
Position-time graph for a particle is shown in the figure. Starting from t=0, at what time t, the average velocity is zero?
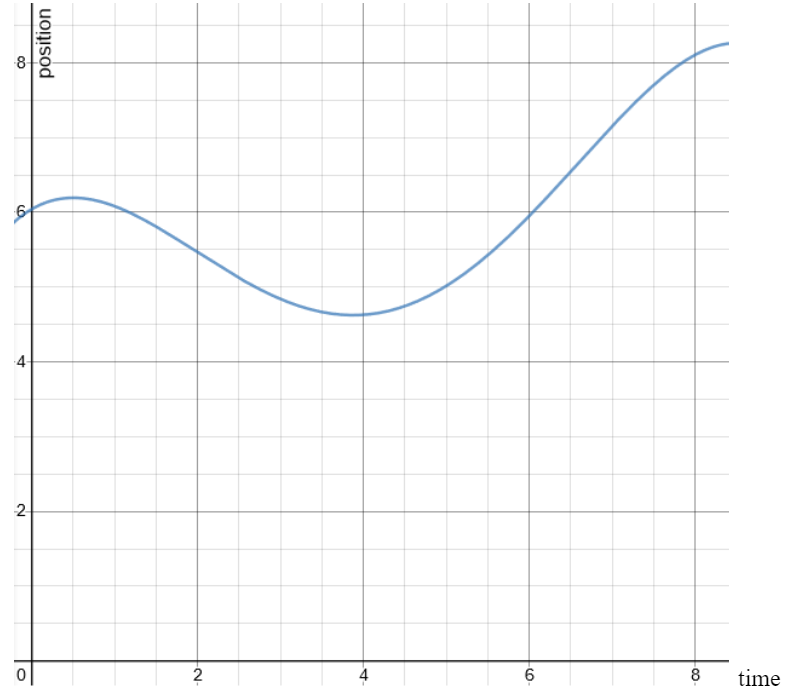
Position on the y-axis and time on the x-axis
A. 1 s
B. 3 s
C. 6 s
D. 7 s

Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Velocity is rate of change of displacement with respect to the time. For a particular path, we can define instantaneous velocity and average velocity. Velocity at a particular time instant is called instantaneous velocity and velocity over a certain duration of time is average velocity. Hence average velocity is total displacement upon time.
Formula used:
Average velocity = total displacement/total time
Displacement = final position – initial position
Complete step-by-step solution:
In order to find out the time instant where average velocity becomes zero, we should find out a point where total displacement becomes zero.
If we look at the graph carefully initial position i.e at time t=0 is 6m
Total displacement = final position – initial position
The time instant at which position becomes 6m again is to be found in order to solve this
In the given graph position becomes 6m again at t = 6s
So average velocity = total displacement/total time = (6 – 6)/(6s – 0s) = 0
Hence answer would be option C.
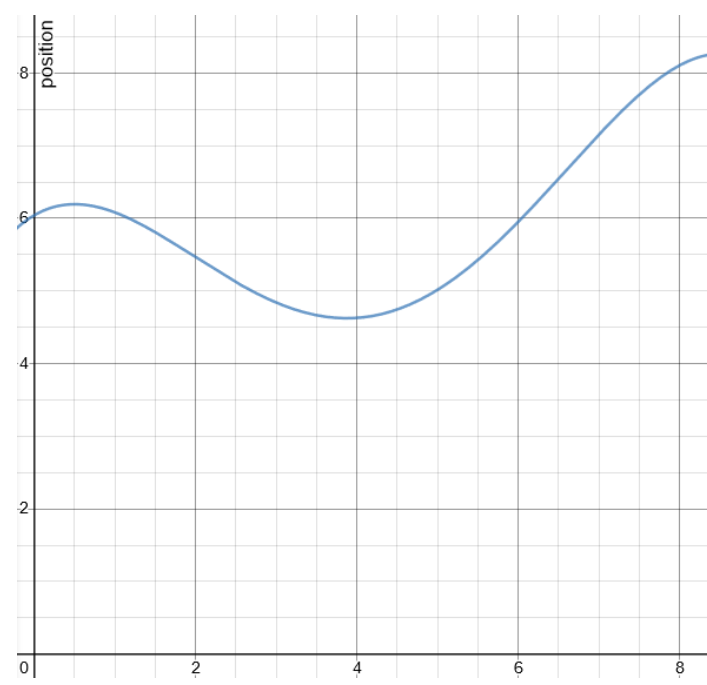
Additional information:
If the body is traveling in a straight path without reversing its direction then the instantaneous velocity of that body will be equal to the average velocity at every instant of its travel. Then we call distance and displacement equal.
Note: If we are asked to find out the time instant where the instantaneous velocity of a particle is zero then we should find out a point where the slope of the position-time graph will be equal to zero as the slope is nothing but the rate of change of position with respect to time which is instantaneous velocity.
Formula used:
Average velocity = total displacement/total time
Displacement = final position – initial position
Complete step-by-step solution:
In order to find out the time instant where average velocity becomes zero, we should find out a point where total displacement becomes zero.
If we look at the graph carefully initial position i.e at time t=0 is 6m
Total displacement = final position – initial position
The time instant at which position becomes 6m again is to be found in order to solve this
In the given graph position becomes 6m again at t = 6s
So average velocity = total displacement/total time = (6 – 6)/(6s – 0s) = 0
Hence answer would be option C.

Additional information:
If the body is traveling in a straight path without reversing its direction then the instantaneous velocity of that body will be equal to the average velocity at every instant of its travel. Then we call distance and displacement equal.
Note: If we are asked to find out the time instant where the instantaneous velocity of a particle is zero then we should find out a point where the slope of the position-time graph will be equal to zero as the slope is nothing but the rate of change of position with respect to time which is instantaneous velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




