
Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of the parent is called?
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Vegetative Propagation is a kind of agamic multiplication wherein new plants are delivered from roots, stems, leaves and buds. Since proliferation is through the vegetative pieces of the plant, it is known as vegetative engendering.
Complete step by step answer:
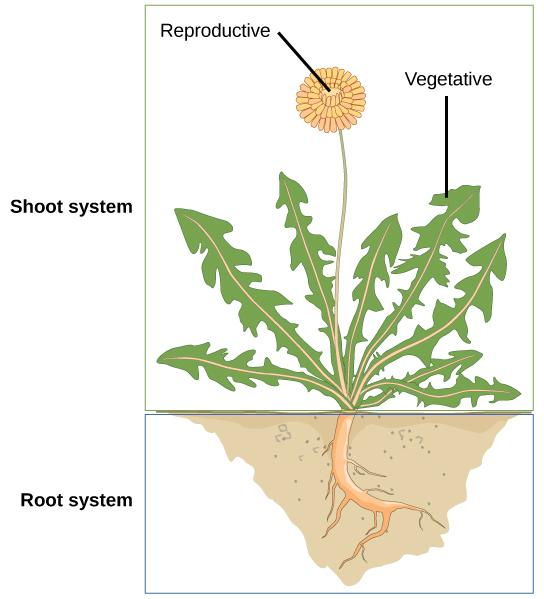
Vegetative parts:
1.Root
2.Stems
3.Leaves
Root: At the point when plants developed from marine species and advanced onto land they needed to beat numerous difficulties to endure and flourish with land. One noteworthy distinction between water based situations, for example, lakes and seas, and living on the land was the partition of supplements. Plant roots were a key variation for plants ashore to permit access supplements and water put away in soil. Living in water, plants can gather CO2, water and different supplements directly from the encompassing water.
Stems: A stem is one of two fundamental basic tomahawks of a vascular plant, the other being the root. It underpins leaves, blossoms and natural products, transports water and disintegrated substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, stores supplements, and creates new living tissue.
Leaves: Leaf, in natural science, any typically leveled green outgrowth from the stem of a vascular plant. As the essential destinations of photosynthesis, leaves fabricate nourishment for plants, which thus eventually feed and continue all land creatures. Naturally, leaves are an essential aspect of the stem framework.
Note: Roots such as corms, stem tubers, rhizomes, and stolon undergo vegetative reproduction. Some plants can produce seeds without fertilization via apomixis where the ovule or ovary gives rise to new seeds.
Complete step by step answer:
Vegetative parts:
1.Root
2.Stems
3.Leaves
Root: At the point when plants developed from marine species and advanced onto land they needed to beat numerous difficulties to endure and flourish with land. One noteworthy distinction between water based situations, for example, lakes and seas, and living on the land was the partition of supplements. Plant roots were a key variation for plants ashore to permit access supplements and water put away in soil. Living in water, plants can gather CO2, water and different supplements directly from the encompassing water.
Stems: A stem is one of two fundamental basic tomahawks of a vascular plant, the other being the root. It underpins leaves, blossoms and natural products, transports water and disintegrated substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, stores supplements, and creates new living tissue.
Leaves: Leaf, in natural science, any typically leveled green outgrowth from the stem of a vascular plant. As the essential destinations of photosynthesis, leaves fabricate nourishment for plants, which thus eventually feed and continue all land creatures. Naturally, leaves are an essential aspect of the stem framework.

Note: Roots such as corms, stem tubers, rhizomes, and stolon undergo vegetative reproduction. Some plants can produce seeds without fertilization via apomixis where the ovule or ovary gives rise to new seeds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




