
Phenyl isocyanide is prepared from aniline by:
(a)- Rosenmund’s reaction
(b)- Kolbe’s reaction
(c)- Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(d)- Fittig reaction
(e)- Carbylamine reaction.
Answer
603.9k+ views
Hint: The catalyst used is chloroform and an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide. This reaction is a type of test reaction that is used to distinguish between primary amines from secondary and tertiary amines.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us study all the options one by one:
(a)- Rosenmund reaction.
Acid chlorides are easily reduced to the corresponding aldehydes by passing hydrogen gas through boiling xylene solution of the acid chloride in the presence of a Pd catalyst supported over\[BaS{{O}_{4}}\].
\[RCOCl+{{H}_{2}}\to RCOH+HCl\]
(b)- Kolbe’s reaction.
Sodium phenoxide when heated with carbon dioxide at 400 K under a pressure of 4-7 atmosphere followed by acidification gives 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (salicylic acid) as the main product.
(c)- Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
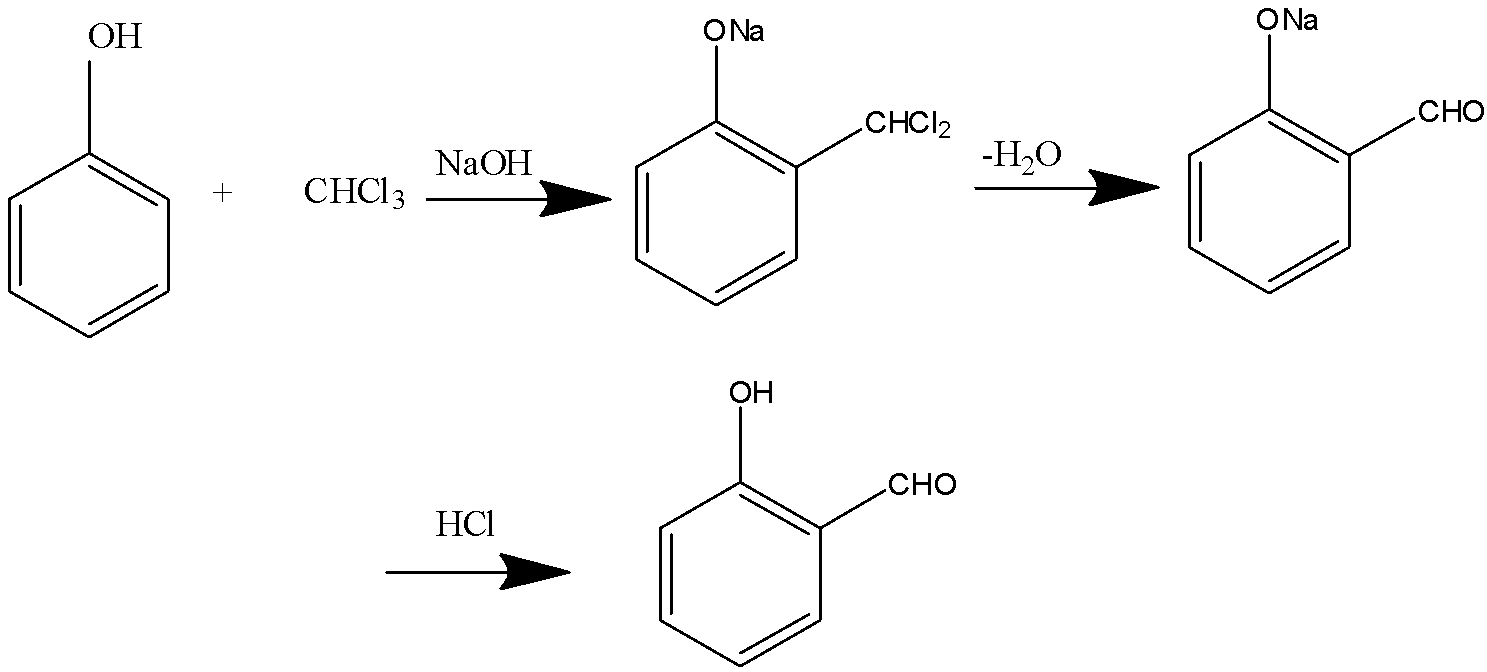
Treatment of phenol with chloroform in the presence of aqueous or potassium hydroxide at 340K followed by hydrolysis of the resulting product gives 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde) as the major product.
(d)- Fittig reaction.
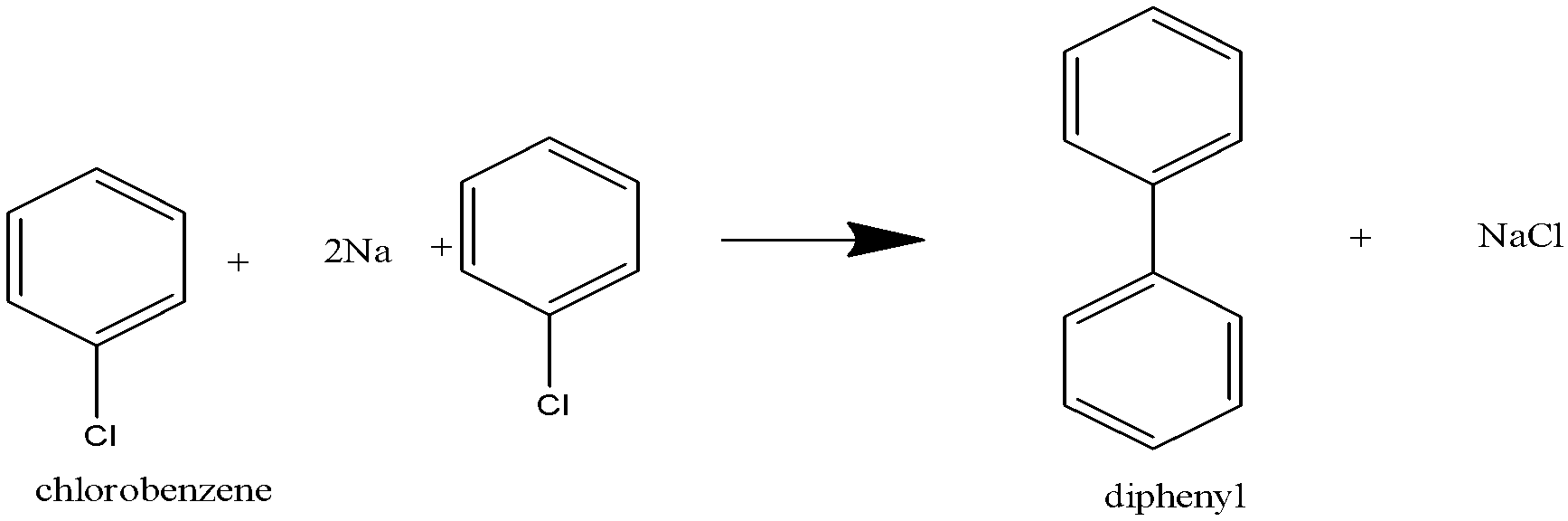
When only haloarenes are treated with sodium, diaryls are produced.
(e)- Carbylamine reaction.
Both aliphatic and aromatic primary amines when warmed with chloroform and an alcoholic solution of KOH produce isocyanides or carbylamines.
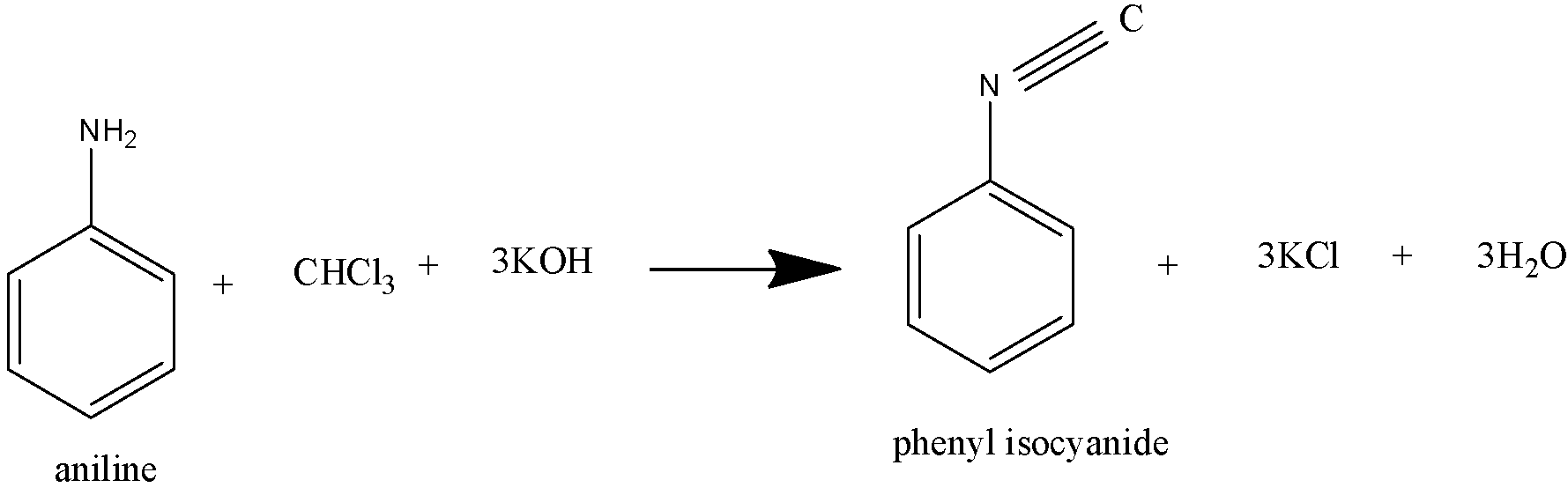
So, from the above observation, we can see that aniline is converted into phenyl isocyanide in the carbylamine reaction.
