
Order of rate of reaction of following compound with phenyl magnesium bromide is:
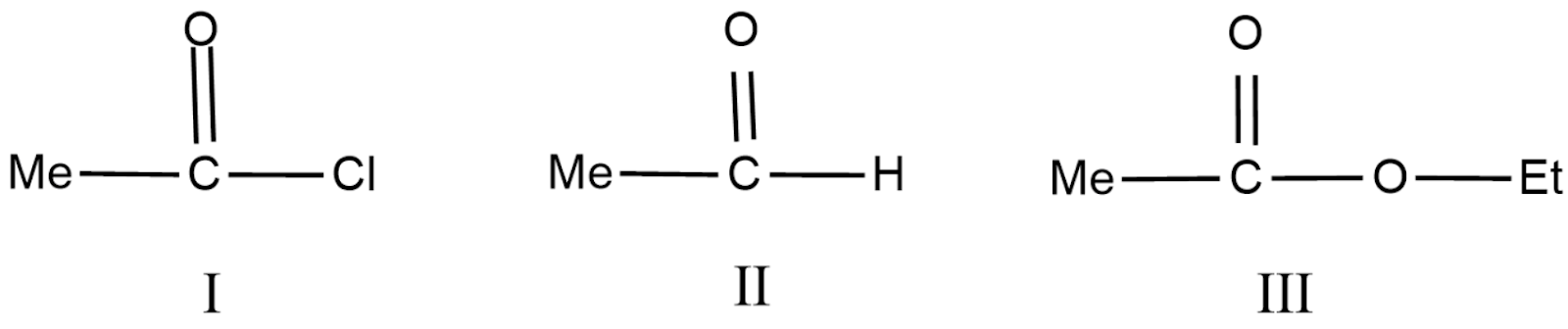
(A) I>II>III
(B) II>III>I
(C) III>I>II
(D) II>I>III

Answer
512.4k+ views
Hint :To answer this question, we first need to understand what is compound. A chemical compound is a substance made up of numerous identical molecules bound together by chemical bonds and made up of atoms from different elements. As a result, a molecule made up of only one element's atoms is not a compound.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Inductive effect – The inductive effect is a chemical term for the transfer of uneven bonding electron sharing through a chain of atoms in a molecule, resulting in a permanent dipole in a bond. Unlike the electromeric effect, which is present in a pie bond, it is present in a sigma bond.
Mesomeric effect - The Mesomeric effect is the polarity created between atoms of a conjugated system via electron transfer or pi–bond electron transfer. In simple words, the mesomeric effect happens when electrons in a conjugated orbital system move away from or towards a substituent group. Mesomeric Effect Example
Two types of mesomeric effects can be distinguished:
+M and -M
In (I) the -Cl group is an electron withdrawing group which increases the rate of reaction due to the -I effect.
In (II) the -h group is a neutral group.
In (III) the -O group contains lone pairs of electron and pi bonds and decreases the rate of reaction due to +M effect.
So, we conclude that final answer is option (A) i.e. I>II>III.
Note :
The reaction rate, also known as the rate of reaction, is the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs, and is proportional to the increase in product concentration per unit time and the reduction in reactant concentration per unit time. The speed at which people react varies a lot.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Inductive effect – The inductive effect is a chemical term for the transfer of uneven bonding electron sharing through a chain of atoms in a molecule, resulting in a permanent dipole in a bond. Unlike the electromeric effect, which is present in a pie bond, it is present in a sigma bond.
Mesomeric effect - The Mesomeric effect is the polarity created between atoms of a conjugated system via electron transfer or pi–bond electron transfer. In simple words, the mesomeric effect happens when electrons in a conjugated orbital system move away from or towards a substituent group. Mesomeric Effect Example
Two types of mesomeric effects can be distinguished:
+M and -M
In (I) the -Cl group is an electron withdrawing group which increases the rate of reaction due to the -I effect.
In (II) the -h group is a neutral group.
In (III) the -O group contains lone pairs of electron and pi bonds and decreases the rate of reaction due to +M effect.
So, we conclude that final answer is option (A) i.e. I>II>III.
Note :
The reaction rate, also known as the rate of reaction, is the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs, and is proportional to the increase in product concentration per unit time and the reduction in reactant concentration per unit time. The speed at which people react varies a lot.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




