
Prokaryotic cells do not possess:
A. Chromosome
B. Mitochondrion
C. Ribosome
D. Plasma Membrane
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint:
Hint: All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells. All these cells arise from pre-existing cells, The activities of an organism are the outcome of the sum total of activities and interactions of its constituent cells.
The cells, which are the structural and functional unit of life are broadly categorized into two main types: Prokaryotic cell, and, Eukaryotic cell.
Complete answer:
The prokaryotic cells are the primitive type of cell which are smaller in size, lack a well-defined nucleus, and lack most of the cell organelles like Endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, etc. They are mostly common in unicellular microbes like bacteria, BGA (Blue-green algae), Mycoplasma, and PPLO (Pleuropneumonia like organisms).
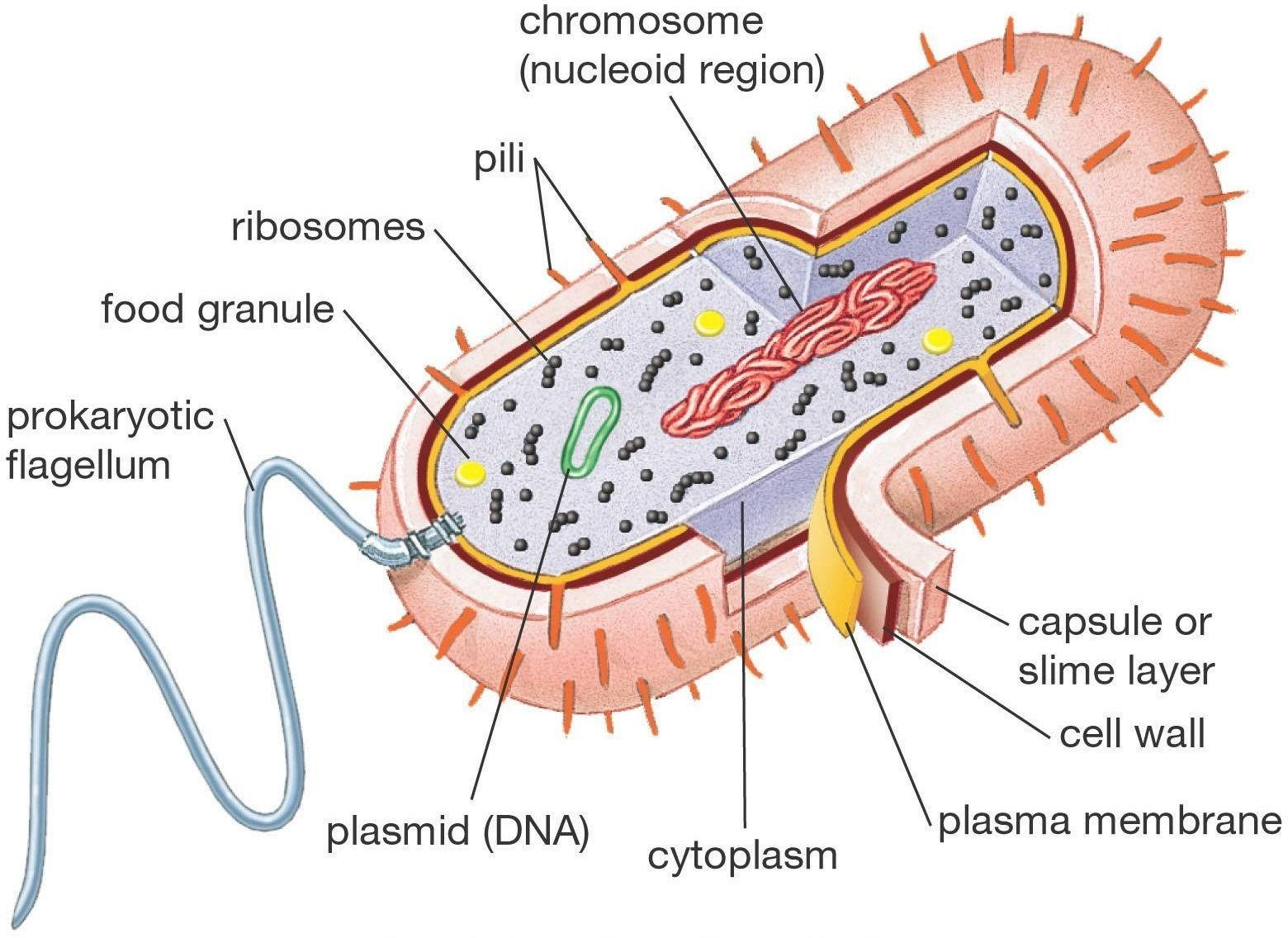
A prokaryotic cell does not have a nuclear membrane. However, the genetic material is present in a region in the cytoplasm known as the nucleoid. They may be spherical, rod-shaped, or spiral in shape. A prokaryotic cell structure is as follows:
1. Capsule: It is an outer protective covering found in the bacterial cells, in addition to the cell wall. It helps in moisture retention, protects the cell when engulfed, and helps in the attachment of cells to nutrients and surfaces.
