
Primordial sex cells in vertebrates originate from
A) Ectoderm
B) Mesoderm
C) Endoderm
D) None of the above
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint:Primordial germ cells are special cells which are precursor to male and female gametes.These after meiosis forms haploid sperm and egg which forms a new organism on fertilization.
Complete answer:
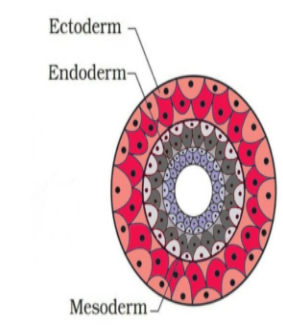
>Primordial germ cells are isolated from epiblast at the posterior end of the primitive streak in the second week of pregnancy. As epiblast itself is derived from ectoderm, primordial germ cells are also derived from the ectoderm layer which is the outermost layer of cells of an embryo.
>Ectoderm, Endoderm and mesoderm are the germinal layers from which various tissues of the body arise.
>Endoderm is the innermost germ layer, it forms the lining of the gut and other internal organs.
>Ectoderm is the exterior germ layer. It forms skin, brain ,nervous, system and other external tissues.
>Mesoderm layer of germ cells is in the middle, which forms muscles, the skeletal system, and the circulatory system.
>Vertebrates are triploblastic.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note:The presence or the absence of a cavity between the body wall and the gut wall is very important in classification.
>The cavity of the body, which is lined by mesoderm is called coelom. Animals possessing coelom are called coelomates, e.g. annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates .
>In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by continuous mesoderm, instead, the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm. Such a body cavity is called pseudocoelom and the animals possessing such coelom are called pseudocoelomates, e.g.. aschelminthes .
>The animals in which the body cavity is absent are called acoelomates, e.g. Platyhelminthes.
Complete answer:
>Primordial germ cells are isolated from epiblast at the posterior end of the primitive streak in the second week of pregnancy. As epiblast itself is derived from ectoderm, primordial germ cells are also derived from the ectoderm layer which is the outermost layer of cells of an embryo.
>Ectoderm, Endoderm and mesoderm are the germinal layers from which various tissues of the body arise.
>Endoderm is the innermost germ layer, it forms the lining of the gut and other internal organs.
>Ectoderm is the exterior germ layer. It forms skin, brain ,nervous, system and other external tissues.
>Mesoderm layer of germ cells is in the middle, which forms muscles, the skeletal system, and the circulatory system.
>Vertebrates are triploblastic.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘A’.

Note:The presence or the absence of a cavity between the body wall and the gut wall is very important in classification.
>The cavity of the body, which is lined by mesoderm is called coelom. Animals possessing coelom are called coelomates, e.g. annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates .
>In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by continuous mesoderm, instead, the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm. Such a body cavity is called pseudocoelom and the animals possessing such coelom are called pseudocoelomates, e.g.. aschelminthes .
>The animals in which the body cavity is absent are called acoelomates, e.g. Platyhelminthes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




