
Prove geometrically that $ \cos \left( {x + y} \right) = \cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y $ .
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: We will assume a circle of unit radius to prove the above result. Then we will assume four points on the circumference of the circle with respective angles. From the construction , we will have two congruent triangles, and hence the concurrent part of the congruent triangle will be equal. Now, we will use the distance formula to find the distances between two points. Now , by relating the expression that we got from congruence and distance formula, we will prove the above result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following is the schematic diagram of the circle.
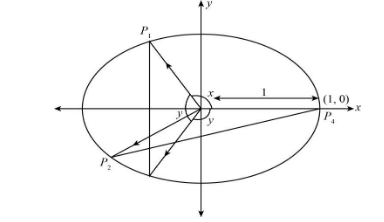
We will assume a circle of unit radius and having centre as $ \left( {0,0} \right) $ . Now we will consider four points $ {P_1} $ , $ {P_2} $ , $ {P_3} $ and $ {P_4} $ in such a way that $ \angle {P_4}O{P_1} = x $ , $ \angle {P_1}O{P_2} = y $ , therefore we can say that $ \angle {P_4}O{P_3} = x + y $ .
From the construction and our assumptions, we have $ \angle {P_4}O{P_3} = - y $ . Now, we will join $ O{P_1} $ , $ O{P_2} $ , $ O{P_3} $ , $ O{P_4} $ , $ {P_1}{P_3} $ and $ {P_2}{P_4} $ .
We can write the coordinates of the points $ {P_1} $ , $ {P_2} $ , $ {P_3} $ and $ {P_4} $ as shown:
$ {P_1} = \left( {\cos x,\sin x} \right) $
$ {P_2} = \left( {\cos \left( {x + y} \right),\sin \left( {x + y} \right)} \right) $
$ {P_3} = \left( {\cos \left( { - y} \right),\sin \left( { - y} \right)} \right) $
$ {P_4} = \left( {1,0} \right) $
From our construction we have $ \Delta O{P_1}{P_3} $ and $ \Delta O{P_2}{P_4} $ as congruent triangles. Hence we can say that the concurrent part of the congruent triangle will be equal . Therefore,
\[{P_1}{P_3} = {P_2}{P_4}\] ……(i)
Now , we will use the distance formula to find the distance \[{P_1}{P_3}\] and \[{P_2}{P_4}\].
We can express the distance formula as:
$ {\rm{Distance}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} $
To find \[{P_1}{P_3}\] we have points $ {P_1}\left( {\cos x,\sin x} \right) $ and $ {P_3}\left( {\cos \left( { - y} \right),\sin \left( { - y} \right)} \right) $ using distance formula we can express \[{P_1}{P_3}\] as:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {{{\left( {\cos x - \cos \left( { - y} \right)} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\sin x - \sin \left( { - y} \right)} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {{{\left( {\cos x - \cos y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\sin x + \sin y} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {{{\cos }^2}x + {{\cos }^2}y - 2\cos x\cos y + {{\sin }^2}x + {{\sin }^2}y + 2\sin x\sin y}
\end{array}\]
In the above expression, we will substitute 1 for \[{\cos ^2}x + {\sin ^2}y\] , we will get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
\Rightarrow {P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {1 + 1 - 2\left( {\cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y} \right)} \\
{P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {2 - 2\left( {\cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y} \right)}
\end{array}\]
We will square both sides of the above expression.
\[\Rightarrow {\left( {{P_1}{P_3}} \right)^2} = 2 - 2\left( {\cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y} \right)\]…….(ii)
To find \[{P_2}{P_4}\] we have points $ {P_2}\left( {\cos \left( {x + y} \right),\sin \left( {x + y} \right)} \right) $ and $ {P_4}\left( {1,0} \right) $ using distance formula we can express \[{P_2}{P_4}\] as:
\[\begin{array}{l}
\Rightarrow {P_2}{P_4} = \sqrt {{{\left( {\cos \left( {x + y} \right) - 1} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\sin \left( {x + y} \right) - 0} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {P_2}{P_4} = \sqrt {{{\cos }^2}\left( {x + y} \right) + 1 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right) + {{\sin }^2}\left( {x + y} \right)}
\end{array}\]
In the above expression, we will substitute 1 for \[{\cos ^2}\left( {x + y} \right) + {\sin ^2}\left( {x + y} \right)\] , we will get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
\Rightarrow {P_2}{P_4} = \sqrt {1 + 1 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right)} \\
\Rightarrow {P_2}{P_4} = \sqrt {2 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right)}
\end{array}\]
We will square both sides of the above expression.
\[\Rightarrow {\left( {{P_2}{P_4}} \right)^2} = 2 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right)\]…….(iii)
But we know from equation (i)
\[\Rightarrow {P_1}{P_3} = {P_2}{P_4}\]
We will substitute \[{P_1}{P_3}\] and \[{P_2}{P_4}\] from equation (ii) and (iii) in the above expression as:
\[
2 - 2\left( {\cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y} \right) = 2 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right)\\
\cos \left( {x + y} \right) = \cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y
\]
Hence, it is proved that \[\cos \left( {x + y} \right) = \cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y\].
