
What about the concentration of acids in both reactions?

Answer
498.6k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are asked to find out what is the effect of the shape or size of particles of a reactant on the reaction and thus the concentration of the solution. We are given calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid and are asked to find out the concentration of the resulting solution in both cases.
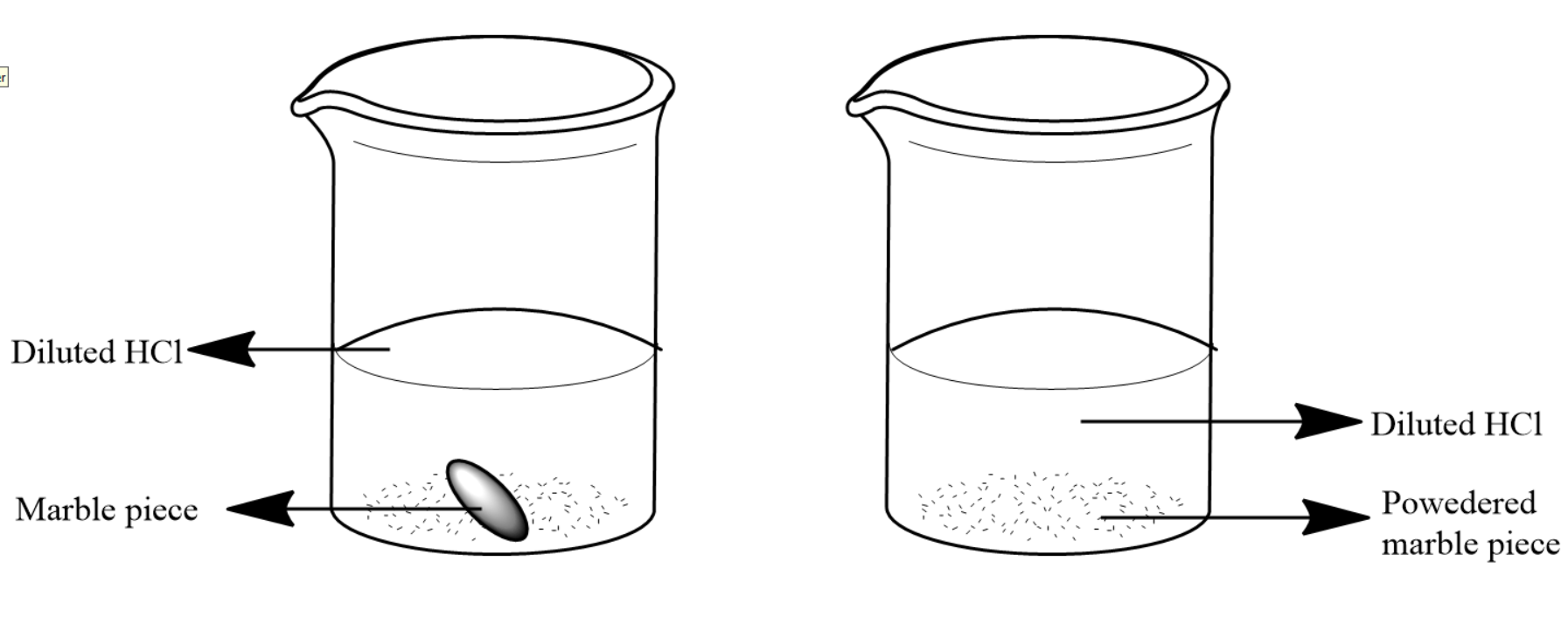
Complete answer: Here we are given a marble piece and powdered marble piece in equal amounts of diluted hydrochloric acid in separate beakers. We know that marble pieces are chemically Calcium carbonate and they can react with Hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride and carbon dioxide gas. The carbon dioxide gas will escape leaving us with a solution of calcium chloride. The reaction is as shown below:
\[ CaC{O_3}\; + {\text{ }}2HCl{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}CaC{l_2}\; + {\text{ }}{H_2}O{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}C{O_2}\]
We know that the concentration of any solution will only depend upon the amount of solute and solvent taken. Even if the taken solute is in powdered form or in a bulk solid form, as long as the amount of calcium carbonate in the sample doesn’t change there will not be any change in the concentration of the solution.
Thus we can say that both the solutions will have the same concentration.
Note:
It is important to note that when reacting together it is easier for the powdered form of any substance to react than its bulk solid form. This is because the surface area of the powdered form will be very large compared to the marble piece and therefore the reaction can occur faster. The concentration of the solution will be the same in both the beakers even though the one will take more time to reach that concentration.
Complete answer: Here we are given a marble piece and powdered marble piece in equal amounts of diluted hydrochloric acid in separate beakers. We know that marble pieces are chemically Calcium carbonate and they can react with Hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride and carbon dioxide gas. The carbon dioxide gas will escape leaving us with a solution of calcium chloride. The reaction is as shown below:
\[ CaC{O_3}\; + {\text{ }}2HCl{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}CaC{l_2}\; + {\text{ }}{H_2}O{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}C{O_2}\]
We know that the concentration of any solution will only depend upon the amount of solute and solvent taken. Even if the taken solute is in powdered form or in a bulk solid form, as long as the amount of calcium carbonate in the sample doesn’t change there will not be any change in the concentration of the solution.
Thus we can say that both the solutions will have the same concentration.
Note:
It is important to note that when reacting together it is easier for the powdered form of any substance to react than its bulk solid form. This is because the surface area of the powdered form will be very large compared to the marble piece and therefore the reaction can occur faster. The concentration of the solution will be the same in both the beakers even though the one will take more time to reach that concentration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