So, the correct answer is “Option E”.
Note: Don’t get confused between reamer-teimann and carbylamines reaction because both of them have chloroform as one of the reactants. In contrast, secondary and tertiary amines do not give the carbylamine reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us study all the options one by one:
(a)- Rosenmund reaction.
Acid chlorides are easily reduced to the corresponding aldehydes by passing hydrogen gas through boiling xylene solution of the acid chloride in the presence of a Pd catalyst supported over\[BaS{{O}_{4}}\].
\[RCOCl+{{H}_{2}}\to RCOH+HCl\]
(b)- Kolbe’s reaction.
Sodium phenoxide when heated with carbon dioxide at 400 K under a pressure of 4-7 atmosphere followed by acidification gives 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (salicylic acid) as the main product.
(c)- Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Treatment of phenol with chloroform in the presence of aqueous or potassium hydroxide at 340K followed by hydrolysis of the resulting product gives 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde) as the major product.

(d)- Fittig reaction.
When only haloarenes are treated with sodium, diaryls are produced.

(e)- Carbylamine reaction.
Both aliphatic and aromatic primary amines when warmed with chloroform and an alcoholic solution of KOH produce isocyanides or carbylamines.

So, from the above observation, we can see that aniline is converted into phenyl isocyanide in the carbylamine reaction.
So, the correct answer is “Option E”.
Note: Don’t get confused between reamer-teimann and carbylamines reaction because both of them have chloroform as one of the reactants. In contrast, secondary and tertiary amines do not give the carbylamine reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




