
How many optically active isomers are possible for $ {C_5}{H_{11}}Cl $ ?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(4) 4
(D) 5
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: We are asked to find the number of optically active isomers. Optical isomers are the two compounds that have the same number and types of atoms, also have the same no. of bonds but the two compounds are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Complete answer:
Now we are given the molecular formula $ {C_5}{H_{11}}Cl $ . Let us replace the Cl with H. We will get:
$ {C_5}{H_{11}}Cl\xrightarrow[{ - Cl}]{{ + {H^ + }}}{C_5}{H_{12}} $
The formula is in the form $ {C_n}{H_{2n + 2}} $ which resembles an alkane. Hence, we know that the given compound is an alkyl halide. The optical isomers can be given from the structural isomers. There are total 6 structural isomers which are shown below: The (*) signs determine the chiral centre of that compound.
(a)
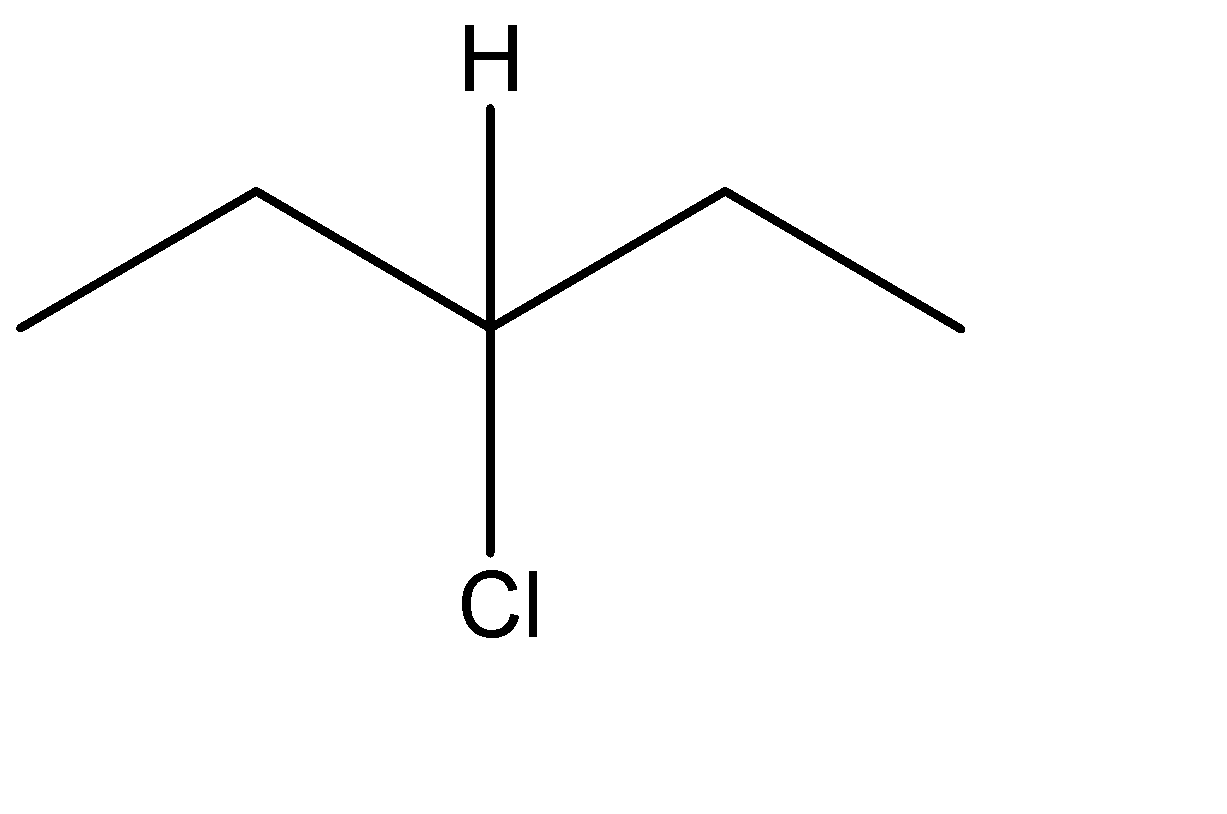
(b)
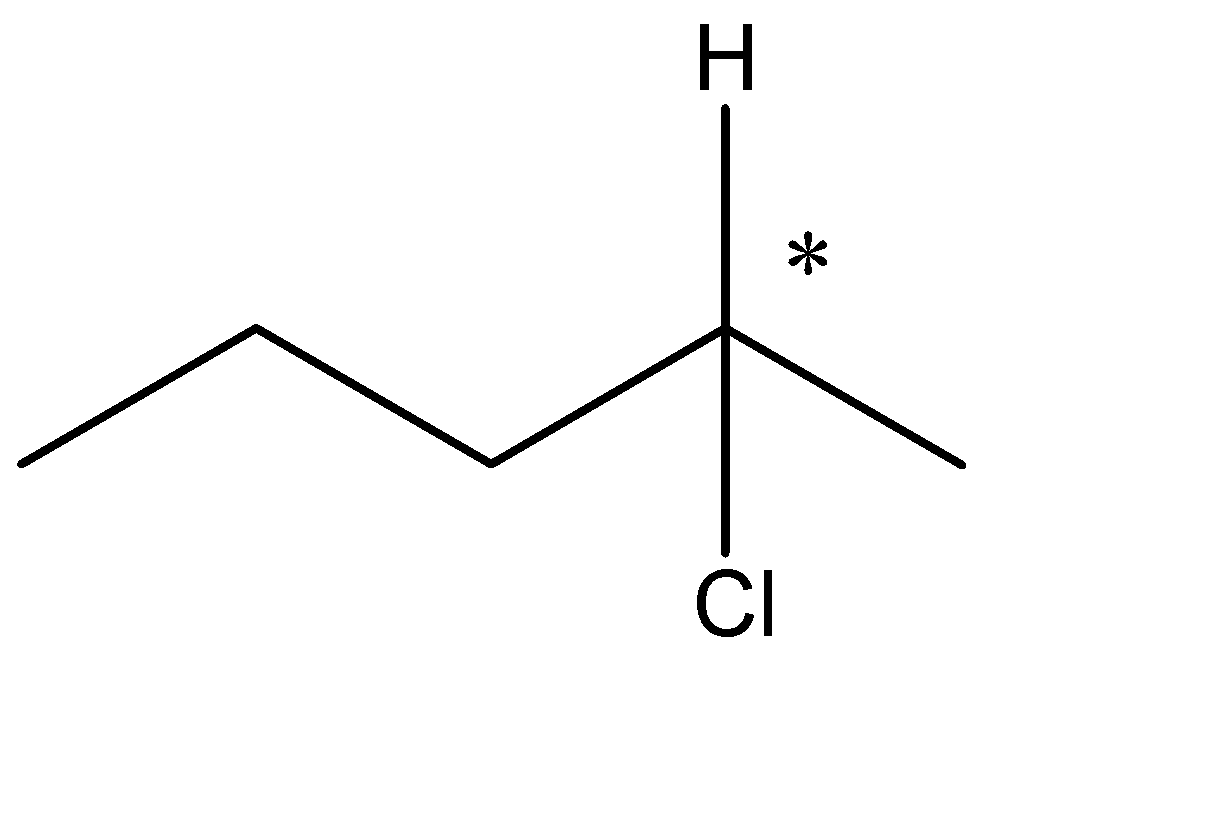
(c)
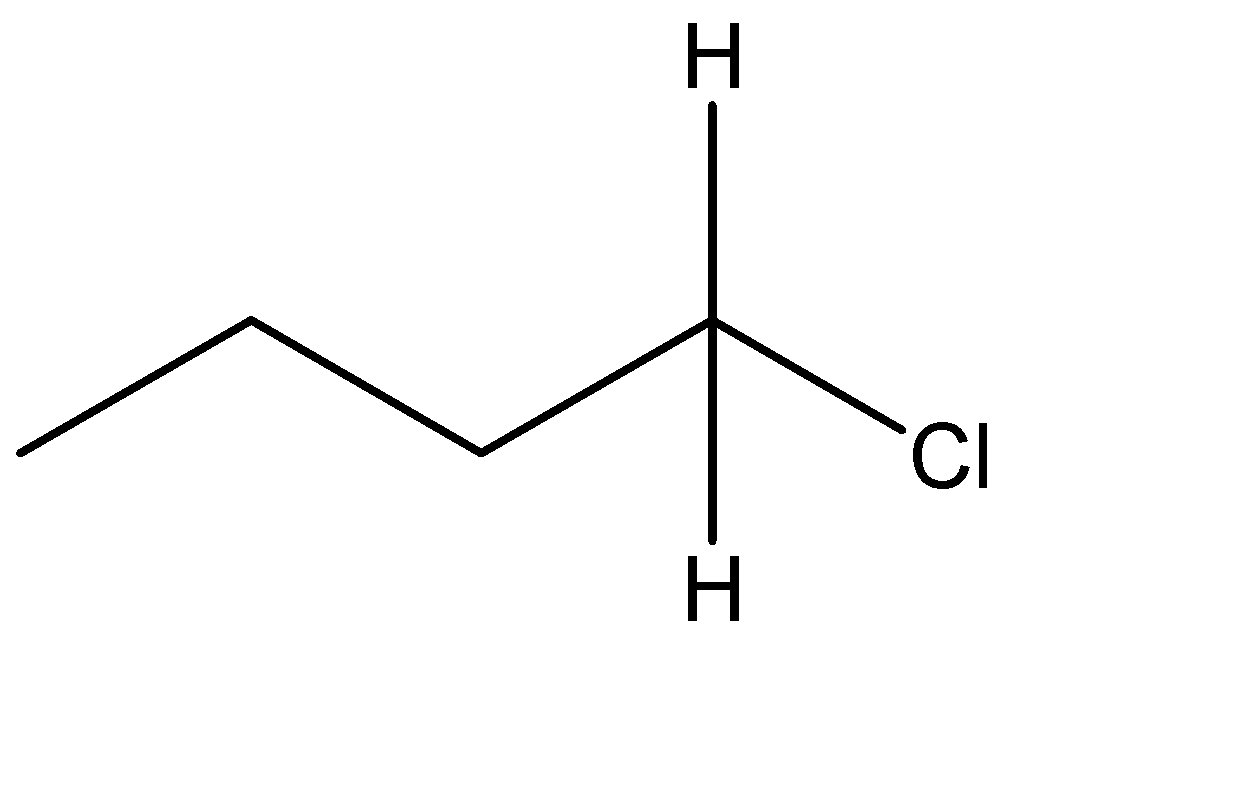
(d)
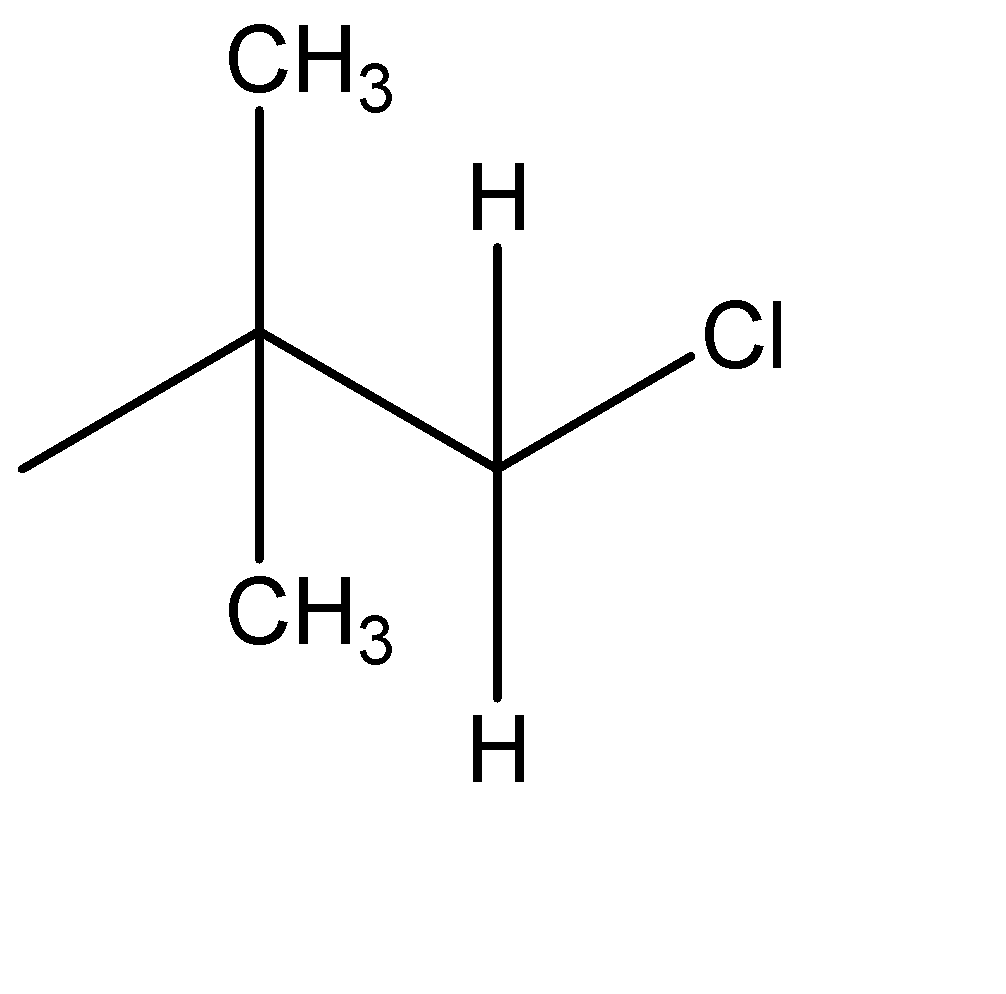
(e)
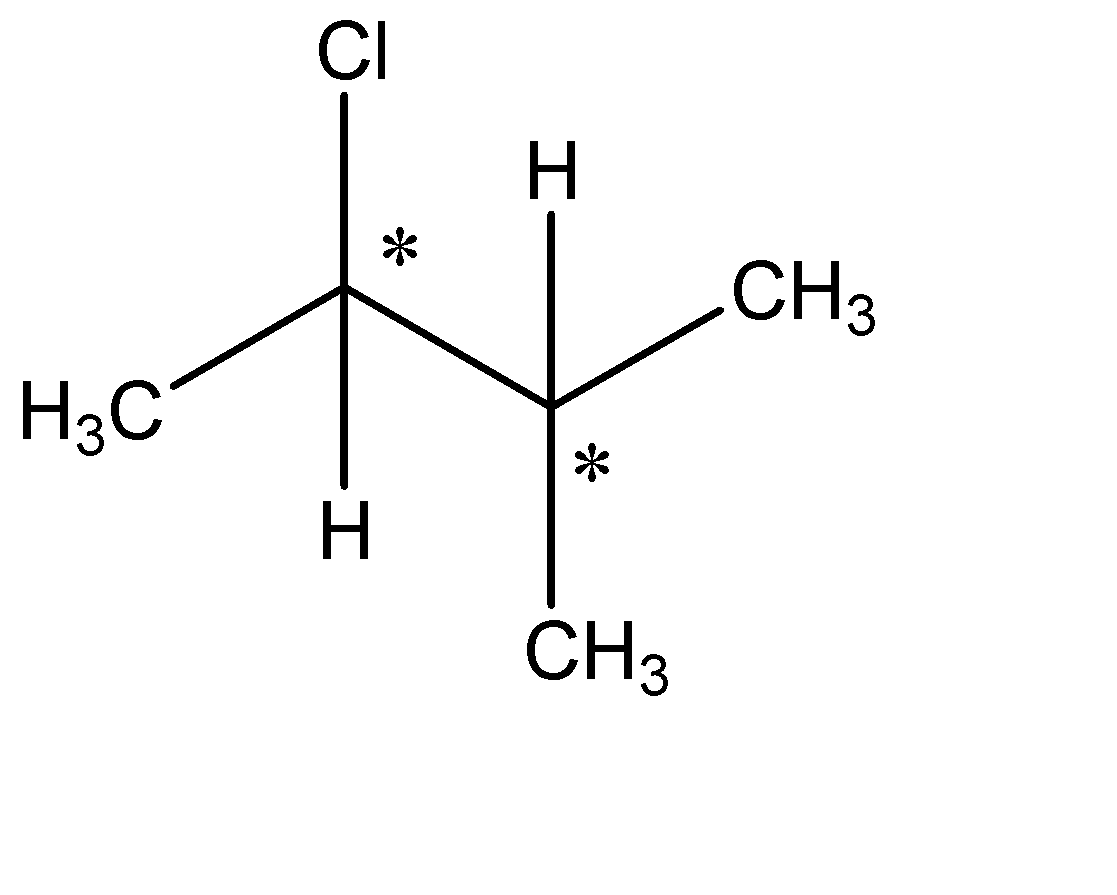
(f)
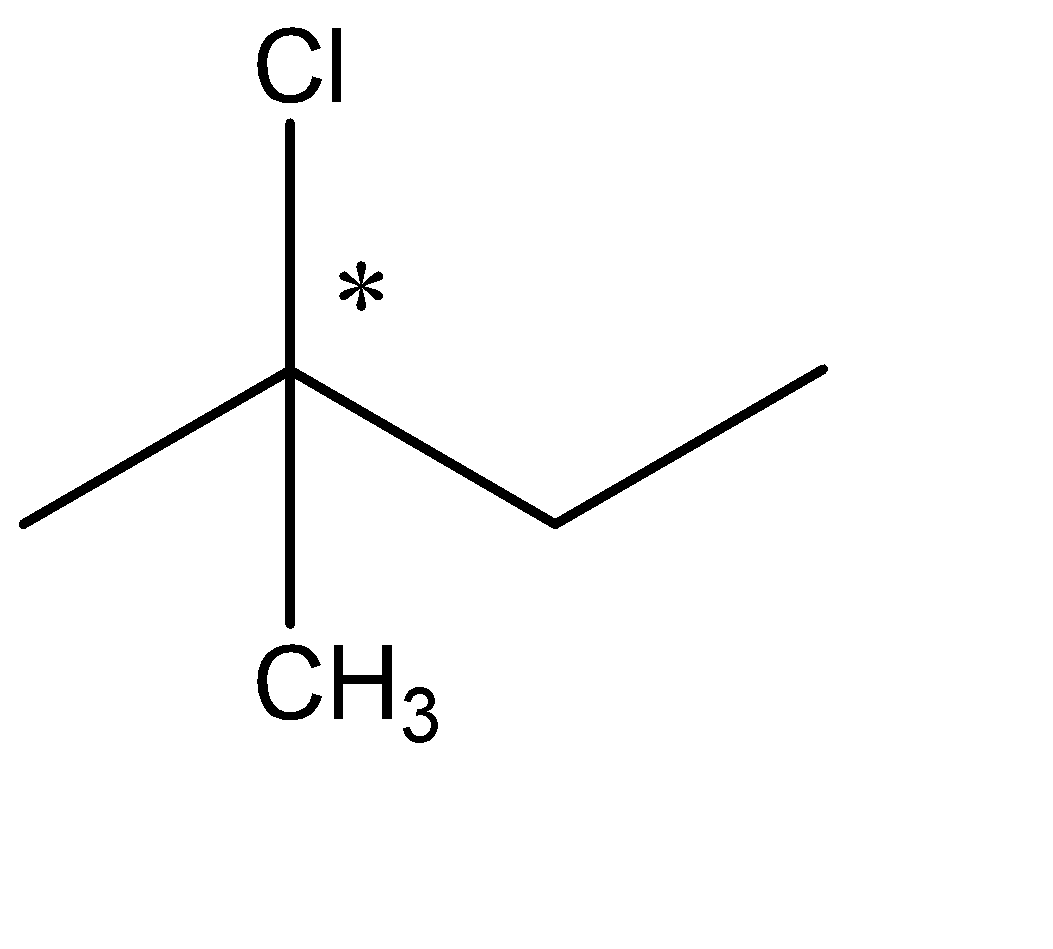
The chiral carbons are optically active ones. The compound with one chiral centre has two optical isomers ( i.e. R and S) and if the