
Place a glass beaker, partially filled with water, in a sink. The beaker has a mass \[390gm\] and an interior volume of \[500c{{m}^{3}}\]. You now start to fill the sink with water and you find, by experiment, that if the beaker is less than half full, it will float; but if it is more than half full, it remains on the bottom of the sink as it rises to its rim. What is the density of the material of which the beaker is made?
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: We need to first find the mass of the water in the half filled beaker. Then using the law of floatation we find the volume of water displaced by the beaker. Difference between them gives the volume of the beaker. Mass of the beaker is given to us. So ultimately we calculate the density of the material of the beaker.
Formula used:
Law of floatation, ${{W}_{d}}={{W}_{b+w}}$
Complete step by step answer:
We can understand from the question that when the beaker is half filled, it is going to float when water in the sink is up to the rim of the beaker. Let us consider V to be the total volume of water displaced in the sink.
To find the mass of the water in the beaker when it is half filled, we take half of the volume. i.e. \[250c{{m}^{3}}\]
Then, $m=250c{{m}^{3}}\times 1\dfrac{g}{c{{m}^{3}}}=250g$
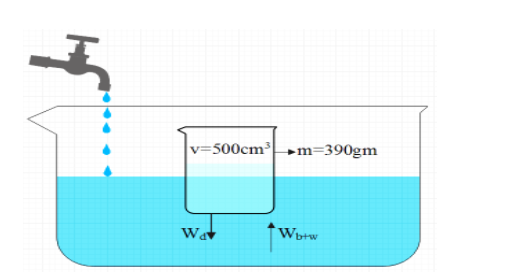
Let us apply the law of floatation now
Weight of the water displaced by the beaker=weight of the water and the beaker
\[\begin{align}
& {{W}_{d}}={{W}_{b+w}} \\
& \Rightarrow (0.39+0.25)\times 9.8=V\times 1000\times 9.8 \\
& \Rightarrow V=640\times {{10}^{-6}}{{m}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow V=640c{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
So volume of solid mass of beaker will be,
\[V=\left( 640c{{m}^{3}}-500c{{m}^{3}} \right)=140c{{m}^{3}}\]
Mass of the beaker given to us as 390g.
Then the density of the beaker will be,
$D=\dfrac{m}{V}=\dfrac{390g}{140c{{m}^{3}}}=2.79\dfrac{g}{c{{m}^{3}}}$
Hence the density of the beaker is $2.79\dfrac{g}{c{{m}^{3}}}$ .
Note:
Equilibrium is the state of a system in which all the forces are balanced. The buoyant force acting on the sphere is due to the liquid displaced by it when it is completely immersed in the liquid. The force is directly proportional to the weight of the liquid displaced by it. For this system to be in equilibrium, the weight of the sphere should be equal to the summation of the tension of the string and the buoyant force.
Formula used:
Law of floatation, ${{W}_{d}}={{W}_{b+w}}$
Complete step by step answer:
We can understand from the question that when the beaker is half filled, it is going to float when water in the sink is up to the rim of the beaker. Let us consider V to be the total volume of water displaced in the sink.
To find the mass of the water in the beaker when it is half filled, we take half of the volume. i.e. \[250c{{m}^{3}}\]
Then, $m=250c{{m}^{3}}\times 1\dfrac{g}{c{{m}^{3}}}=250g$

Let us apply the law of floatation now
Weight of the water displaced by the beaker=weight of the water and the beaker
\[\begin{align}
& {{W}_{d}}={{W}_{b+w}} \\
& \Rightarrow (0.39+0.25)\times 9.8=V\times 1000\times 9.8 \\
& \Rightarrow V=640\times {{10}^{-6}}{{m}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow V=640c{{m}^{3}} \\
\end{align}\]
So volume of solid mass of beaker will be,
\[V=\left( 640c{{m}^{3}}-500c{{m}^{3}} \right)=140c{{m}^{3}}\]
Mass of the beaker given to us as 390g.
Then the density of the beaker will be,
$D=\dfrac{m}{V}=\dfrac{390g}{140c{{m}^{3}}}=2.79\dfrac{g}{c{{m}^{3}}}$
Hence the density of the beaker is $2.79\dfrac{g}{c{{m}^{3}}}$ .
Note:
Equilibrium is the state of a system in which all the forces are balanced. The buoyant force acting on the sphere is due to the liquid displaced by it when it is completely immersed in the liquid. The force is directly proportional to the weight of the liquid displaced by it. For this system to be in equilibrium, the weight of the sphere should be equal to the summation of the tension of the string and the buoyant force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




