
Orbital \[{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\] is involved in which of the following hybridizations?
This question has multiple correct options.
A.$s{{p}^{3}}d$ (square pyramidal)
B.$ds{{p}^{2}}$
C.$s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$
D.$s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{3}}$
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint:In organic chemistry, hybridisation is used to explain the covalent bonds in organic molecules. It is defined as the intermixing of atomic orbital of different shape and has the same energy to give the same number of hybrid orbital of the same energy, orientation and shape so that there will be minimum repulsion between the hybrid orbitals.
Complete step-by-step answer:\[{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\]orbital lies in the xy plane in which the lobes are directed along x and y axis. The lobes of orbitals ${{p}_{x}}$ and ${{p}_{y}}$ are along the x and y axis.
Let us discuss the above options:
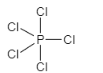
A.The shape for $s{{p}^{3}}d$hybridization is trigonal bipyramidal. It contains one $s$ orbital with three $p$ orbitals that are ${{p}_{x}},{{p}_{y}}$ and ${{p}_{z}}$ and one $d$ orbital that is ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ . The example of $s{{p}^{3}}d$hybridization is $PC{{l}_{5}}$ . Therefore, this option is incorrect.
Let us see the structure:
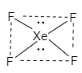
B.As we have discussed that \[{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\]orbital lies in the xy plane in which the lobes are directed along x and y axis. The lobes of orbitals ${{p}_{x}}$ and ${{p}_{y}}$ are along the x and y axis. In $ds{{p}^{2}}$ , it has square planar geometry that means the four hybridized orbital lies in xy plane. ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$ orbital is used in $ds{{p}^{2}}$ geometry having square planar shape. This hybridization involves $s,{{p}_{x}}$ and ${{p}_{y}}$ orbital. The example of $ds{{p}^{2}}$geometry is $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ geometry. Therefore, this option is correct.
Let us see the structure:
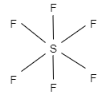
C.The shape of $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization is octahedral. It contains $s,p$ and $d$ orbitals which undergo mixing to form six identical $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$orbitals. They are inclined at an angle of ${{90}^{{}^\circ }}$ to one another. Here, the $d$ orbital is ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$ and ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ . Therefore, this option is correct. The example of $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$is $S{{F}_{6}}$ .
Let us see the structure:
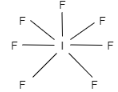
D.The shape of $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{3}}$ hybridization is pentagonal bipyramidal. It contains one$s$ orbital with $p$ orbitals that are three ${{p}_{x}},{{p}_{y}}$ and ${{p}_{z}}$ and three $d$ orbitals. The $d$ orbitals involved are ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}},{{d}_{xy}}$ . Therefore, this option is correct. The example is Iodine heptafluoride.
Let us see the structure:
Note:It is to note that the type of hybridisation tells us the geometry of a molecule. The hybridised orbitals have equal energy and shape. In hybridisation, atomic orbitals are combined to form a new atomic orbital. The number of hybrid orbitals is equal to the number of orbitals in the hybridisation.
Complete step-by-step answer:\[{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\]orbital lies in the xy plane in which the lobes are directed along x and y axis. The lobes of orbitals ${{p}_{x}}$ and ${{p}_{y}}$ are along the x and y axis.
Let us discuss the above options:
A.The shape for $s{{p}^{3}}d$hybridization is trigonal bipyramidal. It contains one $s$ orbital with three $p$ orbitals that are ${{p}_{x}},{{p}_{y}}$ and ${{p}_{z}}$ and one $d$ orbital that is ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ . The example of $s{{p}^{3}}d$hybridization is $PC{{l}_{5}}$ . Therefore, this option is incorrect.
Let us see the structure:

B.As we have discussed that \[{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}\]orbital lies in the xy plane in which the lobes are directed along x and y axis. The lobes of orbitals ${{p}_{x}}$ and ${{p}_{y}}$ are along the x and y axis. In $ds{{p}^{2}}$ , it has square planar geometry that means the four hybridized orbital lies in xy plane. ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$ orbital is used in $ds{{p}^{2}}$ geometry having square planar shape. This hybridization involves $s,{{p}_{x}}$ and ${{p}_{y}}$ orbital. The example of $ds{{p}^{2}}$geometry is $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ geometry. Therefore, this option is correct.
Let us see the structure:

C.The shape of $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization is octahedral. It contains $s,p$ and $d$ orbitals which undergo mixing to form six identical $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$orbitals. They are inclined at an angle of ${{90}^{{}^\circ }}$ to one another. Here, the $d$ orbital is ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}}$ and ${{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}}$ . Therefore, this option is correct. The example of $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$is $S{{F}_{6}}$ .
Let us see the structure:

D.The shape of $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{3}}$ hybridization is pentagonal bipyramidal. It contains one$s$ orbital with $p$ orbitals that are three ${{p}_{x}},{{p}_{y}}$ and ${{p}_{z}}$ and three $d$ orbitals. The $d$ orbitals involved are ${{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}},{{d}_{xy}}$ . Therefore, this option is correct. The example is Iodine heptafluoride.
Let us see the structure:

Note:It is to note that the type of hybridisation tells us the geometry of a molecule. The hybridised orbitals have equal energy and shape. In hybridisation, atomic orbitals are combined to form a new atomic orbital. The number of hybrid orbitals is equal to the number of orbitals in the hybridisation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