2. Cell Wall: It is the outermost layer of the cell which gives shape to the cell.
3. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is mainly composed of enzymes, salts, cell organelles and is a gel-like component.
4. Cell Membrane: This layer surrounds the cytoplasm and regulates the entry and exit of substances in the cells.
5. Pili: These are hair-like outgrowths that attach to the surface of other bacterial cells.
6. Flagella: These are long structures in the form of a whip, that help in the locomotion of a cell.
7. Ribosomes: These are involved in protein synthesis.
8. Plasmids: Plasmids are non-chromosomal DNA structures. These are not involved in reproduction.
9. Nucleoid Region: It is the region in the cytoplasm where the genetic material is present.
A prokaryotic cell lacks certain organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies, therefore option B is correct.
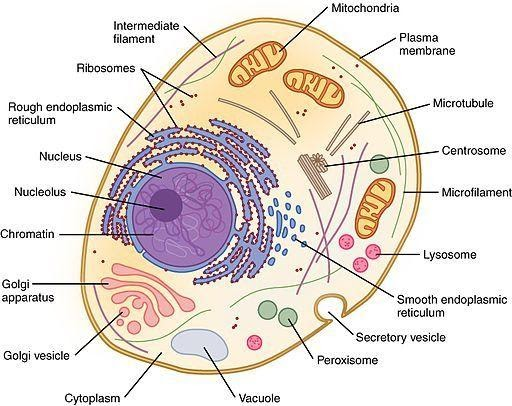
The eukaryotic cell is the modern type of cells that are well-organized and present in all the higher categories of plants and mammals. The genetic material is organized inside the nucleus which is enclosed by a nuclear membrane. Organelles like ER, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, and chloroplasts are present.
Note:
Sometimes, certain prokaryotic cells in addition to the genomic DNA, also possess small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA. These are known as plasmids. The plasmids confer special phenotypic characters to the cells. The presence or absence of plasmid in a cell does not affect the normal physiological activities of a cell.
Hint: All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells. All these cells arise from pre-existing cells, The activities of an organism are the outcome of the sum total of activities and interactions of its constituent cells.
The cells, which are the structural and functional unit of life are broadly categorized into two main types: Prokaryotic cell, and, Eukaryotic cell.
Complete answer:
The prokaryotic cells are the primitive type of cell which are smaller in size, lack a well-defined nucleus, and lack most of the cell organelles like Endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, etc. They are mostly common in unicellular microbes like bacteria, BGA (Blue-green algae), Mycoplasma, and PPLO (Pleuropneumonia like organisms).
A prokaryotic cell does not have a nuclear membrane. However, the genetic material is present in a region in the cytoplasm known as the nucleoid. They may be spherical, rod-shaped, or spiral in shape. A prokaryotic cell structure is as follows:
1. Capsule: It is an outer protective covering found in the bacterial cells, in addition to the cell wall. It helps in moisture retention, protects the cell when engulfed, and helps in the attachment of cells to nutrients and surfaces.
2. Cell Wall: It is the outermost layer of the cell which gives shape to the cell.
3. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is mainly composed of enzymes, salts, cell organelles and is a gel-like component.
4. Cell Membrane: This layer surrounds the cytoplasm and regulates the entry and exit of substances in the cells.
5. Pili: These are hair-like outgrowths that attach to the surface of other bacterial cells.
6. Flagella: These are long structures in the form of a whip, that help in the locomotion of a cell.
7. Ribosomes: These are involved in protein synthesis.
8. Plasmids: Plasmids are non-chromosomal DNA structures. These are not involved in reproduction.
9. Nucleoid Region: It is the region in the cytoplasm where the genetic material is present.
A prokaryotic cell lacks certain organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies, therefore option B is correct.

The eukaryotic cell is the modern type of cells that are well-organized and present in all the higher categories of plants and mammals. The genetic material is organized inside the nucleus which is enclosed by a nuclear membrane. Organelles like ER, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, and chloroplasts are present.

Note:
Sometimes, certain prokaryotic cells in addition to the genomic DNA, also possess small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA. These are known as plasmids. The plasmids confer special phenotypic characters to the cells. The presence or absence of plasmid in a cell does not affect the normal physiological activities of a cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




