
Prove that for any two sets A and B $A=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)$
Answer
612.9k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that $A-B=A\bigcap {{B}^{c}}$ and apply distributive law of union over the intersection of sets, i.e. $A\bigcup \left( B\bigcap C \right)=\left( A\bigcup B \right)\bigcap \left( A\bigcup C \right)$. Use $B\bigcup {{B}^{c}}=U$, where U is the universal set and use the fact that if $A\subset B$ then $A\bigcap B=A$. Simplify the above expression using these properties of intersection and union of sets.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We know that $A-B=A\bigcap {{B}^{c}}$
Hence we have $\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{c}} \right)$
Let $C=A\bigcap B$
We have
$\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=C\bigcup \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{c}} \right)$
We know that union distributes over the intersection of two sets. Hence we have
$C\bigcup \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{c}} \right)=\left( C\bigcup A \right)\bigcap \left( C\bigcup {{B}^{c}} \right)$
Now $C\bigcup A=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup A$
We know that the union of two sets is associative, i.e. $A\bigcup B=B\bigcup A$
Hence we have
$C\bigcup A=A\bigcup \left( A\bigcap B \right)$
Using the distributive law of union over the intersection of two sets, we have
$C\bigcup A=\left( A\bigcup A \right)\bigcap (A\bigcup B)$
Now we know that $A\bigcup A=A$ (idempotent law).
Hence we have,
$C\bigcup A=A\bigcap \left( A\bigcup B \right)$
Since $A\subset A\bigcup B,\forall B\subset U$ and $A\bigcap B=A$ if $A\subset B$, we have
$C\bigcup A=A$
Also, $C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup {{B}^{c}}$
Using commutative law of union of sets, we have
$C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}={{B}^{c}}\bigcup \left( A\bigcap B \right)$
Using the distributive law of union over the intersection of sets, we have
$C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}=\left( {{B}^{c}}\bigcup A \right)\bigcap \left( {{B}^{c}}\bigcup B \right)$
We know that ${{B}^{c}}\bigcup B=U$
Hence we have
$C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}=\left( {{B}^{c}}\bigcup A \right)\bigcap U$
Since ${{B}^{c}}\bigcup A\subset U$, we have
$C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}={{B}^{c}}\bigcup A$
Hence we have
$\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=\left( C\bigcup A \right)\bigcap \left( C\bigcup {{B}^{c}} \right)=A\bigcap \left( {{B}^{c}}\bigcup A \right)$
We know that $A\subset A\bigcup B,\forall B\subset U$
Hence we have
$A\subset {{B}^{c}}\bigcup A$
Hence $\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=A$
Q.E.D
Note: We can also verify the above result using Venn diagrams
Diagram for $A\bigcap B$:
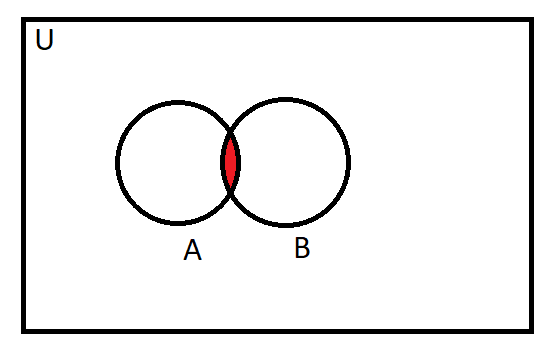
Diagram for A-B:
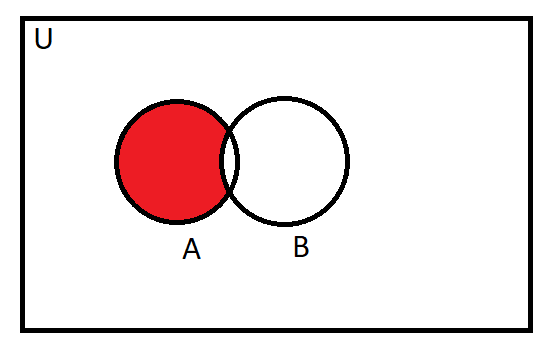
Diagram for $\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)$:
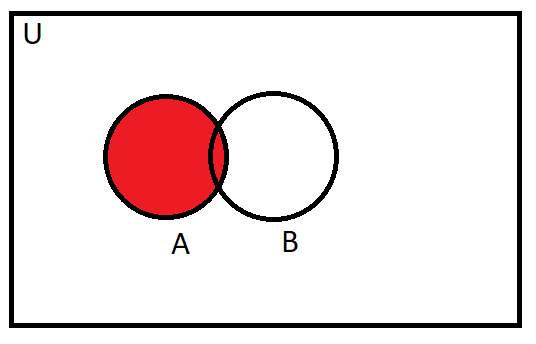
Hence $A=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)$
Complete step-by-step solution -
We know that $A-B=A\bigcap {{B}^{c}}$
Hence we have $\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{c}} \right)$
Let $C=A\bigcap B$
We have
$\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=C\bigcup \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{c}} \right)$
We know that union distributes over the intersection of two sets. Hence we have
$C\bigcup \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{c}} \right)=\left( C\bigcup A \right)\bigcap \left( C\bigcup {{B}^{c}} \right)$
Now $C\bigcup A=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup A$
We know that the union of two sets is associative, i.e. $A\bigcup B=B\bigcup A$
Hence we have
$C\bigcup A=A\bigcup \left( A\bigcap B \right)$
Using the distributive law of union over the intersection of two sets, we have
$C\bigcup A=\left( A\bigcup A \right)\bigcap (A\bigcup B)$
Now we know that $A\bigcup A=A$ (idempotent law).
Hence we have,
$C\bigcup A=A\bigcap \left( A\bigcup B \right)$
Since $A\subset A\bigcup B,\forall B\subset U$ and $A\bigcap B=A$ if $A\subset B$, we have
$C\bigcup A=A$
Also, $C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup {{B}^{c}}$
Using commutative law of union of sets, we have
$C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}={{B}^{c}}\bigcup \left( A\bigcap B \right)$
Using the distributive law of union over the intersection of sets, we have
$C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}=\left( {{B}^{c}}\bigcup A \right)\bigcap \left( {{B}^{c}}\bigcup B \right)$
We know that ${{B}^{c}}\bigcup B=U$
Hence we have
$C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}=\left( {{B}^{c}}\bigcup A \right)\bigcap U$
Since ${{B}^{c}}\bigcup A\subset U$, we have
$C\bigcup {{B}^{c}}={{B}^{c}}\bigcup A$
Hence we have
$\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=\left( C\bigcup A \right)\bigcap \left( C\bigcup {{B}^{c}} \right)=A\bigcap \left( {{B}^{c}}\bigcup A \right)$
We know that $A\subset A\bigcup B,\forall B\subset U$
Hence we have
$A\subset {{B}^{c}}\bigcup A$
Hence $\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=A$
Q.E.D
Note: We can also verify the above result using Venn diagrams
Diagram for $A\bigcap B$:

Diagram for A-B:

Diagram for $\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)$:

Hence $A=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




