
Polysubstitution is a major drawback in:
(A)- Reimer Tiemann reaction
(B)- Friedel Craft acylation
(C)- Friedel Craft alkylation
(D)- Acetylation of aniline
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: The polysubstitution over the benzene ring is possible if the substituent attached to it is ring activating, that is, increasing the electron-density over it. So, looking at the given reaction mechanism, the substituent and its effect can be determined.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reactions which take place as follows:
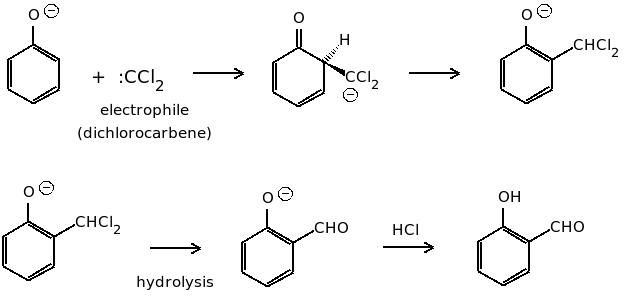
- In Riemer Tiemann reaction, in presence of the base, the chloroform forms the reactive carbene intermediate which is attacked by the phenol which is also deprotonated by the base. This is followed by the base hydrolysis to form the ortho-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
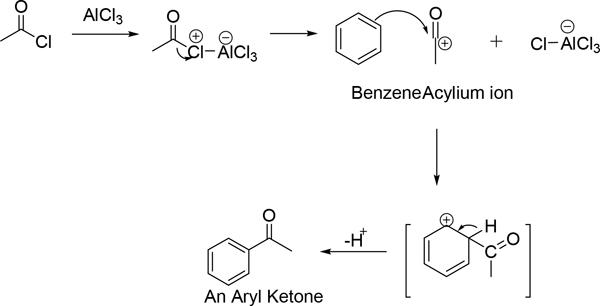
- In Friedel craft acylation, the acyl chloride or an anhydride is presence of the strong Lewis acid $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ as catalyst, forms a acylium ion which acts as a electrophile, which reacts with the benzene ring to form a monoacylated product.
- In Acetylation of aniline, the reaction of the aniline which acts as the nucleophile, with the acetic anhydride having the acyl group as the electrophile, in presence of the glacial acetic acid undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction and forms acetanilide, where the hydrogen atom from the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ is replaced by $(-OCC{{H}_{3}})$ group.
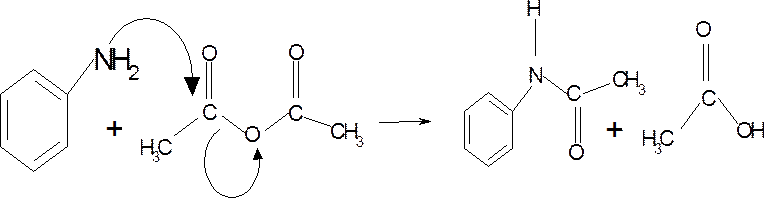
- In Friedel craft alkylation, the benzene ring undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution with the alkyl halide, in presence of a Lewis acid $FeC{{l}_{3}}$ as catalyst, to form a monosubstituted alkyl product.
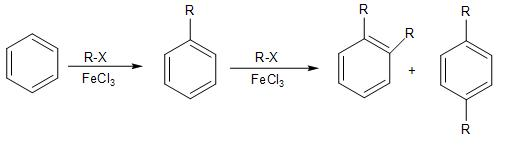
Here the alkyl substituent over the benzene ring due to its positive inductive effect, increases the electron density over the ring and activates it at ortho- and para- position. Thus, making it more susceptible for the polyalkylation to occur further. Due to this reason, the Friedel craft acylation is preferred over it, in which the acyl group over the benzene ring, which is an electron-withdrawing group, deactivates it.
Therefore, Polysubstitution is a major drawback in option (C)- Friedel craft alkylation.
Note: The deactivating groups restrict the further substitution over the ring at the ortho- and para- position by decreasing the electron-density over these positions. So, mostly meta- substituted products are formed in this case.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reactions which take place as follows:
- In Riemer Tiemann reaction, in presence of the base, the chloroform forms the reactive carbene intermediate which is attacked by the phenol which is also deprotonated by the base. This is followed by the base hydrolysis to form the ortho-hydroxybenzaldehyde.

- In Friedel craft acylation, the acyl chloride or an anhydride is presence of the strong Lewis acid $AlC{{l}_{3}}$ as catalyst, forms a acylium ion which acts as a electrophile, which reacts with the benzene ring to form a monoacylated product.

- In Acetylation of aniline, the reaction of the aniline which acts as the nucleophile, with the acetic anhydride having the acyl group as the electrophile, in presence of the glacial acetic acid undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction and forms acetanilide, where the hydrogen atom from the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ is replaced by $(-OCC{{H}_{3}})$ group.
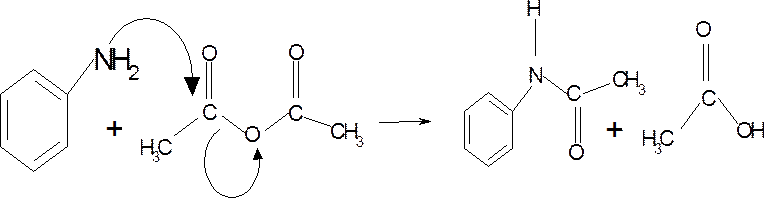
- In Friedel craft alkylation, the benzene ring undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution with the alkyl halide, in presence of a Lewis acid $FeC{{l}_{3}}$ as catalyst, to form a monosubstituted alkyl product.

Here the alkyl substituent over the benzene ring due to its positive inductive effect, increases the electron density over the ring and activates it at ortho- and para- position. Thus, making it more susceptible for the polyalkylation to occur further. Due to this reason, the Friedel craft acylation is preferred over it, in which the acyl group over the benzene ring, which is an electron-withdrawing group, deactivates it.
Therefore, Polysubstitution is a major drawback in option (C)- Friedel craft alkylation.
Note: The deactivating groups restrict the further substitution over the ring at the ortho- and para- position by decreasing the electron-density over these positions. So, mostly meta- substituted products are formed in this case.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




