
How do I prove $\cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ ?
Answer
543.3k+ views
Hint: To prove that $\cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ in the given question, we will take the Left Hand Side of the equation and try to get the value of Right hand side of the equation. So, we will start from the Left Hand Side of the equation by expanding the equation $\cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)$ with use of formula $\cos \left( a-b \right)=\cos a.\cos b+\sin a.\sin b$ . After that will use the value of applying the value of $\cos 2\pi $ in the expression of the equation that will help us to get the final result that is equal to the right hand side of the equation.
Complete step by step solution:
Since, the given question is $\cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ , where we need to prove that Left Hand Side is equal to Right Hand Side that means $\cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)$ is equal to $\cos \theta $ . So, we take Left Hand Side of the equation as:
$\Rightarrow \cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)$
Now, we can write the above equation as $\cos 2\pi .\cos \theta +\sin 2\pi .\sin \theta $ by using the formula $\cos \left( a-b \right)=\cos a.\cos b+\sin a.\sin b$ as:
$\Rightarrow \cos 2\pi .\cos \theta +\sin 2\pi .\sin \theta $ … $\left( i \right)$
As we know that the value of $\pi $ is $180{}^\circ $ . So, by using it we can get the value of $2\pi $ that must be equal to $360{}^\circ $ as:
$\Rightarrow \pi =180{}^\circ $
Now, we will multiply by 2 in the above equation as:
$\Rightarrow 2\times \pi =2\times 180{}^\circ $
So, we will get the value of $2\pi $ as:
$\Rightarrow 2\pi =360{}^\circ $
Here, we will put this value in the equation $\left( i \right)$ that will give us the equation as:
$\Rightarrow \cos 360{}^\circ .\cos \theta +\sin 360{}^\circ .\sin \theta $
Now, we will put the value of $\cos 360{}^\circ $ and $\sin 360{}^\circ $ that is $1$and $0$ respectively as:
$\Rightarrow 1\times \cos \theta +0\times \sin \theta $
Since, we know that the multiplication of $0$ with any number gives always $0$ . So, we will have $\cos \theta $ from the above equation as:
$\Rightarrow \cos \theta +0$
$\Rightarrow \cos \theta $
And this is equal to the Right Hand Side of the equation. Hence, the equation has been proved.
Note: Here, we need to remember that the values of $\cos \theta $ and sin $\theta $ at different quadrants. Here is diagram related to the trigonometric function with respect to quadrant as:
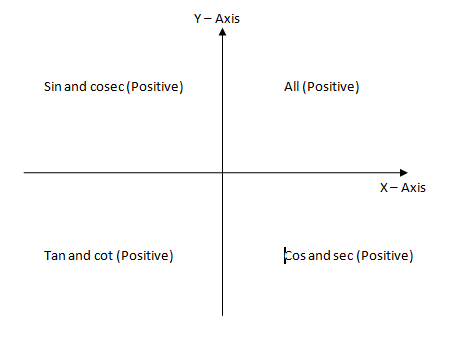
Complete step by step solution:
Since, the given question is $\cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ , where we need to prove that Left Hand Side is equal to Right Hand Side that means $\cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)$ is equal to $\cos \theta $ . So, we take Left Hand Side of the equation as:
$\Rightarrow \cos \left( 2\pi -\theta \right)$
Now, we can write the above equation as $\cos 2\pi .\cos \theta +\sin 2\pi .\sin \theta $ by using the formula $\cos \left( a-b \right)=\cos a.\cos b+\sin a.\sin b$ as:
$\Rightarrow \cos 2\pi .\cos \theta +\sin 2\pi .\sin \theta $ … $\left( i \right)$
As we know that the value of $\pi $ is $180{}^\circ $ . So, by using it we can get the value of $2\pi $ that must be equal to $360{}^\circ $ as:
$\Rightarrow \pi =180{}^\circ $
Now, we will multiply by 2 in the above equation as:
$\Rightarrow 2\times \pi =2\times 180{}^\circ $
So, we will get the value of $2\pi $ as:
$\Rightarrow 2\pi =360{}^\circ $
Here, we will put this value in the equation $\left( i \right)$ that will give us the equation as:
$\Rightarrow \cos 360{}^\circ .\cos \theta +\sin 360{}^\circ .\sin \theta $
Now, we will put the value of $\cos 360{}^\circ $ and $\sin 360{}^\circ $ that is $1$and $0$ respectively as:
$\Rightarrow 1\times \cos \theta +0\times \sin \theta $
Since, we know that the multiplication of $0$ with any number gives always $0$ . So, we will have $\cos \theta $ from the above equation as:
$\Rightarrow \cos \theta +0$
$\Rightarrow \cos \theta $
And this is equal to the Right Hand Side of the equation. Hence, the equation has been proved.
Note: Here, we need to remember that the values of $\cos \theta $ and sin $\theta $ at different quadrants. Here is diagram related to the trigonometric function with respect to quadrant as:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




