
Projectile is projected at an angle ($\alpha$>45°) with an initial velocity u. The time t, at which its magnitude of horizontal velocity will be equal the magnitude of vertical velocity is :-
(1) $t=\dfrac{u}{g}(\cos \alpha -\sin \alpha )$
(2) $t=\dfrac{u}{g}(\cos \alpha +\sin \alpha )$
(3) $t=\dfrac{u}{g}(\sin \alpha -\cos \alpha )$
(4) $t=\dfrac{u}{g}({{\sin }^{2}}\alpha -{{\cos }^{2}}\alpha )$
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: From the projectile projected at an angle ($\alpha \rangle {{45}^{0}}$) with an initial velocity u, first find the expression for vertical velocity component and then the horizontal velocity component. Then equate both the velocity equal and find the value of time in the equation.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure below shows projectile motion, object projected at an angle $\alpha$, where $\alpha \rangle {{45}^{0}}$, and ${{v}_{x}},{{v}_{y}}$ and v are x-component of velocity, y-component of velocity and velocity respectively.
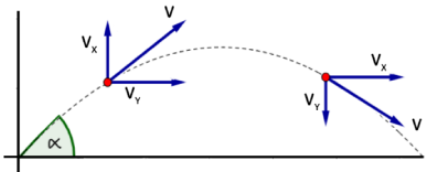
The formula for horizontal or x-component of velocity is,
${{v}_{x}}=u\cos (\alpha )$ ….(i)
Where, u is initial velocity of projectile and $\alpha$is angle of projection.
The formula for vertical or y-component of velocity is,
${{v}_{y}}=u\sin (\alpha )-gt$ ….(ii)
Where, u is initial velocity of projectile, $\alpha$is angle of projection and g is acceleration due to gravity and time t is time of projectile motion.
Now to calculate the time t, at which magnitude of horizontal velocity will be equal the magnitude of vertical velocity we equate equation(i) and equation(ii) we get,
$u\cos (\alpha )=u\sin (\alpha )-gt$
$\Rightarrow gt=u\sin (\alpha )-u\cos (\alpha )$
$\Rightarrow gt=u[\sin (\alpha )-\cos (\alpha )]$
$\Rightarrow t=\dfrac{u[\sin (\alpha )-\cos (\alpha )]}{g}$
Hence, the correct answer is option (3).
Additional Information:
The horizontal or x-component of velocity and vertical or y-component of velocity of an object in projectile motion are independent of each other. There is acceleration only in vertical direction and not in horizontal direction i.e. the velocity in horizontal direction is constant equal to g, the acceleration due to gravity (free fall).
Note:
It is important for students to memorize the formulae of horizontal or x-component of velocity and vertical or y-component of velocity of an object in projectile motion, also it is easier if one remembers the formula of time of projectile motion, to solve such questions quickly.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure below shows projectile motion, object projected at an angle $\alpha$, where $\alpha \rangle {{45}^{0}}$, and ${{v}_{x}},{{v}_{y}}$ and v are x-component of velocity, y-component of velocity and velocity respectively.

The formula for horizontal or x-component of velocity is,
${{v}_{x}}=u\cos (\alpha )$ ….(i)
Where, u is initial velocity of projectile and $\alpha$is angle of projection.
The formula for vertical or y-component of velocity is,
${{v}_{y}}=u\sin (\alpha )-gt$ ….(ii)
Where, u is initial velocity of projectile, $\alpha$is angle of projection and g is acceleration due to gravity and time t is time of projectile motion.
Now to calculate the time t, at which magnitude of horizontal velocity will be equal the magnitude of vertical velocity we equate equation(i) and equation(ii) we get,
$u\cos (\alpha )=u\sin (\alpha )-gt$
$\Rightarrow gt=u\sin (\alpha )-u\cos (\alpha )$
$\Rightarrow gt=u[\sin (\alpha )-\cos (\alpha )]$
$\Rightarrow t=\dfrac{u[\sin (\alpha )-\cos (\alpha )]}{g}$
Hence, the correct answer is option (3).
Additional Information:
The horizontal or x-component of velocity and vertical or y-component of velocity of an object in projectile motion are independent of each other. There is acceleration only in vertical direction and not in horizontal direction i.e. the velocity in horizontal direction is constant equal to g, the acceleration due to gravity (free fall).
Note:
It is important for students to memorize the formulae of horizontal or x-component of velocity and vertical or y-component of velocity of an object in projectile motion, also it is easier if one remembers the formula of time of projectile motion, to solve such questions quickly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




