
Phagocytosis
(a) Is carried by cells of the adaptive immune system.
(b) Is restricted to macrophages.
(c) Is important in bacterial infections.
(d) Is a process that does not involve energy.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Other than feeding in unicellular organisms the processes of phagocytosis is also used by the immune system of higher organisms mainly against a particular microorganism.
Complete answer:
Phagocytosis is important in bacterial infections. Phagocytosis is the process by which certain living cells known as phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles. A free-living unicellular organism, such as an amoeba, or one of the body cells, such as a white blood cell is the phagocyte. In multicellular or higher organisms or animals, it is mainly a defensive reaction against infection and invasion of bacteria or foreign substances or antigens.
Additional Information:
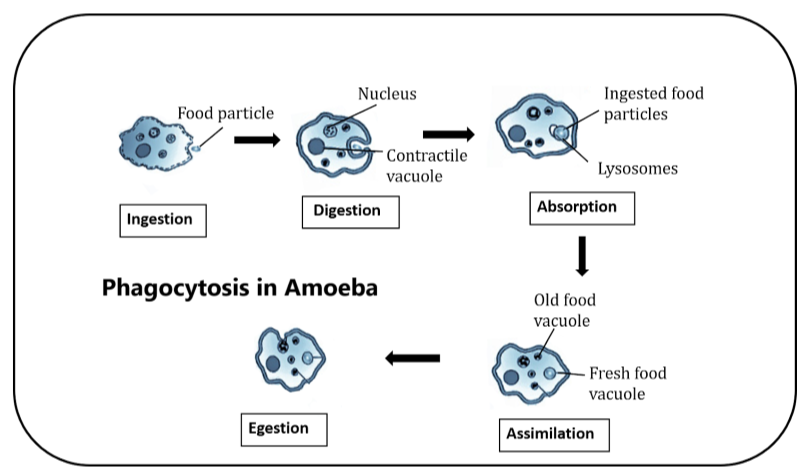
- In unicellular organisms, phagocytosis is a means of nutrition or feeding such as in amoebas and sponges.
- In humans, the most-effective phagocytic cells are two kinds of white blood cells: the macrophages and the neutrophils.
- The macrophages and therefore the neutrophils are carried along by the circulating blood until they reach a neighborhood of infected tissue, where they undergo the vessel wall into that tissue.
- Both macrophages and neutrophils are drawn toward a neighborhood of infection or inflammation by means of drugs given off by the bacteria, they engulf particles after colliding with them.
- Before phagocytosis is accomplished, the phagocyte and the bacteria or particle must adhere to each other.
- The cell flows around the object until it has been engulfed completely.
- The engulfed object is then enclosed within a membrane-bound vacuole known as a phagosome.
- The phagocyte digests the ingested particle with the assistance of hydrolytic enzymes, which are present within membrane-enclosed sacs called lysosomes that are found within the cell.
- Phagocytic enzymes are secreted into the vacuole during which digestion takes place.
So, the correct answer is, ’(c) Is important in bacterial infections’.
Note:
- The particles that generally undergo phagocytosis by white blood cells include bacteria, dead tissue cells, protozoa, various dust particles, pigments, and other minute foreign bodies.
- The phagocyte digests the ingested particle with the assistance of hydrolytic enzymes, which are present within membrane- enclosed sacs called lysosomes that are found within the cell.
- Phagocytic enzymes are secreted into the vacuole during which digestion takes place.
Complete answer:
Phagocytosis is important in bacterial infections. Phagocytosis is the process by which certain living cells known as phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles. A free-living unicellular organism, such as an amoeba, or one of the body cells, such as a white blood cell is the phagocyte. In multicellular or higher organisms or animals, it is mainly a defensive reaction against infection and invasion of bacteria or foreign substances or antigens.
Additional Information:
- In unicellular organisms, phagocytosis is a means of nutrition or feeding such as in amoebas and sponges.

- In humans, the most-effective phagocytic cells are two kinds of white blood cells: the macrophages and the neutrophils.
- The macrophages and therefore the neutrophils are carried along by the circulating blood until they reach a neighborhood of infected tissue, where they undergo the vessel wall into that tissue.
- Both macrophages and neutrophils are drawn toward a neighborhood of infection or inflammation by means of drugs given off by the bacteria, they engulf particles after colliding with them.
- Before phagocytosis is accomplished, the phagocyte and the bacteria or particle must adhere to each other.
- The cell flows around the object until it has been engulfed completely.
- The engulfed object is then enclosed within a membrane-bound vacuole known as a phagosome.
- The phagocyte digests the ingested particle with the assistance of hydrolytic enzymes, which are present within membrane-enclosed sacs called lysosomes that are found within the cell.
- Phagocytic enzymes are secreted into the vacuole during which digestion takes place.
So, the correct answer is, ’(c) Is important in bacterial infections’.
Note:
- The particles that generally undergo phagocytosis by white blood cells include bacteria, dead tissue cells, protozoa, various dust particles, pigments, and other minute foreign bodies.
- The phagocyte digests the ingested particle with the assistance of hydrolytic enzymes, which are present within membrane- enclosed sacs called lysosomes that are found within the cell.
- Phagocytic enzymes are secreted into the vacuole during which digestion takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




