
Points A and B are in the first quadrant. Point \[O\] is the origin. If the slope of \[{OA}\] is \[1\] , the slope of \[{OB}\] is \[7\] and \[OA = OB\] then what is the slope of \[{AB}\]?
A). \[- \dfrac{1}{5}\]
B). \[- \dfrac{1}{4}\]
C). \[- \dfrac{1}{3}\]
D). \[- \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: In this question, given that the points \[A\] and \[B\] are in the first quadrant. The point \[O\] is the origin. And also given the slope of \[{OA}\] and \[{OB}\] are \[1\] and \[7\] respectively. Then here we need to find the slope of \[{AB}\] . By using slope formula and distance formula we can find the slope of \[{AB}\].
Formula used :
Slope, \[m\ = \dfrac{\left(\text{Change in y} \right)}{\text{Change in x}}\]
\[m = (y{_2}- y{_1} ) /(x{_2} - x{_1})\]
The formula for the distance between two points \[(a,\ b)\] and \[(c,\ d)\] is
\[d = \sqrt{\left( c – a \right)^{2} + \left( d – b \right)^{2}}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
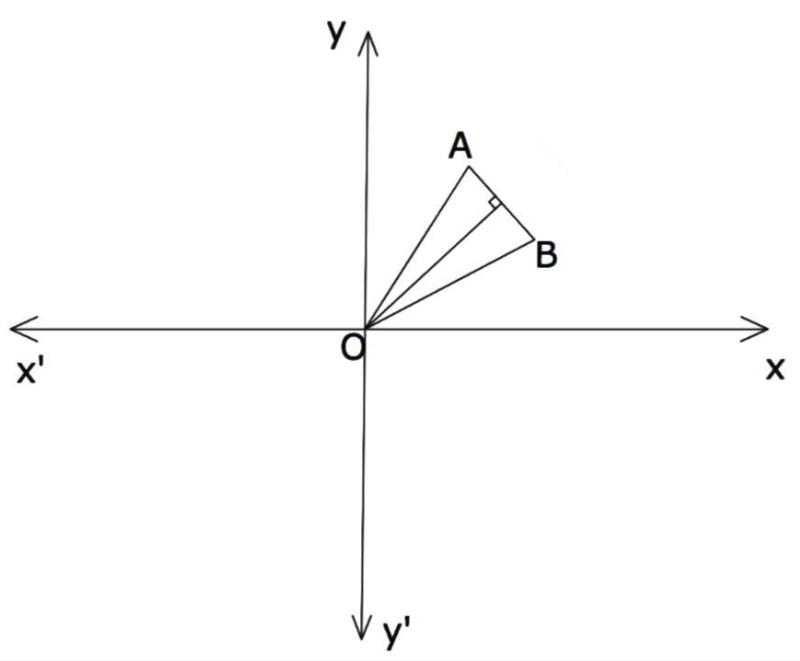
Let the point \[A\] be \[(a,\ b)\] and \[B\] be \[(c,\ d)\] be in the first quadrant. The point \[O\] in the origin be \[(0,\ 0)\]
Given,
Slope, \[OA\ = 1\]
\[\dfrac{\left( b – 0 \right)}{a – 0}\ = 1\]
\[\dfrac{b}{a} = 1\]
By cross multiplying,
We get,
\[b = a\]
Slope , \[OB = 7\]
\[\dfrac{\left( d – 0 \right)}{c – 0}\ = 7\]
\[\dfrac{d}{c} = 7\]
By cross multiplying,
We get,
\[d = 7c\]
Also given that,
\[OA = OB\]
By using distance formula,
\[\sqrt{\left( a – 0 \right)^{2} + \left( b – 0 \right)^{2}} = \sqrt{\left( c – 0 \right)^{2}\left( d – 0 \right)^{2}}\]
On squaring both sides,
We get,
\[a^{2} + b^{2} = c^{2} + d^{2}\]
By substituting the values \[b = a\]an \[d = 7c\]
\[a^{2} + a^{2} = c^{2} + \left( 7c \right)^{2}\]
By removing the parentheses,
\[a^{2} + a^{2} = c^{2} + 49c^{2}\]
By adding,
We get,
\[2a^{2} = 50c^{2}\]
By simplifying,
We get,
\[a^{2} = 25c^{2}\]
By taking square root on both sides,
We get,
\[a = \pm 5c\]
Thus we get \[a = 5c\]or \[a = - 5c\]
Since A is in the first quadrant,
\[a = 5c\]
Now we can find the slope of AB
Slope,
\[AB = \dfrac{\left( d – b \right)}{c – a}\]
By substituting the known values,
We get,
\[AB = \dfrac{7c – a}{c – a}\ \]Since\[\ b = a\]
By substituting the value of \[a = 5c\]
\[AB = \dfrac{7c – 5c}{c – 5c}\]
By simplifying,
We get,
\[AB = \dfrac{2c}{- 4c}\]
By dividing,
We get,
\[{slope\ }AB = - \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Thus the slope of \[{AB}\] is \[- \dfrac{1}{2}\]
The slope of \[{AB}\] is \[- \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Note: The slope of a line is defined as the measure of its Steepness. It is calculated by dividing the change in \[y\] coordinate by change in \[x\] co-ordinate. Mathematically, slope is denoted by the letter \[m\]. Slope is positive when m is greater than \[0\] and when m is less than \[0\], slope is negative. If the slope is equal to \[0\] that means it is a constant function.
