
Pacemaker enzyme of the EMP pathway is
a) Hexokinase
b) Pyruvate kinase
c) Enolase
d) Phosphofructokinase
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: A pacemaker regulates the heartbeat and it can increase or decrease the heartbeat as per the requirements of the body. Glycolysis is also regulated through allosteric inhibition and the cell can increase or decrease its rate in response to the energy requirements.
Complete answer:
Phosphofructokinase is regarded as the pacemaker of the EMP pathway or glycolysis because it is the most important regulatory enzyme of glycolysis and it allows the cell to control the rate of glycolysis as per the energy requirement. The allosteric regulation is done by this enzyme in the step of glycolysis when fructose 6-phosphate is converted into fructose 1,6 – biphosphate with the utilization of ATP molecule. This step is also called committed step of glycolysis and if the ratio of ATP to ADP is high enough, the catalytic property of this enzyme is inhibited because ATP acts as a natural inhibitor and in turn, the rate of glycolysis is also affected because the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate is not done. In this way, this enzyme gives precise control of the glucose and other molecules that go down further in the process of glycolysis. The mechanism of action of this enzyme has been given below –
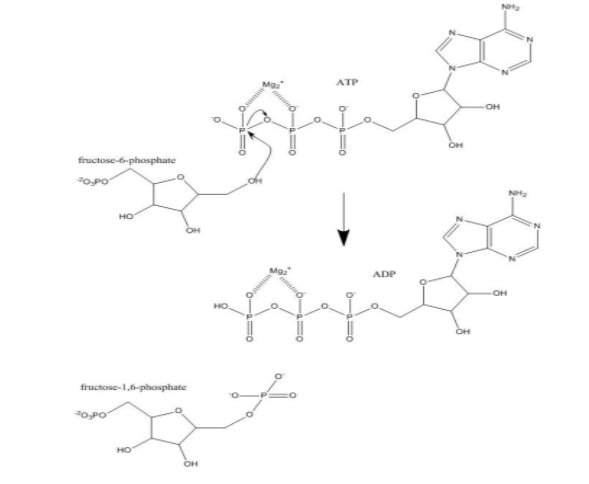
So, the correct answer is ‘Phosphofructokinase’.
Note:A genetic mutation in the enzyme PFK i.e. Phosphofructokinase leads to a condition known as Tarui’s disease. In this disease, some cells lose the ability to utilize carbohydrates as a source of energy. The symptoms include spasms, muscle weakness, myoglobin in urine, and compensated hemolysis.
Three phosphofructokinase genes are found in humans – PFKP (in platelets), PFKM (in muscles), and PFKL (in the liver).
Complete answer:
Phosphofructokinase is regarded as the pacemaker of the EMP pathway or glycolysis because it is the most important regulatory enzyme of glycolysis and it allows the cell to control the rate of glycolysis as per the energy requirement. The allosteric regulation is done by this enzyme in the step of glycolysis when fructose 6-phosphate is converted into fructose 1,6 – biphosphate with the utilization of ATP molecule. This step is also called committed step of glycolysis and if the ratio of ATP to ADP is high enough, the catalytic property of this enzyme is inhibited because ATP acts as a natural inhibitor and in turn, the rate of glycolysis is also affected because the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate is not done. In this way, this enzyme gives precise control of the glucose and other molecules that go down further in the process of glycolysis. The mechanism of action of this enzyme has been given below –

So, the correct answer is ‘Phosphofructokinase’.
Note:A genetic mutation in the enzyme PFK i.e. Phosphofructokinase leads to a condition known as Tarui’s disease. In this disease, some cells lose the ability to utilize carbohydrates as a source of energy. The symptoms include spasms, muscle weakness, myoglobin in urine, and compensated hemolysis.
Three phosphofructokinase genes are found in humans – PFKP (in platelets), PFKM (in muscles), and PFKL (in the liver).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




