
Posterior vena cava is made of
A. Renal and gonadal vein
B. Gonadal and hepatic
C. Renal and hepatic
D. Renal, gonadal and hepatic
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: Vena cava is a large vein carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart. It has a thinner wall than the aorta because the pressure of the blood is not as high so it does not need to pump as hard.
Complete Answer:
It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right auricle at the lower right, back side of the heart.
Now, let us find the solution from the option.
- The posterior or inferior vena cava is a huge vein that bears low oxygen level blood from the bottom and central portion of the body into the heart’s right atrium. It runs posterior or behind the abdominal cavity.
- Besides its direction via the abdomen, blood flow from the internal organs joins the inferior vena cava through a series of large veins, including the gonadal, renal, suprarenal, and inferior phrenic nerves.
- The hepatic vein gives blood from the digestive organs present in the abdomen after it has been transported via the hepatic portal system present in the liver. Blood from the tissues of the bottom back, involving the spinal cord and muscles of the backside, invades the vena cava via the lumbar veins.
- Many smaller veins also give blood to the vena cava from the tissues of the irregular body wall. After getting into the heart, the inferior vena cava links to the right atrium on its posterior side, inferior to the connection of the superior vena cava.
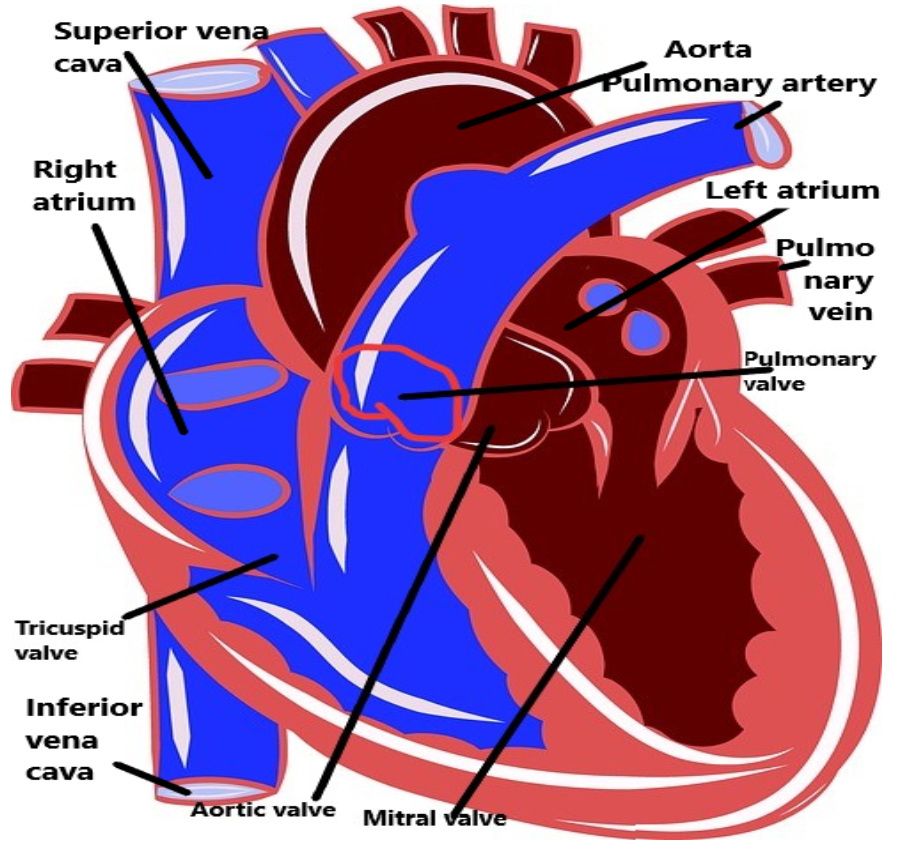
Fig- posterior vena cava.
Thus, the correct option is D. i.e. Renal, gonadal and hepatic.
Note: The inferior vena cava is the lower of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava bears blood from the top half area of the body. Together, the venae cavae (in addition to the coronary sinus, which transports blood from the muscle of the heart itself) form the venous counterparts of the aorta.
Complete Answer:
It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right auricle at the lower right, back side of the heart.
Now, let us find the solution from the option.
- The posterior or inferior vena cava is a huge vein that bears low oxygen level blood from the bottom and central portion of the body into the heart’s right atrium. It runs posterior or behind the abdominal cavity.
- Besides its direction via the abdomen, blood flow from the internal organs joins the inferior vena cava through a series of large veins, including the gonadal, renal, suprarenal, and inferior phrenic nerves.
- The hepatic vein gives blood from the digestive organs present in the abdomen after it has been transported via the hepatic portal system present in the liver. Blood from the tissues of the bottom back, involving the spinal cord and muscles of the backside, invades the vena cava via the lumbar veins.
- Many smaller veins also give blood to the vena cava from the tissues of the irregular body wall. After getting into the heart, the inferior vena cava links to the right atrium on its posterior side, inferior to the connection of the superior vena cava.

Fig- posterior vena cava.
Thus, the correct option is D. i.e. Renal, gonadal and hepatic.
Note: The inferior vena cava is the lower of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava bears blood from the top half area of the body. Together, the venae cavae (in addition to the coronary sinus, which transports blood from the muscle of the heart itself) form the venous counterparts of the aorta.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




