
Plot the following points in the cartesian plane whose x, y coordinates are given.
x 2 3 -10 -9 -4 y -3 -3 41 10 -6
| x | 2 | 3 | -10 | -9 | -4 |
| y | -3 | -3 | 41 | 10 | -6 |
Answer
557.7k+ views
Hint: The x and y coordinates of the points have been given individually. We convert them in the form of $\left( x,y \right)$. The distances are from the origin. The x coordinate defines the distance of the point from the origin along the Y-axis. Same goes for y points. We plot those points in the graph according to their distance.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been provided with points on cartesian coordinates in the form of $\left( x,y \right)$.
Given all points will be turned into the form of $\left( x,y \right)$ where the distances are from the origin. The x coordinate defines the distance of the point from the origin along Y-axis.
The y coordinate defines the distance of the point from the origin along X-axis.
Now we plot all these points on the graph.
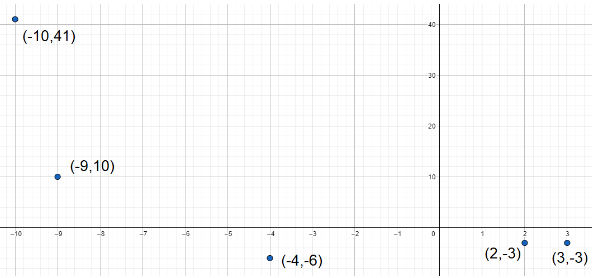
Let’s take every point one by one to find their positions. In every case we start from origin.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( 2,-3 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 2 units in a straight line along the X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 3 units in a straight line along the negative Y-axis from X axis.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( 3,-3 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 3 units in a straight line along the X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 3 units in a straight line along the negative Y-axis from X-axis.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( -10,41 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 10 units in a straight line along the negative X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 41 units in a straight line along the Y-axis from the X-axis.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( -9,10 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 9 units in a straight line along the negative X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 10 units in a straight line along the Y-axis from the X-axis.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( -4,-6 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 4 units in a straight line along the negative X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 6 units in a straight line along the negative Y-axis from the X-axis.
Note: We need to remember that the unit distance is fixed along both axes. Although we are finding the distance from origin, we are not finding the straight-line distance. For the straight-line distance, we have to apply Pythagoras’ theorem. We have a point $\left( x,y \right)$. Then the straight-line distance will be $\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}$ unit.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been provided with points on cartesian coordinates in the form of $\left( x,y \right)$.
Given all points will be turned into the form of $\left( x,y \right)$ where the distances are from the origin. The x coordinate defines the distance of the point from the origin along Y-axis.
The y coordinate defines the distance of the point from the origin along X-axis.
Now we plot all these points on the graph.

Let’s take every point one by one to find their positions. In every case we start from origin.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( 2,-3 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 2 units in a straight line along the X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 3 units in a straight line along the negative Y-axis from X axis.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( 3,-3 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 3 units in a straight line along the X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 3 units in a straight line along the negative Y-axis from X-axis.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( -10,41 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 10 units in a straight line along the negative X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 41 units in a straight line along the Y-axis from the X-axis.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( -9,10 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 9 units in a straight line along the negative X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 10 units in a straight line along the Y-axis from the X-axis.
$\left( x,y \right)=\left( -4,-6 \right)$. Here, the x-distance is 4 units in a straight line along the negative X-axis from the Y-axis and the y-distance is 6 units in a straight line along the negative Y-axis from the X-axis.
Note: We need to remember that the unit distance is fixed along both axes. Although we are finding the distance from origin, we are not finding the straight-line distance. For the straight-line distance, we have to apply Pythagoras’ theorem. We have a point $\left( x,y \right)$. Then the straight-line distance will be $\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}$ unit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




