
Post-transcriptional modification of mRNA in eukaryotes is called
(a) Translation
(b) Splicing
(c) Sequencing
(d) Restriction
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: A mechanism involving the precise identification and excision of intervening sequences from between coding regions of transcribed pre-mRNAs is the post transcriptional modification of mRNA in eukaryotes.
Complete answer:
The primary transcript (the newly made RNA molecule) is not yet considered a messenger RNA when a eukaryotic gene is transcribed in the nucleus. It's an "immature" molecule called a pre-mRNA, instead.
To become a mature mRNA molecule that can escape the nucleus and be translated, the pre-mRNA has to go through some modifications. This includes splicing, capping, and adding a poly-A tail, both of which can potentially be controlled to result in a different product (accelerated, slowed down, or altered).
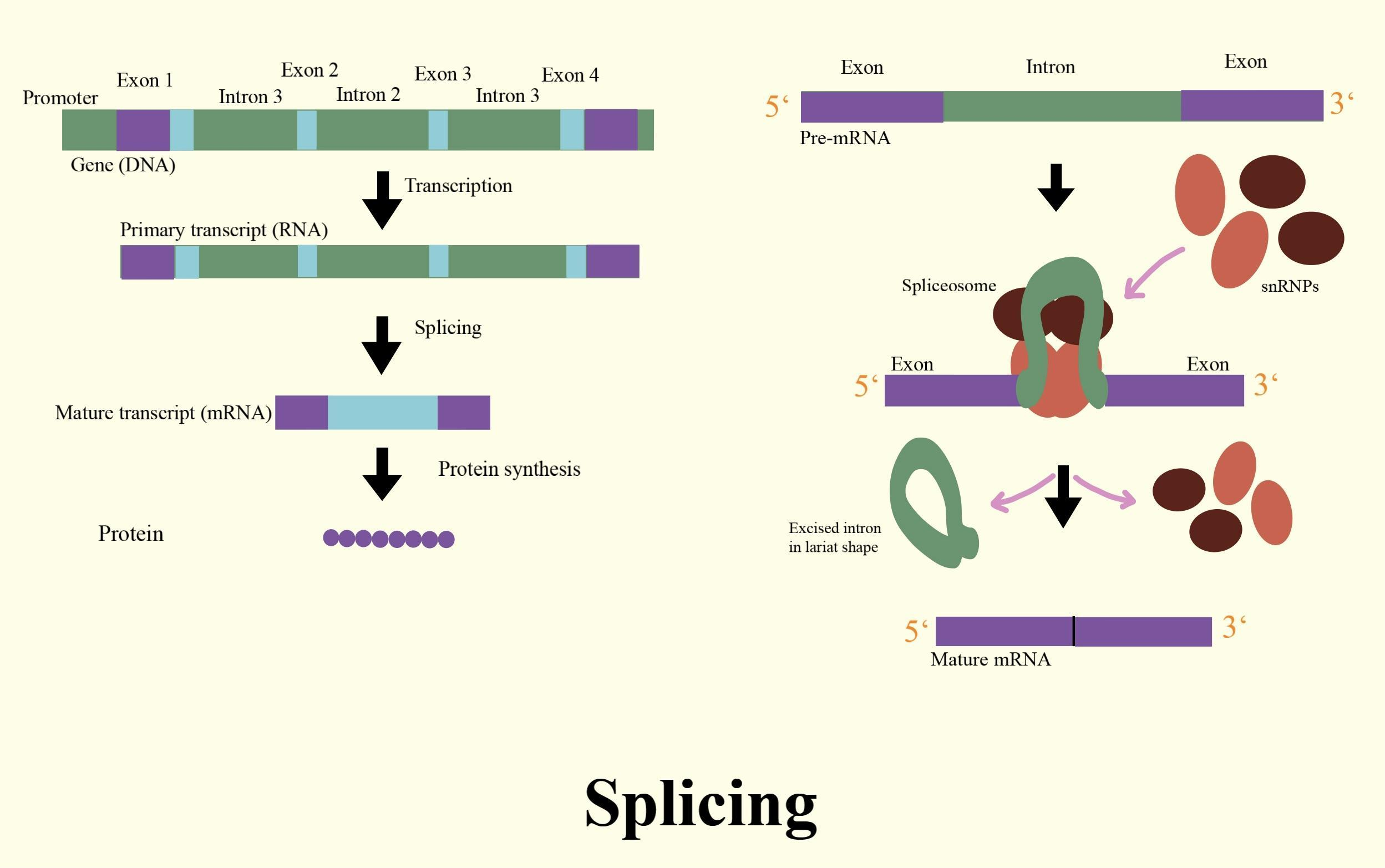
Three events include post-transcriptional modification of mRNA in eukaryotes.
- Splicing: deleting introns from the primary transcript and ligating exons to create a continuous sequence that determines a functional polypeptide.
- Capping of eukaryotic mRNAs: this refers to the addition to the 5' end of almost all eukaryotic mRNAs of 7-Methylguanosine in an unusual 5', 5’-triphosphate linkage.
- Tailing- Refers to 3'end cleavage and the addition of residues of 80 to 250 A to create a poly A tail.
RNA splicing is a form of RNA processing where a newly produced transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA ( mRNA) from a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA). Introns (non-coding regions) are separated during splicing, and exons (coding regions) are fused together.
A multimega Dalton ribonucleoprotein complex known as the spliceosome performs splicing.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(b) Splicing’.
Note: In a cell's nucleus, DNA transcription occurs. In this process, the RNA that is synthesized is then transferred to the cytoplasm of the cell where it is converted into a protein. The RNA that is synthesized during DNA transcription is ready for translation into a protein in prokaryotes. However, eukaryotic RNA from DNA transcription is not ready for translation immediately. It is thus subject to regulation.
Complete answer:
The primary transcript (the newly made RNA molecule) is not yet considered a messenger RNA when a eukaryotic gene is transcribed in the nucleus. It's an "immature" molecule called a pre-mRNA, instead.
To become a mature mRNA molecule that can escape the nucleus and be translated, the pre-mRNA has to go through some modifications. This includes splicing, capping, and adding a poly-A tail, both of which can potentially be controlled to result in a different product (accelerated, slowed down, or altered).

Three events include post-transcriptional modification of mRNA in eukaryotes.
- Splicing: deleting introns from the primary transcript and ligating exons to create a continuous sequence that determines a functional polypeptide.
- Capping of eukaryotic mRNAs: this refers to the addition to the 5' end of almost all eukaryotic mRNAs of 7-Methylguanosine in an unusual 5', 5’-triphosphate linkage.
- Tailing- Refers to 3'end cleavage and the addition of residues of 80 to 250 A to create a poly A tail.
RNA splicing is a form of RNA processing where a newly produced transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA ( mRNA) from a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA). Introns (non-coding regions) are separated during splicing, and exons (coding regions) are fused together.
A multimega Dalton ribonucleoprotein complex known as the spliceosome performs splicing.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(b) Splicing’.
Note: In a cell's nucleus, DNA transcription occurs. In this process, the RNA that is synthesized is then transferred to the cytoplasm of the cell where it is converted into a protein. The RNA that is synthesized during DNA transcription is ready for translation into a protein in prokaryotes. However, eukaryotic RNA from DNA transcription is not ready for translation immediately. It is thus subject to regulation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