Note: In this question, we are using the trigonometric identity to resolve our expression. We are also using the predefined distance formula. Make sure to revise concept of trigonometry and basic formulas of distance to get the result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following is the schematic diagram of the circle.

We will assume a circle of unit radius and having centre as $ \left( {0,0} \right) $ . Now we will consider four points $ {P_1} $ , $ {P_2} $ , $ {P_3} $ and $ {P_4} $ in such a way that $ \angle {P_4}O{P_1} = x $ , $ \angle {P_1}O{P_2} = y $ , therefore we can say that $ \angle {P_4}O{P_3} = x + y $ .
From the construction and our assumptions, we have $ \angle {P_4}O{P_3} = - y $ . Now, we will join $ O{P_1} $ , $ O{P_2} $ , $ O{P_3} $ , $ O{P_4} $ , $ {P_1}{P_3} $ and $ {P_2}{P_4} $ .
We can write the coordinates of the points $ {P_1} $ , $ {P_2} $ , $ {P_3} $ and $ {P_4} $ as shown:
$ {P_1} = \left( {\cos x,\sin x} \right) $
$ {P_2} = \left( {\cos \left( {x + y} \right),\sin \left( {x + y} \right)} \right) $
$ {P_3} = \left( {\cos \left( { - y} \right),\sin \left( { - y} \right)} \right) $
$ {P_4} = \left( {1,0} \right) $
From our construction we have $ \Delta O{P_1}{P_3} $ and $ \Delta O{P_2}{P_4} $ as congruent triangles. Hence we can say that the concurrent part of the congruent triangle will be equal . Therefore,
\[{P_1}{P_3} = {P_2}{P_4}\] ……(i)
Now , we will use the distance formula to find the distance \[{P_1}{P_3}\] and \[{P_2}{P_4}\].
We can express the distance formula as:
$ {\rm{Distance}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} $
To find \[{P_1}{P_3}\] we have points $ {P_1}\left( {\cos x,\sin x} \right) $ and $ {P_3}\left( {\cos \left( { - y} \right),\sin \left( { - y} \right)} \right) $ using distance formula we can express \[{P_1}{P_3}\] as:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {{{\left( {\cos x - \cos \left( { - y} \right)} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\sin x - \sin \left( { - y} \right)} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {{{\left( {\cos x - \cos y} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\sin x + \sin y} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {{{\cos }^2}x + {{\cos }^2}y - 2\cos x\cos y + {{\sin }^2}x + {{\sin }^2}y + 2\sin x\sin y}
\end{array}\]
In the above expression, we will substitute 1 for \[{\cos ^2}x + {\sin ^2}y\] , we will get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
\Rightarrow {P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {1 + 1 - 2\left( {\cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y} \right)} \\
{P_1}{P_3} = \sqrt {2 - 2\left( {\cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y} \right)}
\end{array}\]
We will square both sides of the above expression.
\[\Rightarrow {\left( {{P_1}{P_3}} \right)^2} = 2 - 2\left( {\cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y} \right)\]…….(ii)
To find \[{P_2}{P_4}\] we have points $ {P_2}\left( {\cos \left( {x + y} \right),\sin \left( {x + y} \right)} \right) $ and $ {P_4}\left( {1,0} \right) $ using distance formula we can express \[{P_2}{P_4}\] as:
\[\begin{array}{l}
\Rightarrow {P_2}{P_4} = \sqrt {{{\left( {\cos \left( {x + y} \right) - 1} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\sin \left( {x + y} \right) - 0} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow {P_2}{P_4} = \sqrt {{{\cos }^2}\left( {x + y} \right) + 1 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right) + {{\sin }^2}\left( {x + y} \right)}
\end{array}\]
In the above expression, we will substitute 1 for \[{\cos ^2}\left( {x + y} \right) + {\sin ^2}\left( {x + y} \right)\] , we will get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
\Rightarrow {P_2}{P_4} = \sqrt {1 + 1 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right)} \\
\Rightarrow {P_2}{P_4} = \sqrt {2 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right)}
\end{array}\]
We will square both sides of the above expression.
\[\Rightarrow {\left( {{P_2}{P_4}} \right)^2} = 2 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right)\]…….(iii)
But we know from equation (i)
\[\Rightarrow {P_1}{P_3} = {P_2}{P_4}\]
We will substitute \[{P_1}{P_3}\] and \[{P_2}{P_4}\] from equation (ii) and (iii) in the above expression as:
\[
2 - 2\left( {\cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y} \right) = 2 - 2\cos \left( {x + y} \right)\\
\cos \left( {x + y} \right) = \cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y
\]
Hence, it is proved that \[\cos \left( {x + y} \right) = \cos x\cos y - \sin x\sin y\].
Note: In this question, we are using the trigonometric identity to resolve our expression. We are also using the predefined distance formula. Make sure to revise concept of trigonometry and basic formulas of distance to get the result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




