
What is the phase angle of the source voltage with respect to the current? Does the source voltage lag or lead current?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: First find out the total impedance of an electric circuit containing all the three components that are resistor, capacitor and inductor. Then calculate the root mean square current by using the root mean square voltage which is the AC equivalent of the DC or the source voltage applied.
Complete step by step answer:
To get a better understanding of phase angle let us make a phasor diagram for an LCR circuit.
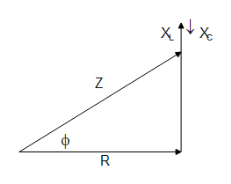
The angle $\varphi $ denotes the phase angle between voltage and current.
Now the total impedance of the circuit is given by
$Z = \sqrt {{R^2} + {{({X_L} - {X_C})}^2}} $
Where $R$ is the resistance of the circuit, ${X_L}$ is the inductive reactance and ${X_C}$ is the capacitive reactance.
Now the current is defined as
${I_{rms}} = \dfrac{{{V_{rms}}}}{Z}$
$\tan \varphi = \dfrac{{{X_L} - {X_C}}}{R}$ (from the phasor diagram)
$ \therefore \varphi = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{{X_L} - {X_C}}}{R}$
Which is the required phase angle.
Now for the second part of the question, we have three cases that need to be discussed.
Case 1: For an LCR circuit if ${X_L} > {X_C}$ , the current will be more inductive than capacitive and the current will lag behind the source voltage.
Case 2: For an LCR circuit if ${X_L} < {X_C}$ , the current will be more capacitive than inductive and the current will lead to the source voltage.
Case 3: For the LCR circuit if ${X_L} = {X_C}$ , then the circuit will resist and current and source voltage will be in the same phase.
Note: It is helpful to treat phase as if it is defined in a vector plane for simpler understanding. In a purely inductive circuit, the phase is positive while in a purely capacitive circuit the phase will be negative. In the case of a resistive circuit, the circuit is said to be in a resonant condition which has numerous circuit applications and the phase angle is zero.
Complete step by step answer:
To get a better understanding of phase angle let us make a phasor diagram for an LCR circuit.

The angle $\varphi $ denotes the phase angle between voltage and current.
Now the total impedance of the circuit is given by
$Z = \sqrt {{R^2} + {{({X_L} - {X_C})}^2}} $
Where $R$ is the resistance of the circuit, ${X_L}$ is the inductive reactance and ${X_C}$ is the capacitive reactance.
Now the current is defined as
${I_{rms}} = \dfrac{{{V_{rms}}}}{Z}$
$\tan \varphi = \dfrac{{{X_L} - {X_C}}}{R}$ (from the phasor diagram)
$ \therefore \varphi = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{{X_L} - {X_C}}}{R}$
Which is the required phase angle.
Now for the second part of the question, we have three cases that need to be discussed.
Case 1: For an LCR circuit if ${X_L} > {X_C}$ , the current will be more inductive than capacitive and the current will lag behind the source voltage.
Case 2: For an LCR circuit if ${X_L} < {X_C}$ , the current will be more capacitive than inductive and the current will lead to the source voltage.
Case 3: For the LCR circuit if ${X_L} = {X_C}$ , then the circuit will resist and current and source voltage will be in the same phase.
Note: It is helpful to treat phase as if it is defined in a vector plane for simpler understanding. In a purely inductive circuit, the phase is positive while in a purely capacitive circuit the phase will be negative. In the case of a resistive circuit, the circuit is said to be in a resonant condition which has numerous circuit applications and the phase angle is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




