
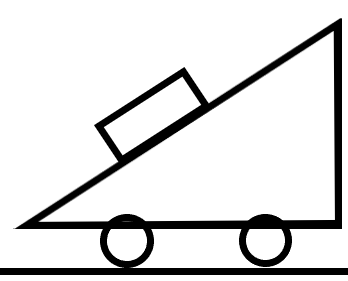
Picture a cart with an inclined top surface (see diagram). Assume \[\theta ={{30}^{0}}\]. At what rate must the cart accelerate to the slide to keep a frictionless block on it from sliding off (in \[m{{s}^{-2}}\])?
A) 4.9
B) 5.7
C) 8.5
D) 17.0

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the relation of the acceleration that will be acting on the cart which can keep a box without sliding down the frictionless contact between the cart and the block. We can relate the gravitational force and the external force.
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given a situation in which a cart with an inclined top surface is accelerating in a direction with a box kept on the inclined plane. The contact between the box and the cart is such that there exists no friction between the two surfaces. So, we can understand that for the box not to be sliding down the plane, there should be acceleration along the horizontal.
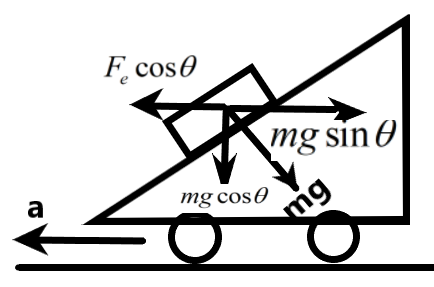
We know that for a body undergoing acceleration, a force will be acting on it. Also, the gravitational force acts along the vertical direction of the system. We can resolve the components of both the forces and equate the horizontal components to get the required acceleration.
i.e.,
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{g}}\sin \theta ={{F}_{e}}\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =ma\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow g\sin {{30}^{0}}=a\cos {{30}^{0}} \\
& \Rightarrow (9.8)\dfrac{1}{2}=a(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}) \\
& \therefore a=5.66m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}\]
The acceleration produced by the cart so that the box placed on its inclined plane will be at rest without sliding is at 5.7 \[m{{s}^{-2}}\].
This is the required solution.
The correct answer is option B.
Note: The external force acting on the body is completely balancing the box on the inclined surface. In practical situations, the frictional force between the cart and the box is necessary to keep the box from sliding depending on the angle of inclination.
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given a situation in which a cart with an inclined top surface is accelerating in a direction with a box kept on the inclined plane. The contact between the box and the cart is such that there exists no friction between the two surfaces. So, we can understand that for the box not to be sliding down the plane, there should be acceleration along the horizontal.

We know that for a body undergoing acceleration, a force will be acting on it. Also, the gravitational force acts along the vertical direction of the system. We can resolve the components of both the forces and equate the horizontal components to get the required acceleration.
i.e.,
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{g}}\sin \theta ={{F}_{e}}\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =ma\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow g\sin {{30}^{0}}=a\cos {{30}^{0}} \\
& \Rightarrow (9.8)\dfrac{1}{2}=a(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}) \\
& \therefore a=5.66m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}\]
The acceleration produced by the cart so that the box placed on its inclined plane will be at rest without sliding is at 5.7 \[m{{s}^{-2}}\].
This is the required solution.
The correct answer is option B.
Note: The external force acting on the body is completely balancing the box on the inclined surface. In practical situations, the frictional force between the cart and the box is necessary to keep the box from sliding depending on the angle of inclination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




