
How do poriferan animals differ from coelenterate animals?
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: Primarily, the animals of these two phyla differ in the level of organization of their bodies. Also, the animals belonging to the former group are considered to be more primitive and less developed than later.
Complete answer:
The differences between the poriferan animals and coelenterate animals have been listed in the table below –
Note:
-Coelenterates or cnidarians are found in two body forms – Polyp and Medusa. Here, the polyp form is sessile and cylindrical and the best example of this form is Hydra. The other form Medusa is free-swimming and umbrella-shaped is represented by Jellyfish.
-There is an alternation of generation between the two forms of cnidarians in which polyps produce medusa asexually which medusa produces polyps sexually.
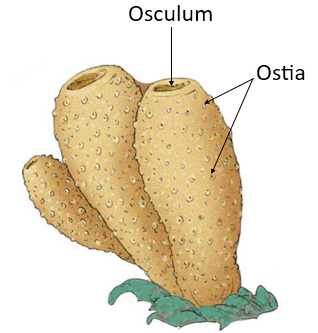
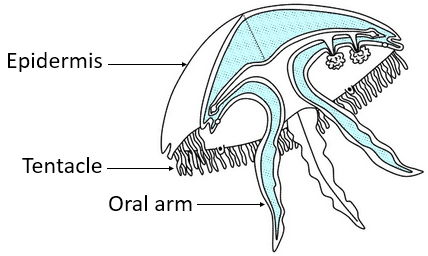
Fig.- Sponge Fig.- Jellyfish
Complete answer:
The differences between the poriferan animals and coelenterate animals have been listed in the table below –
| Sl. No. | Poriferans | Coelenterates |
| 1. | These are multicellular organisms but have a cellular grade of organization. | These are multicellular organisms with tissue grade of organization. |
| 2. | These animals are generally marine and mostly asymmetrical. | These are also mostly marine but here the symmetry is radial. |
| 3. | These organisms possess a water transport system which is known as a canal system. | These animals do not have a canal system but have a gastro-vascular cavity with a single opening, known as hypostome. |
| 4. | The mode of digestion is only intracellular in these organisms. | Here, the mode of digestion can be both extracellular and intracellular. |
| 5. | Poriferans have special types of cells that line the central body cavity and the canals, these cells are called Choanocytes or collar cells. | These organisms have cnidoblasts or cnidocytes on the tentacles and body which have stinging capsules. |
| 6. | The skeleton in poriferans is made up of spongin fibers that are also called spicules. | Calcium carbonate is the main constituent of the skeleton of these organisms. |
| 7. | Sycon, Spongilla, and Euspongia are some of the examples of Poriferans. | Organisms like Physalia, Adamsia, Pennatula, Gorgonia, and Meandrina are examples of coelenterates. |
Note:
-Coelenterates or cnidarians are found in two body forms – Polyp and Medusa. Here, the polyp form is sessile and cylindrical and the best example of this form is Hydra. The other form Medusa is free-swimming and umbrella-shaped is represented by Jellyfish.
-There is an alternation of generation between the two forms of cnidarians in which polyps produce medusa asexually which medusa produces polyps sexually.


Fig.- Sponge Fig.- Jellyfish
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




