
Point out the correct statement:
A) Below $ {710^ \circ }C $ , C is better reducing agent than CO
B) Below $ {710^ \circ }C $ , CO is better reducing agent than C
C) Below $ {710^ \circ }C $ , CO is Oxidizing agent
D) Below $ {710^ \circ }C $ , $ C{O_2} $ is a reducing agent.
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: This question is based upon the Ellingham diagram. Ellingham diagram is a graph that shows the temperature dependence of the stability of the compounds. This analysis is used to evaluate the ease with which the oxides and sulphides can be reduced. This diagram was first given by Harold Ellingham in 1944.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The Ellingham Diagram is a graph of $ \Delta G $ v/s temperature for different reactions. The Ellingham diagram for reactions involving CO, C and $ C{O_2} $ can be given as follows.
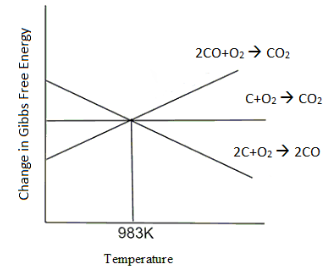
From this graph we can conclude that the $ \Delta {G^ \circ } $ values for reactions where all the lines meet are the same. Here the three lines meet at 983K. This is the crossover point.
On either side of the crossover point, the reaction on the lower side (i.e., the reaction with more negative value of $ \Delta {G^ \circ } $ ) will be more spontaneous and will proceed in the forward direction as it has a negative $ \Delta {G^ \circ } $ value. Whereas, the reaction on the upper side of the crossover point will have a more positive value of $ \Delta {G^ \circ } $ and the reaction will proceed in the backward direction.
At the temperature below $ {710^ \circ }C $ , the reaction line of $ 2CO + {O_2} \to 2C{O_2} $ has the most negative value and will be the most spontaneous. Hence, we can say that the line of (CO, $ C{O_2} $ ) lies below the (C, $ C{O_2} $ ) line. Hence below $ {710^ \circ }C $ , CO is a better reducing agent.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option (B).
Note:
If we consider the conditions above $ {710^ \circ }C $ , we can see that the line of (C, CO) lies below (CO, $ C{O_2} $ ). At higher temperatures C is a better reducing agent than CO. The data from the Ellingham diagram is used to determine a better oxidising/ reducing agent for a process.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The Ellingham Diagram is a graph of $ \Delta G $ v/s temperature for different reactions. The Ellingham diagram for reactions involving CO, C and $ C{O_2} $ can be given as follows.

From this graph we can conclude that the $ \Delta {G^ \circ } $ values for reactions where all the lines meet are the same. Here the three lines meet at 983K. This is the crossover point.
On either side of the crossover point, the reaction on the lower side (i.e., the reaction with more negative value of $ \Delta {G^ \circ } $ ) will be more spontaneous and will proceed in the forward direction as it has a negative $ \Delta {G^ \circ } $ value. Whereas, the reaction on the upper side of the crossover point will have a more positive value of $ \Delta {G^ \circ } $ and the reaction will proceed in the backward direction.
At the temperature below $ {710^ \circ }C $ , the reaction line of $ 2CO + {O_2} \to 2C{O_2} $ has the most negative value and will be the most spontaneous. Hence, we can say that the line of (CO, $ C{O_2} $ ) lies below the (C, $ C{O_2} $ ) line. Hence below $ {710^ \circ }C $ , CO is a better reducing agent.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option (B).
Note:
If we consider the conditions above $ {710^ \circ }C $ , we can see that the line of (C, CO) lies below (CO, $ C{O_2} $ ). At higher temperatures C is a better reducing agent than CO. The data from the Ellingham diagram is used to determine a better oxidising/ reducing agent for a process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




