
Pneumotaxic centre which can moderate the function of the respiratory rhythm centre is present in
(a) Pons region of the brain
(b) Thalamus
(c) Spinal cord
(d) Right cerebral hemisphere
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: This is the region which connects the medulla and midbrain and helps in transmitting information between the spinal cord and higher brain region via the neuronal circuit. The major function is to relay motor information between cerebral cortex and cerebellum.
Complete step by step answer:
Pons has sensory tract and motor tract same as medulla which contains nuclei known as pontine nuclei that deals with respiration, swallowing, bladder control, equilibrium, eyeball movement, facial expression etc. The major function of the Pons region is to regulate breathing rate and is involved in the control of sleep cycles. It also regulates your arousal and wakefulness states.
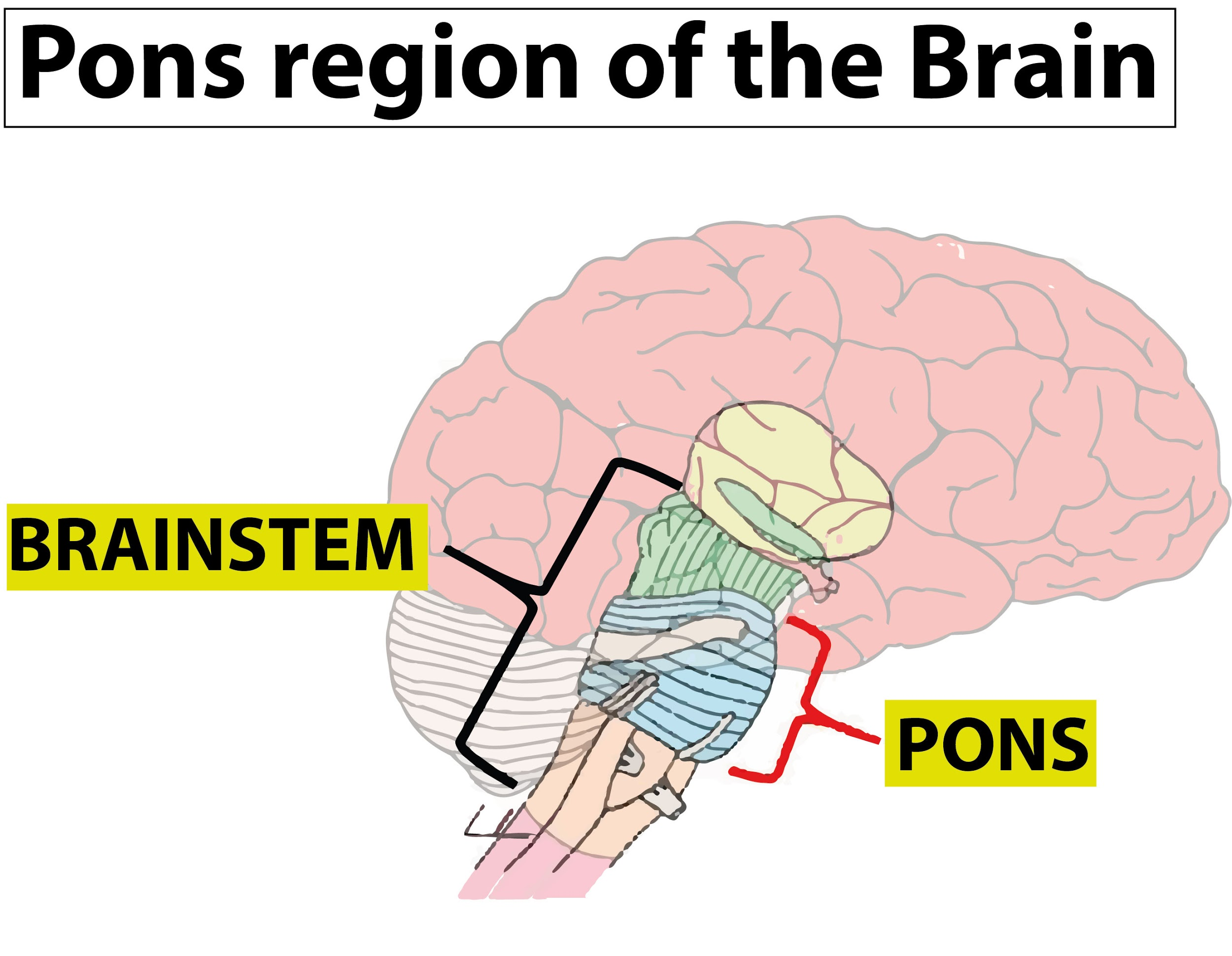
Additional Information:
- In Latin ‘pons’ means bridge and which indicates the function of the pons between cerebral cortex and cerebellum.
- Pons connects the cerebrum with the lower part of the brain and spinal cord and consist of a nerve fibre or white matter passing from higher- level brain to spinal cord.
- The brain stem consists of major four regions: midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata and cerebrum or hindbrain.
- Brain stem is a passway for fibre tracts running between the cerebrum and spinal cord.
- Brain stem is heavily involved with the interaction of face and head with rigidly programmed automatic behaviours necessary for survival.
- Brain stem region is about an inch in length and microscopically, it consists of deep gray matter surrounded by white matter fibre tracts.
- The embryological development of pons and medulla arise from rhombencephalon or hindbrain together with the cerebellum.
- Visually pons look like an enlarged section of the medulla oblongata but the actual structure of pons is quite different.
- Pons region of the brain is the origin of several carnival nerves.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Pons region of the brain.’
Note:
- Pons dorsal surface forms the upper part of the floor of fourth ventricles and literally, it continues with the middle cerebellar peduncle.
- The fifth and eighth carnival nerves are directly connected to the pons region.
- In the groove between the pons and the medulla emerge, from medial to lateral three types of nerves: abducens nerve, facial nerve and vestibular nerves.
Complete step by step answer:
Pons has sensory tract and motor tract same as medulla which contains nuclei known as pontine nuclei that deals with respiration, swallowing, bladder control, equilibrium, eyeball movement, facial expression etc. The major function of the Pons region is to regulate breathing rate and is involved in the control of sleep cycles. It also regulates your arousal and wakefulness states.

Additional Information:
- In Latin ‘pons’ means bridge and which indicates the function of the pons between cerebral cortex and cerebellum.
- Pons connects the cerebrum with the lower part of the brain and spinal cord and consist of a nerve fibre or white matter passing from higher- level brain to spinal cord.
- The brain stem consists of major four regions: midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata and cerebrum or hindbrain.
- Brain stem is a passway for fibre tracts running between the cerebrum and spinal cord.
- Brain stem is heavily involved with the interaction of face and head with rigidly programmed automatic behaviours necessary for survival.
- Brain stem region is about an inch in length and microscopically, it consists of deep gray matter surrounded by white matter fibre tracts.
- The embryological development of pons and medulla arise from rhombencephalon or hindbrain together with the cerebellum.
- Visually pons look like an enlarged section of the medulla oblongata but the actual structure of pons is quite different.
- Pons region of the brain is the origin of several carnival nerves.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(a) Pons region of the brain.’
Note:
- Pons dorsal surface forms the upper part of the floor of fourth ventricles and literally, it continues with the middle cerebellar peduncle.
- The fifth and eighth carnival nerves are directly connected to the pons region.
- In the groove between the pons and the medulla emerge, from medial to lateral three types of nerves: abducens nerve, facial nerve and vestibular nerves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




