
Prove that the function f given by $f(x) = x - \left[ x \right]$ is increasing on $(0,1)$.
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: First we will learn about the greatest integer function using that we’ll find the value of the function $f(x)$. Then we will differentiate the function with-respect-to x to find the derivative of the function to find whether the function is increasing or not in the interval $(0,1)$
Complete step by step answer:
Given data: $f(x) = x - \left[ x \right]$
We know that $\left[ x \right]$ is the greatest integer function where it gives an integer value lesser or equal to ‘x’.
Now, we have given the domain for the function $f(x)$ i.e. $(0,1)$
From the definition of the greatest integer function, we can say that in the interval $(0,1)$
$ \Rightarrow \left[ x \right] = 0$
Hence, where $x \in (0,1)$
So we have $f(x) = x - 0$
\[ \Rightarrow f(x) = x\]
On differentiating with-respect-to x, we get,
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = 1$ and $1 > 0$
Now, we know that if the derivative of a function is always positive in $(a,b)$, then it is increasing in$(a,b)$
similarly if the derivative of a function is always negative $(c,d)$, the function will be decreasing in the interval$(c,d)$.
Therefore we can say that the function is increasing in $(0,1)$
Note: We can also that the function f is increasing in $(0,1)$ by plotting the graph of the function in the interval of $(0,1)$
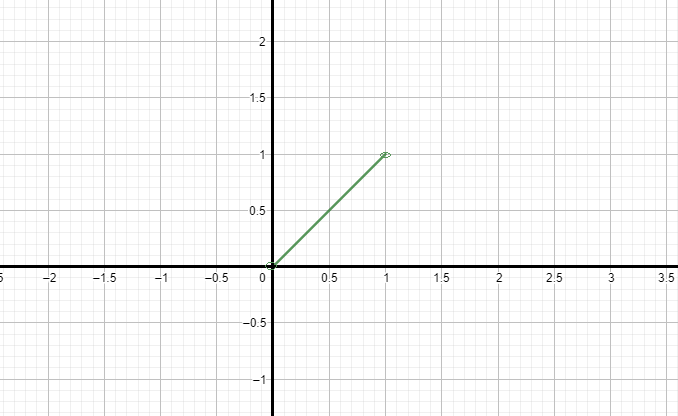
In the graph also we can see that the function is increasing in the interval $(0,1)$.
Complete step by step answer:
Given data: $f(x) = x - \left[ x \right]$
We know that $\left[ x \right]$ is the greatest integer function where it gives an integer value lesser or equal to ‘x’.
Now, we have given the domain for the function $f(x)$ i.e. $(0,1)$
From the definition of the greatest integer function, we can say that in the interval $(0,1)$
$ \Rightarrow \left[ x \right] = 0$
Hence, where $x \in (0,1)$
So we have $f(x) = x - 0$
\[ \Rightarrow f(x) = x\]
On differentiating with-respect-to x, we get,
$ \Rightarrow f'(x) = 1$ and $1 > 0$
Now, we know that if the derivative of a function is always positive in $(a,b)$, then it is increasing in$(a,b)$
similarly if the derivative of a function is always negative $(c,d)$, the function will be decreasing in the interval$(c,d)$.
Therefore we can say that the function is increasing in $(0,1)$
Note: We can also that the function f is increasing in $(0,1)$ by plotting the graph of the function in the interval of $(0,1)$

In the graph also we can see that the function is increasing in the interval $(0,1)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




