
Phenol can be converted into salicylic acid by heating with:
A.\[C{O_2}\] (under pressure) and alkali
B.\[CC{l_4}\] and alkali
C.\[CHC{l_3}\] and alkali followed by oxidation
D.All of the above
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: We need to know that the phenol is an aromatic organic chemical compound having the molecular formula, \[{C_6}{H_5}OH\]. It is a white crystalline solid and volatile in nature. The phenol contains one phenyl group and one hydroxyl group. The hydroxyl group is attached with the phenyl ring. And it is slightly acidic in nature.
Complete answer:
The phenol will not convert into salicylaldehyde, when it is heated with carbon dioxide under pressure and in the presence of alkali. Hence, option (A) is incorrect.
When the phenol is heated with carbon tetrachloride alkali, then the phenol will not convert into salicylaldehyde. Hence, option (B) is incorrect.
When the phenol is heated with chloroform and potassium hydroxide which act as a base (or sodium hydroxide) then there is a formation of aldehyde which is known as salicylaldehyde with potassium chloride and water. And this reaction is known as the Reimer – Tiemann reaction. Here, the aldehydic group \[\left( { - CHO} \right)\] attacks the ortho position of the phenol. The reaction can be written as,
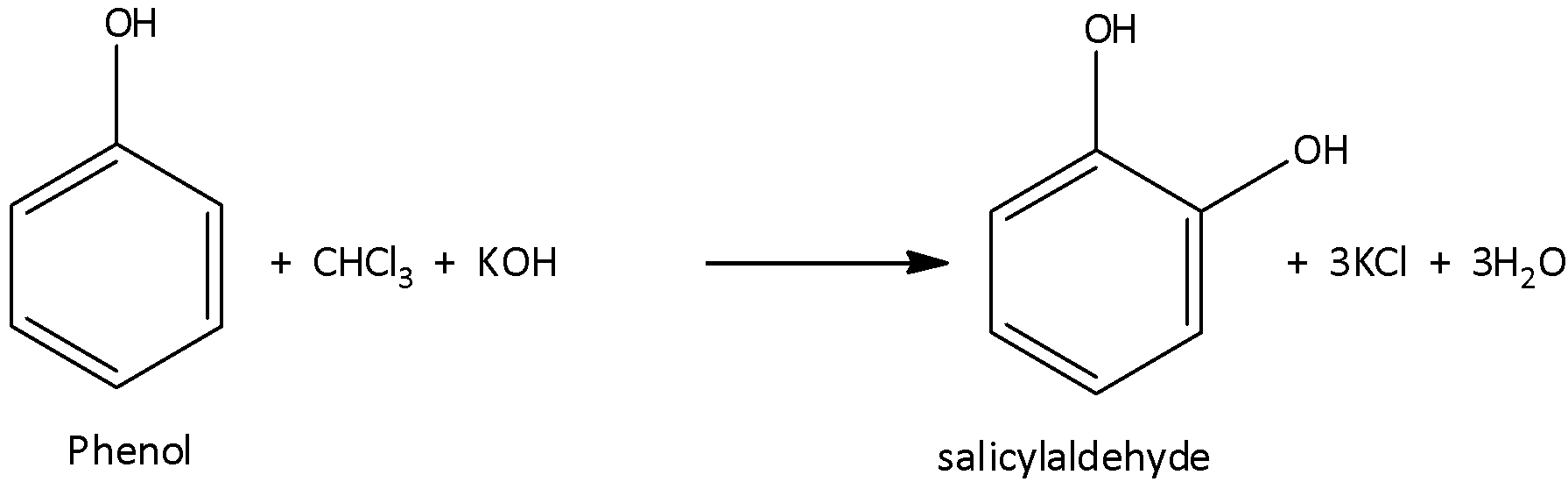
Here the reaction starts with the deprotonation of\[CHC{l_3}\]in the presence of a strong base and forms a chloroform carbanion. This will readily undergo the alpha elimination reaction which gives dichlorocarbene.
The phenol also undergoes the deprotonation by aqueous hydroxide, forming phenoxide which is negatively charged. And this negative charge will delocalize the benzene ring which becomes highly nucleophilic. Hence, there undergoes a nucleophilic attack on the dichlorocarbene and forms an intermediate which is known as dichloromethyl substituted phenol. At last, this intermediate undergoes basic hydrolysis and there is a formation of ortho – hydroxy benzaldehyde which is known as salicylaldehyde. Hence, option (C) is correct.
When the phenol is heated with chloroform followed by an alkali solution, then the phenol is converted into salicylaldehyde. Hence, option (D) is incorrect.
Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
We must remember that when the phenol is reacted with chloroform in the presence of bases, there is a formation of salicylaldehyde by attacking the aldehydic group on the ortho position of the phenol. This reaction is known as the Reimer – Tiemann reaction. Here, the first step is the deprotonation of chloroform. The carbene is highly electron deficient. Because, the chlorine atom has an electron – withdrawing nature.
Complete answer:
The phenol will not convert into salicylaldehyde, when it is heated with carbon dioxide under pressure and in the presence of alkali. Hence, option (A) is incorrect.
When the phenol is heated with carbon tetrachloride alkali, then the phenol will not convert into salicylaldehyde. Hence, option (B) is incorrect.
When the phenol is heated with chloroform and potassium hydroxide which act as a base (or sodium hydroxide) then there is a formation of aldehyde which is known as salicylaldehyde with potassium chloride and water. And this reaction is known as the Reimer – Tiemann reaction. Here, the aldehydic group \[\left( { - CHO} \right)\] attacks the ortho position of the phenol. The reaction can be written as,

Here the reaction starts with the deprotonation of\[CHC{l_3}\]in the presence of a strong base and forms a chloroform carbanion. This will readily undergo the alpha elimination reaction which gives dichlorocarbene.
The phenol also undergoes the deprotonation by aqueous hydroxide, forming phenoxide which is negatively charged. And this negative charge will delocalize the benzene ring which becomes highly nucleophilic. Hence, there undergoes a nucleophilic attack on the dichlorocarbene and forms an intermediate which is known as dichloromethyl substituted phenol. At last, this intermediate undergoes basic hydrolysis and there is a formation of ortho – hydroxy benzaldehyde which is known as salicylaldehyde. Hence, option (C) is correct.
When the phenol is heated with chloroform followed by an alkali solution, then the phenol is converted into salicylaldehyde. Hence, option (D) is incorrect.
Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
We must remember that when the phenol is reacted with chloroform in the presence of bases, there is a formation of salicylaldehyde by attacking the aldehydic group on the ortho position of the phenol. This reaction is known as the Reimer – Tiemann reaction. Here, the first step is the deprotonation of chloroform. The carbene is highly electron deficient. Because, the chlorine atom has an electron – withdrawing nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