Formula used :
Slope, \[m\ = \dfrac{\left(\text{Change in y} \right)}{\text{Change in x}}\]
\[m = (y{_2}- y{_1} ) /(x{_2} - x{_1})\]
The formula for the distance between two points \[(a,\ b)\] and \[(c,\ d)\] is
\[d = \sqrt{\left( c – a \right)^{2} + \left( d – b \right)^{2}}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:

Let the point \[A\] be \[(a,\ b)\] and \[B\] be \[(c,\ d)\] be in the first quadrant. The point \[O\] in the origin be \[(0,\ 0)\]
Given,
Slope, \[OA\ = 1\]
\[\dfrac{\left( b – 0 \right)}{a – 0}\ = 1\]
\[\dfrac{b}{a} = 1\]
By cross multiplying,
We get,
\[b = a\]
Slope , \[OB = 7\]
\[\dfrac{\left( d – 0 \right)}{c – 0}\ = 7\]
\[\dfrac{d}{c} = 7\]
By cross multiplying,
We get,
\[d = 7c\]
Also given that,
\[OA = OB\]
By using distance formula,
\[\sqrt{\left( a – 0 \right)^{2} + \left( b – 0 \right)^{2}} = \sqrt{\left( c – 0 \right)^{2}\left( d – 0 \right)^{2}}\]
On squaring both sides,
We get,
\[a^{2} + b^{2} = c^{2} + d^{2}\]
By substituting the values \[b = a\]an \[d = 7c\]
\[a^{2} + a^{2} = c^{2} + \left( 7c \right)^{2}\]
By removing the parentheses,
\[a^{2} + a^{2} = c^{2} + 49c^{2}\]
By adding,
We get,
\[2a^{2} = 50c^{2}\]
By simplifying,
We get,
\[a^{2} = 25c^{2}\]
By taking square root on both sides,
We get,
\[a = \pm 5c\]
Thus we get \[a = 5c\]or \[a = - 5c\]
Since A is in the first quadrant,
\[a = 5c\]
Now we can find the slope of AB
Slope,
\[AB = \dfrac{\left( d – b \right)}{c – a}\]
By substituting the known values,
We get,
\[AB = \dfrac{7c – a}{c – a}\ \]Since\[\ b = a\]
By substituting the value of \[a = 5c\]
\[AB = \dfrac{7c – 5c}{c – 5c}\]
By simplifying,
We get,
\[AB = \dfrac{2c}{- 4c}\]
By dividing,
We get,
\[{slope\ }AB = - \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Thus the slope of \[{AB}\] is \[- \dfrac{1}{2}\]
The slope of \[{AB}\] is \[- \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Note: The slope of a line is defined as the measure of its Steepness. It is calculated by dividing the change in \[y\] coordinate by change in \[x\] co-ordinate. Mathematically, slope is denoted by the letter \[m\]. Slope is positive when m is greater than \[0\] and when m is less than \[0\], slope is negative. If the slope is equal to \[0\] that means it is a constant function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




