
What is the orthocentre of a triangle with corners at \[\left( 4,3 \right),\left( 9,5 \right),\left( 7,6 \right)\]?
Answer
528k+ views
Hint: In this problem, we have to find the orthocentre with the given three points. Here we have given three points, we can first use the points to find the slope of the sides. We can then use the slope and the corresponding point, which we can substitute in the slope point form to find an equation. By this method we can find another equation. We will be having two equations, which we have to solve for the value of x and y which is the orthocentre.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have to find the orthocentre.
We are given three points \[\left( 4,3 \right),\left( 9,5 \right),\left( 7,6 \right)\].
We can now draw the diagram with the given three points.
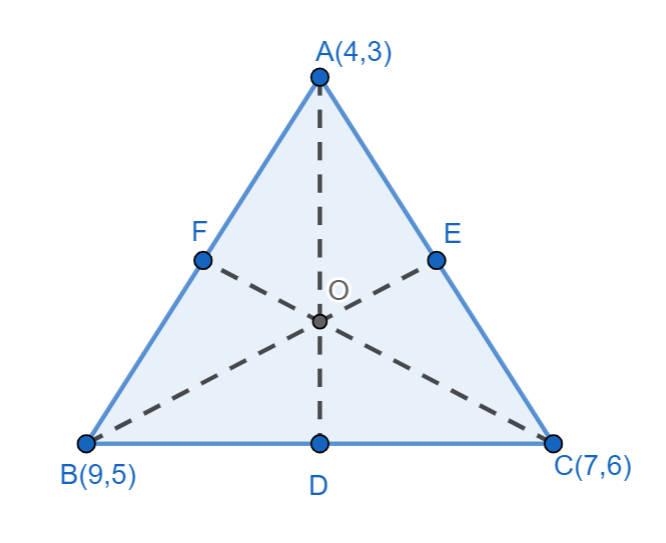
We know that the formula for slope using points is,
\[m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\]
We can now find the slope of AB from the above formula with the given points \[A\left( 4,3 \right),B\left( 9,5 \right)\], we get
\[{{m}_{AB}}=\dfrac{5-3}{9-4}=\dfrac{2}{5}\]
We know that CF is perpendicular to AB, therefore the slope of CF is \[-\dfrac{1}{{{m}_{AB}}}\].
Slope of CF is, \[{{m}_{CF}}=-\dfrac{5}{2}\]
We can now find the slope of BC from the above formula with the given points \[B\left( 9,5 \right),C\left( 7,6 \right)\], we get
\[{{m}_{BC}}=\dfrac{6-5}{7-9}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\]
We know that AD is perpendicular to BC, therefore the slope of AD is \[-\dfrac{1}{{{m}_{BC}}}\].
Slope of AD is, \[{{m}_{AD}}=2\]
We can now find the equation of two lines using the above slope using the slope point form,
\[\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\]
We can now find the equation of CF whose point is \[\left( 7,6 \right)\] and slope is \[{{m}_{CF}}=-\dfrac{5}{2}\].
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y-6=-\dfrac{5}{2}\left( x-7 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 5x+2y=47.....(1) \\
\end{align}\]
We can now find the equation of AD whose point is \[\left( 4,3 \right)\] and slope is \[{{m}_{AD}}=2\].
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y-3=2\left( x-4 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-y=5.....(2) \\
\end{align}\]
We can now solve the equation (1) and (2), we get
We can multiply 2 in the equation (2) and we can add the equation (1) and (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 5x+2y-47+4x-2y-10=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 9x=57 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{19}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
We can now substitute the value of x in (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2\left( \dfrac{19}{3} \right)-y=5 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{23}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the coordinates of the orthocentre, \[O=\left( \dfrac{19}{3},\dfrac{23}{3} \right)\].
Note: We should always remember that we can find the slope using the formula \[m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\], when we have two points. We can find an equation, if we have a slope and a point using the slope point form. We should know that, slope of the perpendicular line is the negative of reciprocal of the slope of the given line.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have to find the orthocentre.
We are given three points \[\left( 4,3 \right),\left( 9,5 \right),\left( 7,6 \right)\].
We can now draw the diagram with the given three points.

We know that the formula for slope using points is,
\[m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\]
We can now find the slope of AB from the above formula with the given points \[A\left( 4,3 \right),B\left( 9,5 \right)\], we get
\[{{m}_{AB}}=\dfrac{5-3}{9-4}=\dfrac{2}{5}\]
We know that CF is perpendicular to AB, therefore the slope of CF is \[-\dfrac{1}{{{m}_{AB}}}\].
Slope of CF is, \[{{m}_{CF}}=-\dfrac{5}{2}\]
We can now find the slope of BC from the above formula with the given points \[B\left( 9,5 \right),C\left( 7,6 \right)\], we get
\[{{m}_{BC}}=\dfrac{6-5}{7-9}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\]
We know that AD is perpendicular to BC, therefore the slope of AD is \[-\dfrac{1}{{{m}_{BC}}}\].
Slope of AD is, \[{{m}_{AD}}=2\]
We can now find the equation of two lines using the above slope using the slope point form,
\[\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\]
We can now find the equation of CF whose point is \[\left( 7,6 \right)\] and slope is \[{{m}_{CF}}=-\dfrac{5}{2}\].
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y-6=-\dfrac{5}{2}\left( x-7 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 5x+2y=47.....(1) \\
\end{align}\]
We can now find the equation of AD whose point is \[\left( 4,3 \right)\] and slope is \[{{m}_{AD}}=2\].
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y-3=2\left( x-4 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-y=5.....(2) \\
\end{align}\]
We can now solve the equation (1) and (2), we get
We can multiply 2 in the equation (2) and we can add the equation (1) and (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 5x+2y-47+4x-2y-10=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 9x=57 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{19}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
We can now substitute the value of x in (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2\left( \dfrac{19}{3} \right)-y=5 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{23}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the coordinates of the orthocentre, \[O=\left( \dfrac{19}{3},\dfrac{23}{3} \right)\].
Note: We should always remember that we can find the slope using the formula \[m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\], when we have two points. We can find an equation, if we have a slope and a point using the slope point form. We should know that, slope of the perpendicular line is the negative of reciprocal of the slope of the given line.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




