
Prothallial cells in the male gametophyte of Selaginella are/is
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint:During the development of male gametophyte, the prothallial cells remain the same. The prothallial cell does not undergo any division and signifies the only vegetative tissue present in the gametophyte.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, first, we need to know about the Selaginella. Selaginella is generally referred to as Spike Moss. In Selaginella Two types of spores are present and they are microspores and megaspores.The former evolve into a male gametophyte while the latter turns into a female gametophyte. The spore germinates, and male gametophyte development begins just before the sporangium dies. The male gametophyte typically grows in situ until the thirteen celled stage. So when the spore liberation takes place it is the release of incompletely developed male gametophyte.
Now lets us find the solution from the given options-
The first division results in the development of the small lenticular cell, the prothallial cell, and the antheridial cell, which is larger. The prothallial cell is not dividing any further. It is the sole representative of the male gametophyte’s entire vegetative tissue. The division only occurs in the antheridial cell.
In division the prothallial cells remain one, the antheridial cell keeps on dividing from one to two primary cells then into four antheridial cells and form jacket cells. At last 13 cells formed the gametophyte where only one is a prothallial cell.
Additional information:
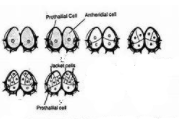
During the division of antheridial cells, they constitute the cells of the jacket layer of the antheridium where two smaller cells are formed which do not divide further and develop into the jacket cells. At last, the gametophyte consists of thirteen cells where one is a prothallial cell, four primary androgonial cells, and four jacket cells. Below is the diagram that shows the development of gametophyte.
Thus, the right answer is option A i.e., 1.
Note: Prothallial cells do not divide; it remains the same as one. The division occurs only in the antheridial cells.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, first, we need to know about the Selaginella. Selaginella is generally referred to as Spike Moss. In Selaginella Two types of spores are present and they are microspores and megaspores.The former evolve into a male gametophyte while the latter turns into a female gametophyte. The spore germinates, and male gametophyte development begins just before the sporangium dies. The male gametophyte typically grows in situ until the thirteen celled stage. So when the spore liberation takes place it is the release of incompletely developed male gametophyte.
Now lets us find the solution from the given options-
The first division results in the development of the small lenticular cell, the prothallial cell, and the antheridial cell, which is larger. The prothallial cell is not dividing any further. It is the sole representative of the male gametophyte’s entire vegetative tissue. The division only occurs in the antheridial cell.
In division the prothallial cells remain one, the antheridial cell keeps on dividing from one to two primary cells then into four antheridial cells and form jacket cells. At last 13 cells formed the gametophyte where only one is a prothallial cell.
Additional information:
During the division of antheridial cells, they constitute the cells of the jacket layer of the antheridium where two smaller cells are formed which do not divide further and develop into the jacket cells. At last, the gametophyte consists of thirteen cells where one is a prothallial cell, four primary androgonial cells, and four jacket cells. Below is the diagram that shows the development of gametophyte.
Thus, the right answer is option A i.e., 1.

Note: Prothallial cells do not divide; it remains the same as one. The division occurs only in the antheridial cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




