
Propionyl chloride is subjected to reduction with \[{H_2}\] in boiling xylene in the presence of Pd supported by \[BaS{O_4}\]. The product formed is
A.Acetone
B.Propionaldehyde
C.Ethanal
D.propanone
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we must first understand the meaning of reduction reactions. Then we must understand the molecular structure of Propanol chloride to understand the possible sites at which the reduction might occur, get the final answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Reduction reaction can be explained as the removal of oxygen atoms from the compound or the addition of hydrogen atoms to the molecule. Both these processes are in stark contrast to oxidation reactions. Hence, reduction reactions can be considered as the opposite of oxidation reactions.
Now, let us understand the question given to us. We are asked to find the products caused by the reduction of Propanol Chloride by hydrogen. To understand the product that is going to be formed, we need to understand the molecular structure of the given compound to understand the site for reduction. The molecular structure can be given by:
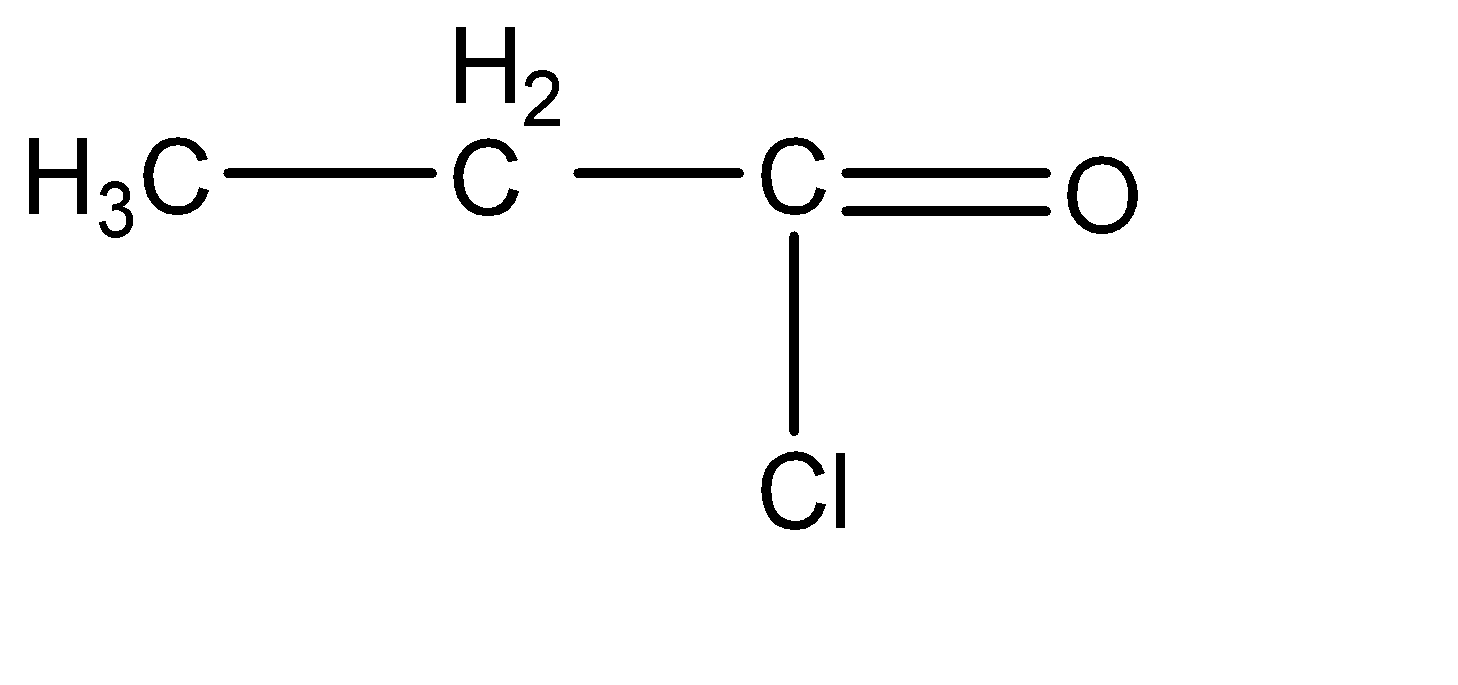
Now, the reduction due to hydrogen molecules would basically be a hydrogen substitution reaction. hence, the only site at which we can substitute the hydrogen atom is the chlorine atom. With the help of the catalysts, we can substitute the chlorine atom to form Propanil or propionaldehyde. The chemical reaction for the same can be given as:
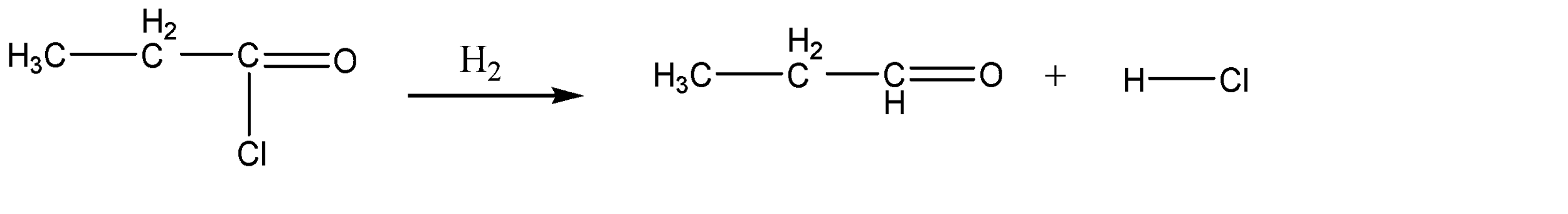
Hence, Option B is the correct option
Note: Another definition of Reduction reaction can be understood as the reactions that involve the gain of electrons by a certain chemical species to decrease its oxidation state. Reduction of compounds causes more stability as compared to before.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Reduction reaction can be explained as the removal of oxygen atoms from the compound or the addition of hydrogen atoms to the molecule. Both these processes are in stark contrast to oxidation reactions. Hence, reduction reactions can be considered as the opposite of oxidation reactions.
Now, let us understand the question given to us. We are asked to find the products caused by the reduction of Propanol Chloride by hydrogen. To understand the product that is going to be formed, we need to understand the molecular structure of the given compound to understand the site for reduction. The molecular structure can be given by:

Now, the reduction due to hydrogen molecules would basically be a hydrogen substitution reaction. hence, the only site at which we can substitute the hydrogen atom is the chlorine atom. With the help of the catalysts, we can substitute the chlorine atom to form Propanil or propionaldehyde. The chemical reaction for the same can be given as:

Hence, Option B is the correct option
Note: Another definition of Reduction reaction can be understood as the reactions that involve the gain of electrons by a certain chemical species to decrease its oxidation state. Reduction of compounds causes more stability as compared to before.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




