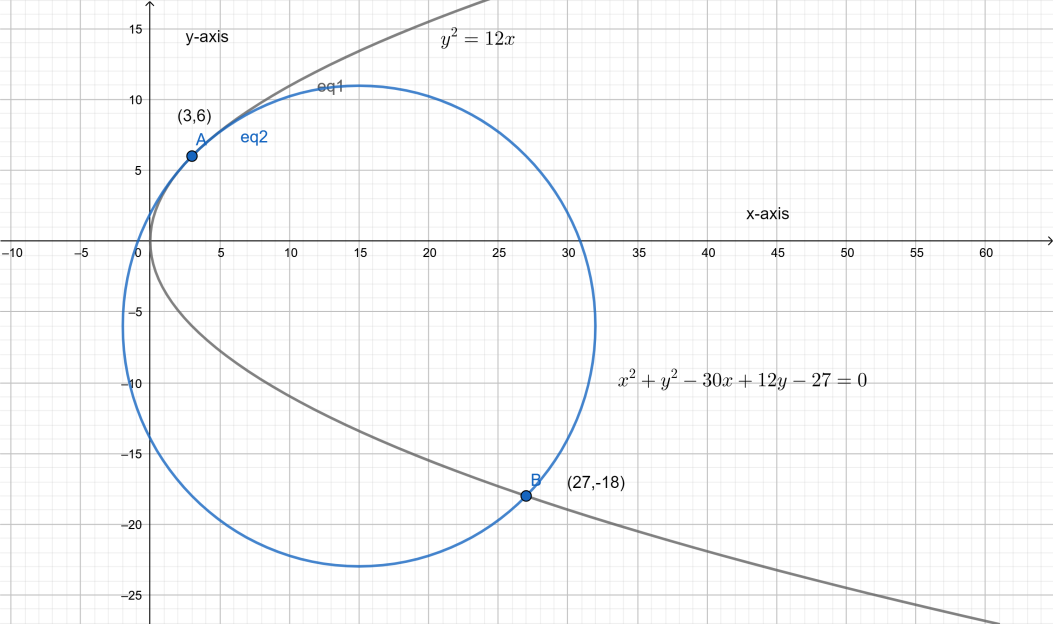
The graph of this would be as follows.
Note: Students should recall all the general equations formulas of parabola and circle before doing this problem. Students should also know that the general equation of parabola having centre $\left( h,k \right)$ is
$\Rightarrow {{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$ . students should be careful while doing the calculations.
Complete step-by-step answer:
From the above question the given parabola is
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=12x$
Now we will rearrange the given parabola as
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=4\times 3\times x$
As we know that the general equation of a parabola is
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=4ax$
Now compare this with the given parabola equation, we will get,
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=4\times 3\times x=4ax$
$\Rightarrow a=3$
and the general point is
$\Rightarrow \left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$
Now we will compare $\left( 3,6 \right)$ with the general point of parabola,
$\Rightarrow \left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)=\left( 3,6 \right)$
From this we will get,
$\Rightarrow 2at=6$
$\Rightarrow 2\times 3\times t=6$
$\Rightarrow t=1$
As we know that the general equation of normal to the parabola is
$\Rightarrow y+tx=2at+a{{t}^{3}}$
Now we have to substitute the values in their respective position we will get,
$\Rightarrow y+x=6+3$
$\Rightarrow y+x=9$
$\Rightarrow y=9-x$
From the question given that the parabola intersects again with this normal,
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=12x$
In place of y, we will substitute the intersection point $y=9-x$
$\Rightarrow {{\left( 9-x \right)}^{2}}=12x$
$\Rightarrow 81-18x+{{x}^{2}}=12x$
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-30x+81=0$
By further simplification we will get,
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-27x-3x+81=0$
$\Rightarrow x\left( x-27 \right)-3\left( x-27 \right)=0$
$\Rightarrow \left( x-27 \right)\left( x-3 \right)=0$
$\Rightarrow x=3,27$
$x=3$is already taken as point of normal and general point of parabola,
So,$x=27$ then
$\Rightarrow y=9-x$
$\Rightarrow y=9-27$
$\Rightarrow y=-18$
Hence the parabola meets normal at $\left( 27,-18 \right)$
Given that this normal chord as diameter then centre of the circle will be the midpoint of these two intersection of normal points with the parabola,
Therefore, the centre is
$\Rightarrow centre=\left( \dfrac{3+27}{2},\dfrac{6-18}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow centre=\left( 15,-6 \right)$
Now the radius of the circle will be the distance from the centre to any of the intersection points, we will find the distance between the centre and the point $\left( 3,6 \right)$ this distance will be the radius.
$\Rightarrow radius=\sqrt{{{\left( 15-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -6-6 \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow radius=\sqrt{{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 12 \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow radius=12\sqrt{2}$
As we know that the general equation of circle having centre $\left( h,k \right)$ and radius r is
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
From this the required circle equation is
$\Rightarrow {{\left( x-15 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-\left( -6 \right) \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 12\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}$
By further simplification we will get,
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-30x+225+{{y}^{2}}+12y+36=288$
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-30x+12y-27=0$
Therefore, hence proved.
The graph of this would be as follows.

Note: Students should recall all the general equations formulas of parabola and circle before doing this problem. Students should also know that the general equation of parabola having centre $\left( h,k \right)$ is
$\Rightarrow {{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( x-h \right)$ . students should be careful while doing the calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




