
Packing fraction in 2D-hexagonal arrangement of identical sphere is:
A. $\dfrac{\pi }{{3\sqrt 2 }}$
B. $\dfrac{\pi }{{3\sqrt 3 }}$
C. $\dfrac{\pi }{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
D. $\dfrac{\pi }{6}$
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:packing fraction is defined as the fraction of the volume in the crystal structure that is occupied by the constituent particle. It is also called packing efficiency or atomic packing factor. This definition is of crystallography.
Complete answer:
For 2D-hexagonal close packing system:
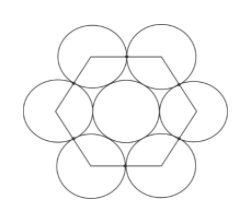
$2r=a$(from diagram)
As we have seen in the figure there is one hexagon which can divide in the 6 equilateral triangles.
So to find the area of the hexagon we will divide the area in 6 equilateral triangles.
So as we all know that area of an equilateral triangle is $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}$, where a is the side of the hexagon or side of the triangle.
So $\text{area of hexagon = 6}$ $ \times $ $\text{area of equilateral triangle}$ = $6 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}$
Now we have $a =2r$
So putting the value of a we get
Total area of hexagon will be $6 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{(2r)^2} = 6 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times 4{r^2} = 6\sqrt 3 {r^2}$
Now from the figure we can say that total spherical constituent in the hexagon will be-
$1 + \dfrac{1}{3} \times 6 = 3$(one sphere of the middle and one third of 6 sphere)
Let radius of one sphere is r
So area of the 3 sphere is $3\pi {r^2}$
$\therefore\,\text{Packing efficiency of Packing fraction = }$$\dfrac{{{\text{Total occupied space}}}}{{{\text{Total area of the hexagon}}}}$
$\text{Packing efficiency of Packing fraction = }$$\dfrac{{3\pi {r^2}}}{{6\sqrt 3 {r^2}}} = \dfrac{\pi }{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
Hence option C will be the correct answer.
Note:
Packing efficiency is the term used In the crystallography. This term is used to define the solidness of an atom. If packing efficiency is more than the atom will be solid and if packing efficiency is less than the atom less solid.
Complete answer:
For 2D-hexagonal close packing system:

$2r=a$(from diagram)
As we have seen in the figure there is one hexagon which can divide in the 6 equilateral triangles.
So to find the area of the hexagon we will divide the area in 6 equilateral triangles.
So as we all know that area of an equilateral triangle is $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}$, where a is the side of the hexagon or side of the triangle.
So $\text{area of hexagon = 6}$ $ \times $ $\text{area of equilateral triangle}$ = $6 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{a^2}$
Now we have $a =2r$
So putting the value of a we get
Total area of hexagon will be $6 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}{(2r)^2} = 6 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times 4{r^2} = 6\sqrt 3 {r^2}$
Now from the figure we can say that total spherical constituent in the hexagon will be-
$1 + \dfrac{1}{3} \times 6 = 3$(one sphere of the middle and one third of 6 sphere)
Let radius of one sphere is r
So area of the 3 sphere is $3\pi {r^2}$
$\therefore\,\text{Packing efficiency of Packing fraction = }$$\dfrac{{{\text{Total occupied space}}}}{{{\text{Total area of the hexagon}}}}$
$\text{Packing efficiency of Packing fraction = }$$\dfrac{{3\pi {r^2}}}{{6\sqrt 3 {r^2}}} = \dfrac{\pi }{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
Hence option C will be the correct answer.
Note:
Packing efficiency is the term used In the crystallography. This term is used to define the solidness of an atom. If packing efficiency is more than the atom will be solid and if packing efficiency is less than the atom less solid.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

What is myopia and hypermetropia How are they corrected class 12 physics CBSE