compound has 2 chiral centres then it will have 4 optical isomers. Therefore, (c) has 2 optical isomers, (e) has 4 and (f) has 2 optical isomers. The total no. of optical isomers hence will be: $ 2 + 4 + 2 = 8 $
Therefore, Option (D) is correct.
Note:
If we are given the structure of the compound and not the molecular formula the no. of optical isomers will be equal to $ {2^{n - 1}} $ where n is the no. of chiral centres. Chiral centres are the ones on which carbon is attached to 4 different groups. If the compound has 3 chiral centres, then the no. of optical isomers will be $ = {2^{3 - 1}} = {2^2} = 4 $ . Therefore, it will have 4 optical isomers.
Complete answer:
Now we are given the molecular formula $ {C_5}{H_{11}}Cl $ . Let us replace the Cl with H. We will get:
$ {C_5}{H_{11}}Cl\xrightarrow[{ - Cl}]{{ + {H^ + }}}{C_5}{H_{12}} $
The formula is in the form $ {C_n}{H_{2n + 2}} $ which resembles an alkane. Hence, we know that the given compound is an alkyl halide. The optical isomers can be given from the structural isomers. There are total 6 structural isomers which are shown below: The (*) signs determine the chiral centre of that compound.
(a)

(b)

(c)

(d)

(e)

(f)

The chiral carbons are optically active ones. The compound with one chiral centre has two optical isomers ( i.e. R and S) and if the compound has 2 chiral centres then it will have 4 optical isomers. Therefore, (c) has 2 optical isomers, (e) has 4 and (f) has 2 optical isomers. The total no. of optical isomers hence will be: $ 2 + 4 + 2 = 8 $
Therefore, Option (D) is correct.
Note:
If we are given the structure of the compound and not the molecular formula the no. of optical isomers will be equal to $ {2^{n - 1}} $ where n is the no. of chiral centres. Chiral centres are the ones on which carbon is attached to 4 different groups. If the compound has 3 chiral centres, then the no. of optical isomers will be $ = {2^{3 - 1}} = {2^2} = 4 $ . Therefore, it will have 4 optical isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




