
Prove that the locus of the center of a circle, which intercepts a chord of a given length \[2a\] on the axis of \[x\] and passes through a given point on the axis of \[y\] distant \[b\] from the origin, is the curve
\[{{x}^{2}}-2yb+{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]
Trace this parabola.
Answer
623.1k+ views
Hint: First, find the locus by considering the given condition in the coordinate plane. Then compare it with parabola \[{{\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}=4a\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the center of the circle be \[\left( h,k \right)\] whose \[x\] intercept is equal to \[2a\]and passes through \[\left( a,b \right)\] on the \[y\] axis.
Length of chord \[AB=2a\].
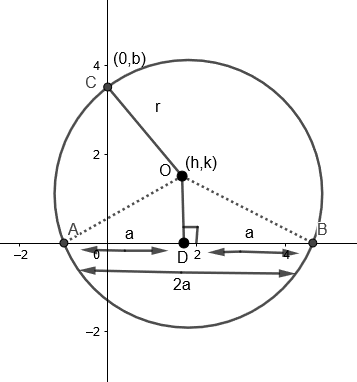
As \[\left( h,k \right)\] is center and axis on circumference.
Therefore, \[OC=\text{radius = }r\]
By distance formula,
\[OC=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[r=\sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-b \right)}^{2}}}\]
Squaring both sides,
We get \[{{r}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{\left( k-b \right)}^{2}}....\left( i \right)\]
Construct \[OD\] which is perpendicular to \[AB\].
As \[OA\] and \[OB\] are the radius of the circle.
Therefore, \[OA=OB=r....\left( ii \right)\]
Hence, \[\Delta OAB\] is an isosceles triangle.
Therefore, we get \[AD=DB=a....\left( iii \right)\]
Now by Pythagoras theorem,
\[A{{D}^{2}}+D{{O}^{2}}=A{{O}^{2}}\]
\[{{a}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\left[ \text{From equation }\left( ii \right)\text{and}\left( iii \right) \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{\left( k-b \right)}^{2}}\left[ \text{From equation }\left( i \right) \right]\]
Also, \[\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\]
Rearranging the equation we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}-2b+{{b}^{2}}\]
Or, \[{{h}^{2}}-2bk+{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]
Replacing \[h\] with \[x\] and \[k\] with \[y\] to get locus.
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-2yb+{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]
Hence proved.
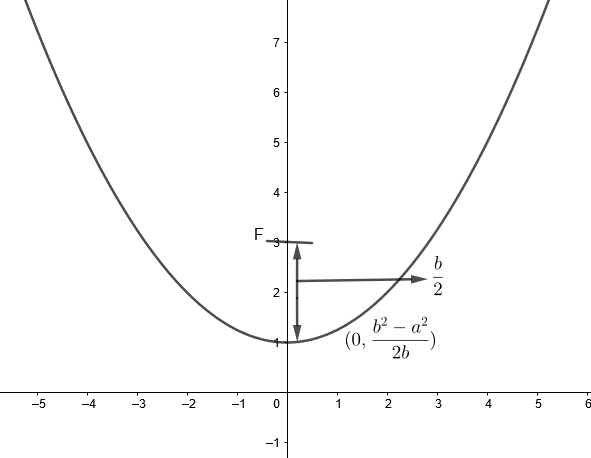
Tracing parabola,
\[{{x}^{2}}-2yb+{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]
\[{{x}^{2}}=2yb+{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\]
\[{{x}^{2}}=2b\left[ y-\dfrac{\left( {{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}{2b} \right]\]
Comparing with
\[{{\left( x-0 \right)}^{2}}=4a{{\left[ y-{{y}_{1}} \right]}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore \]Given parabola has vertex at \[\left[ 0,\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{2b} \right]=\left( 0,{{y}_{1}} \right)\]and focal length \[\left( a \right)=\dfrac{2b}{4}=\dfrac{b}{2}\]
Note: Always rearrange the equation to get standard form. Try to get into minimum variables by always taking use of andaxis.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the center of the circle be \[\left( h,k \right)\] whose \[x\] intercept is equal to \[2a\]and passes through \[\left( a,b \right)\] on the \[y\] axis.
Length of chord \[AB=2a\].

As \[\left( h,k \right)\] is center and axis on circumference.
Therefore, \[OC=\text{radius = }r\]
By distance formula,
\[OC=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[r=\sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-b \right)}^{2}}}\]
Squaring both sides,
We get \[{{r}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{\left( k-b \right)}^{2}}....\left( i \right)\]
Construct \[OD\] which is perpendicular to \[AB\].
As \[OA\] and \[OB\] are the radius of the circle.
Therefore, \[OA=OB=r....\left( ii \right)\]
Hence, \[\Delta OAB\] is an isosceles triangle.
Therefore, we get \[AD=DB=a....\left( iii \right)\]
Now by Pythagoras theorem,
\[A{{D}^{2}}+D{{O}^{2}}=A{{O}^{2}}\]
\[{{a}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\left[ \text{From equation }\left( ii \right)\text{and}\left( iii \right) \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{\left( k-b \right)}^{2}}\left[ \text{From equation }\left( i \right) \right]\]
Also, \[\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\]
Rearranging the equation we get,
\[\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}-2b+{{b}^{2}}\]
Or, \[{{h}^{2}}-2bk+{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]
Replacing \[h\] with \[x\] and \[k\] with \[y\] to get locus.
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-2yb+{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]
Hence proved.
Tracing parabola,
\[{{x}^{2}}-2yb+{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]
\[{{x}^{2}}=2yb+{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\]
\[{{x}^{2}}=2b\left[ y-\dfrac{\left( {{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}} \right)}{2b} \right]\]
Comparing with
\[{{\left( x-0 \right)}^{2}}=4a{{\left[ y-{{y}_{1}} \right]}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore \]Given parabola has vertex at \[\left[ 0,\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{2b} \right]=\left( 0,{{y}_{1}} \right)\]and focal length \[\left( a \right)=\dfrac{2b}{4}=\dfrac{b}{2}\]

Note: Always rearrange the equation to get standard form. Try to get into minimum variables by always taking use of andaxis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A large number of liquid drops each of radius r coalesce class 11 physics CBSE

The period of a conical pendulum in terms of its length class 11 physics CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

In a fight of 600km an aircraft was slowed down du-class-11-maths-CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




