
\[PC{{l}_{3}}\] reacts with water, and then forms acid of phosphorus, what is the basicity of acid of phosphorus?
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we should know that basicity of an acid is the number of replaceable hydrogen atoms present in a molecule of the acid. We should know that the acid which contains one, two, three replaceable hydrogen atoms in its molecule, they are called a monobasic, dibasic and tribasic acid respectively.
Step by step answer:
We should know that Phosphorous trichloride or phosphorous chloride is a colourless liquid. When we react it with water, it reacts violently with water to give the product of phosphoric acid and hydrochloride gas. It reacts violently with water and it produces an exothermic reaction involving release of acid gases.
\[PC{{l}_{3}}+3{{H}_{2}}O\to {{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}+3HCl\]
We should know that Phosphorous acid is a diprotic acid that is, it ionizes two protons. It is better described with the structural formula \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}\] phosphorous acid is prepared by hydrolysis of phosphorus trichloride with acid or steam. Now, we should see the structure of\[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}\].
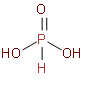
So, by observing the above structures we came to know that in its structure it has one double bond between P and O and two P and OH single bonds and one P and H bond. So, it has two acidic hydrogen that will come from a hydroxide molecule. The hydrogen which has a direct bond with phosphorus cannot be ionised so it is not acidic hydrogen. Hence we can say that only the H atoms attached with oxygen cause basicity. Only two hydrogens will come from the hydroxide molecule, so its basicity will be 2.
So, now we can say that phosphorous acid, \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}\] is dibasic due to the presence of two P-OH bonds whereas phosphoric acid, \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}\] is tribasic due to the presence of three P-OH bonds.
Note:
We should be careful in handling phosphorus trichloride. We should be careful because on exposure to skin it will cause severe burns. Inhalation of this compound leads to burning sensation, coughing. We should be careful when we want to handle large quantities of\[PC{{l}_{3}}\]. We should always work in dry surroundings, such as in a glove box. Avoid contact with water and humid environments.
Step by step answer:
We should know that Phosphorous trichloride or phosphorous chloride is a colourless liquid. When we react it with water, it reacts violently with water to give the product of phosphoric acid and hydrochloride gas. It reacts violently with water and it produces an exothermic reaction involving release of acid gases.
\[PC{{l}_{3}}+3{{H}_{2}}O\to {{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}+3HCl\]
We should know that Phosphorous acid is a diprotic acid that is, it ionizes two protons. It is better described with the structural formula \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}\] phosphorous acid is prepared by hydrolysis of phosphorus trichloride with acid or steam. Now, we should see the structure of\[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}\].

So, by observing the above structures we came to know that in its structure it has one double bond between P and O and two P and OH single bonds and one P and H bond. So, it has two acidic hydrogen that will come from a hydroxide molecule. The hydrogen which has a direct bond with phosphorus cannot be ionised so it is not acidic hydrogen. Hence we can say that only the H atoms attached with oxygen cause basicity. Only two hydrogens will come from the hydroxide molecule, so its basicity will be 2.
So, now we can say that phosphorous acid, \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}\] is dibasic due to the presence of two P-OH bonds whereas phosphoric acid, \[{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}\] is tribasic due to the presence of three P-OH bonds.
Note:
We should be careful in handling phosphorus trichloride. We should be careful because on exposure to skin it will cause severe burns. Inhalation of this compound leads to burning sensation, coughing. We should be careful when we want to handle large quantities of\[PC{{l}_{3}}\]. We should always work in dry surroundings, such as in a glove box. Avoid contact with water and humid environments.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




