
How would you predict the ideal bond angles(s) around each central atom in this molecule?
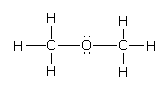

Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint:Then by using the VSEPR theory determine the electron geometry and molecular geometry of the compound.The full form of the VSEPR theory is the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory in which the electron and the molecular geometry of the molecule are different because of the presence of the lone pairs of electrons around the central atom.
Complete step-by-step answer:Here, the compound given is dimethoxy ether whose structure is as follows:Both methyl groups are in the same environment, the carbon of the methyl group is surrounded by three hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.There are four bond pairs of an electron and zero lone pairs of electrons on the carbon atom. It indicates carbon is sp3 hybridized and hence, all ${\text{H}} - {\text{C}} - {\text{H}}$ and ${\text{H}} - {\text{C}} - {\text{O}}$ bond angles are ${109.5^o }$.
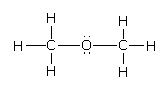
Now, if oxygen is the central atom then there are two bond pairs of an electron and two lone pairs of electrons.As per the VSEPR, the electron geometry is tetrahedral. But because of the presence of the two lone pairs, there is repulsion between the lone pairs and the bond pairs.This repulsion leads to a decrease in the tetrahedral bond angle to ${104^o}$ to ${106^o}$ like in the case of the water.
Note:The electron geometry considers the all electrons pair that is bonding as well as lone pairs of the electrons.While determining the molecular geometry that is the shape of the molecule only bonding electron pairs are considered.The repulsion between lone pairs and the bond pairs affect the bond angle between the molecules.The order of the repulsion is as follows:
${\text{lone}}\,{\text{pair - lone}}\,{\text{pair}}\,{\text{ > }}\,{\text{lone}}\,\,{\text{pair - bond}}\,{\text{pair}}\,\,{\text{ > }}\,\,{\text{bond}}\,\,{\text{pair - bond}}\,\,{\text{pair}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:Here, the compound given is dimethoxy ether whose structure is as follows:Both methyl groups are in the same environment, the carbon of the methyl group is surrounded by three hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.There are four bond pairs of an electron and zero lone pairs of electrons on the carbon atom. It indicates carbon is sp3 hybridized and hence, all ${\text{H}} - {\text{C}} - {\text{H}}$ and ${\text{H}} - {\text{C}} - {\text{O}}$ bond angles are ${109.5^o }$.

Now, if oxygen is the central atom then there are two bond pairs of an electron and two lone pairs of electrons.As per the VSEPR, the electron geometry is tetrahedral. But because of the presence of the two lone pairs, there is repulsion between the lone pairs and the bond pairs.This repulsion leads to a decrease in the tetrahedral bond angle to ${104^o}$ to ${106^o}$ like in the case of the water.
Note:The electron geometry considers the all electrons pair that is bonding as well as lone pairs of the electrons.While determining the molecular geometry that is the shape of the molecule only bonding electron pairs are considered.The repulsion between lone pairs and the bond pairs affect the bond angle between the molecules.The order of the repulsion is as follows:
${\text{lone}}\,{\text{pair - lone}}\,{\text{pair}}\,{\text{ > }}\,{\text{lone}}\,\,{\text{pair - bond}}\,{\text{pair}}\,\,{\text{ > }}\,\,{\text{bond}}\,\,{\text{pair - bond}}\,\,{\text{pair}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




