
Phreatophytes are xerophytes with roots
(a)Spread along the soil surface
(b)Well spread in the soil
(c)Very deep-reaching groundwater fringe
(d)Very deep but well above groundwater
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Phreatophytes are xerophytic plants found in arid as well as wet areas and have significant value in finding water sources in arid areas. They have a specific type of root structure to help in this process.
Complete answer:
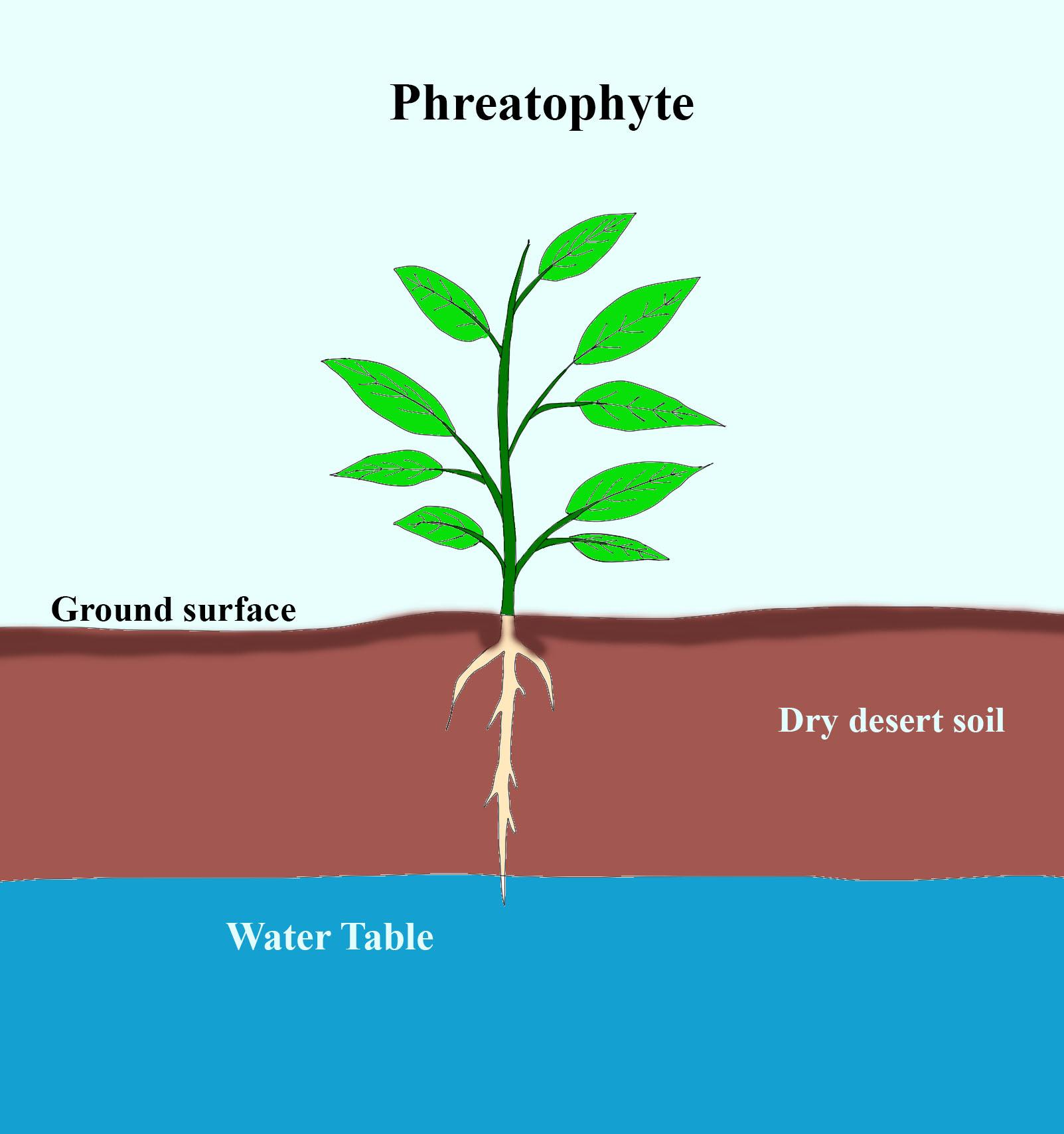
Phreatophytes belong to the xerophytic type of plants and have roots very deep to reach the groundwater fringe. These are supplied with water and have roots that constantly stay in touch with moisture, therefore are found in areas with running water. Along with desert areas, these are also found in wetlands, floodplains, and any place that can hold water.
Additional Information:
As xerophytes, these plants are characteristics of the desert areas but found in wetlands as well. These are very important ecologically as they are fast-growing pioneers and highly resistant to diseases. These have many functions as fodder for livestock, nesting for fauna, as a fuel or construction material and basketry, etc. It also helps in the indication of potable groundwater and some help in the indication of freshwater as they have low tolerance towards salt. This helps in finding drinking and agricultural water sources in arid areas. Some examples of Phreatophytes are Welwitschia, mesquite, alfalfa, etc.
So the correct answer is ' Very deep reaching groundwater fringe'.
Note: Phreatophytes deep root structure is a mode of adaptation in areas where the water level is very low. In areas like deserts, the groundwater level is deep down and the roots are capable of reaching these sources by this adaptation and allows them to access water during long periods of drought in such areas. An example of Phreatophytes is mesquite trees or Prosopis which have the longest taproot of all desert plants which is almost 25m long and reaches the water table.
Complete answer:
Phreatophytes belong to the xerophytic type of plants and have roots very deep to reach the groundwater fringe. These are supplied with water and have roots that constantly stay in touch with moisture, therefore are found in areas with running water. Along with desert areas, these are also found in wetlands, floodplains, and any place that can hold water.

Additional Information:
As xerophytes, these plants are characteristics of the desert areas but found in wetlands as well. These are very important ecologically as they are fast-growing pioneers and highly resistant to diseases. These have many functions as fodder for livestock, nesting for fauna, as a fuel or construction material and basketry, etc. It also helps in the indication of potable groundwater and some help in the indication of freshwater as they have low tolerance towards salt. This helps in finding drinking and agricultural water sources in arid areas. Some examples of Phreatophytes are Welwitschia, mesquite, alfalfa, etc.
So the correct answer is ' Very deep reaching groundwater fringe'.
Note: Phreatophytes deep root structure is a mode of adaptation in areas where the water level is very low. In areas like deserts, the groundwater level is deep down and the roots are capable of reaching these sources by this adaptation and allows them to access water during long periods of drought in such areas. An example of Phreatophytes is mesquite trees or Prosopis which have the longest taproot of all desert plants which is almost 25m long and reaches the water table.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




