
Platinised asbestos is used as a catalyst in the manufacture of${H_2}S{O_4}$. It is an example of-
A. Homogeneous catalyst
B. Heterogeneous catalyst
C. Auto catalyst
D. Induced catalyst
Answer
621.3k+ views
Hint- In order to solve this question, we will first understand the concept of sulphuric acid. Then we will compare induced catalyst, autocatalysis, heterogeneous catalyst and homogeneous catalyst to get the required result.
Complete answer:
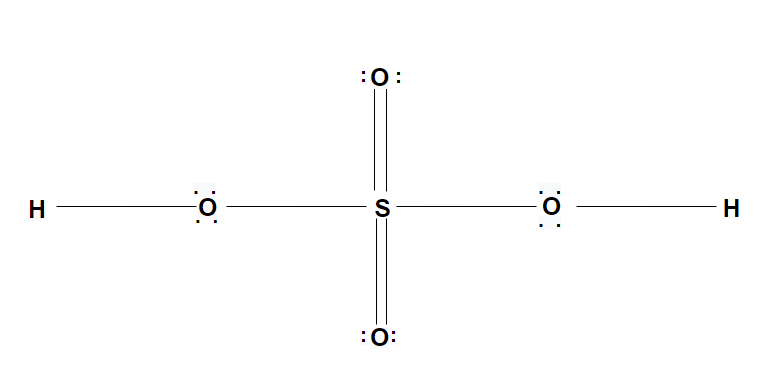
The sulphuric acid${H_2}S{O_4}$is a strong mineral acid. Its uses are one processing, fertilizer manufacturing, oil refining, wastewater processing and chemical synthesis. The molar mass of sulphuric acid is 98.07 g/mol. Sulphuric acid looks colorless and clear.
Heterogeneous catalyst- These are the catalysts whose phase differs from that of the reactants or products. Heterogeneous catalysts involve solid phase catalysts and gas phase reactants. Heterogeneous catalysis is very important because it enables faster, large scale production and selective product formation. Adsorption is an essential step in heterogeneous catalyst where catalyst is adsorbent and reactants are adsorbate.
Platinized asbestos is a solid catalyst whereas the reactants $S{O_2}$and ${O_2}$are products $S{O_3}$are in the gas phase in the manufacture of sulphuric acid. It is an example of heterogeneous catalysis because the phase of the catalyst is different i.e. solid whereas phase of reactants is liquid.
Catalyst- Platinised asbestos is in solid state.
Reactants -$S{O_2}$and ${O_2}$are in liquid state.
Product - $S{O_3}$is in gaseous state.
As both the phases are different, it is clear that Platinised asbestos is used as a catalyst in the manufacture of${H_2}S{O_4}$is an example of heterogeneous catalysis.
Induced catalyst is when a chemical reaction increases the rate of another chemical reaction.
Autocatalyst is if one of the reaction products is also a catalyst for the same or a coupled reaction.
Therefore, we conclude that only option B is correct.
Note- While solving this question, we must know the difference between heterogeneous catalyst i.e. Heterogeneous catalyst involves solid phase catalysts and gas phase reactants and homogeneous catalyst i.e. It refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution.
Complete answer:

The sulphuric acid${H_2}S{O_4}$is a strong mineral acid. Its uses are one processing, fertilizer manufacturing, oil refining, wastewater processing and chemical synthesis. The molar mass of sulphuric acid is 98.07 g/mol. Sulphuric acid looks colorless and clear.
Heterogeneous catalyst- These are the catalysts whose phase differs from that of the reactants or products. Heterogeneous catalysts involve solid phase catalysts and gas phase reactants. Heterogeneous catalysis is very important because it enables faster, large scale production and selective product formation. Adsorption is an essential step in heterogeneous catalyst where catalyst is adsorbent and reactants are adsorbate.
Platinized asbestos is a solid catalyst whereas the reactants $S{O_2}$and ${O_2}$are products $S{O_3}$are in the gas phase in the manufacture of sulphuric acid. It is an example of heterogeneous catalysis because the phase of the catalyst is different i.e. solid whereas phase of reactants is liquid.
Catalyst- Platinised asbestos is in solid state.
Reactants -$S{O_2}$and ${O_2}$are in liquid state.
Product - $S{O_3}$is in gaseous state.
As both the phases are different, it is clear that Platinised asbestos is used as a catalyst in the manufacture of${H_2}S{O_4}$is an example of heterogeneous catalysis.
Induced catalyst is when a chemical reaction increases the rate of another chemical reaction.
Autocatalyst is if one of the reaction products is also a catalyst for the same or a coupled reaction.
Therefore, we conclude that only option B is correct.
Note- While solving this question, we must know the difference between heterogeneous catalyst i.e. Heterogeneous catalyst involves solid phase catalysts and gas phase reactants and homogeneous catalyst i.e. It refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




