
Optical Isomers
A. $2$
B. $4$
C. Zero
D. $3$

Answer
360.6k+ views
Hint: When alkene is treated with hydrogen molecule $({{H}_{2}})$ in presence of a catalyst, hydrogenation occurs across the double bond. And optical isomers are found in a compound having a chiral centre i.e, four different groups are attached to carbon and producing compound should not be superimposed on its mirror image.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
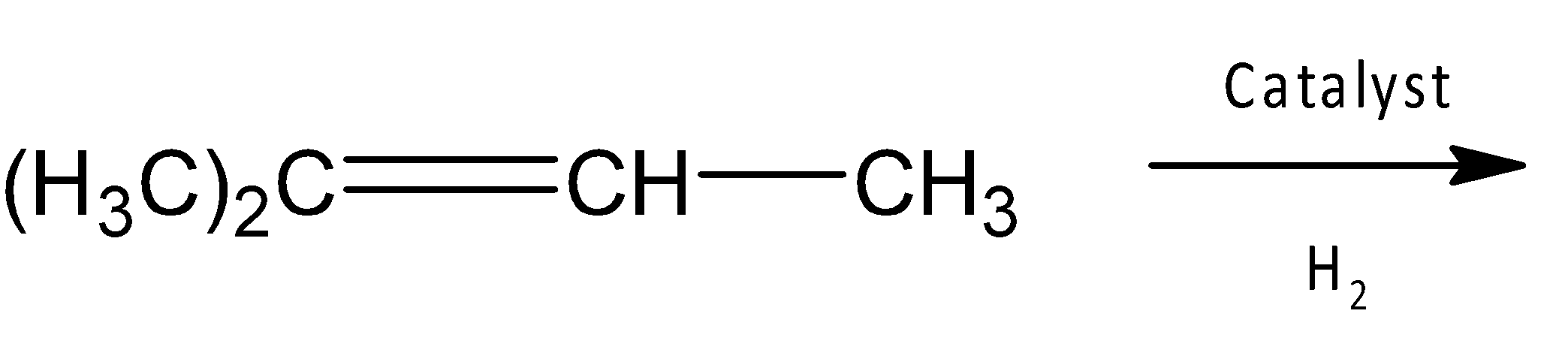
In a hydrogenation process, alkenes react with hydrogen gas molecules in presence of a metal catalyst, thereby hydrogen molecules are added to the double bond of alkene in such a way that each carbon atom bonds with one hydrogen atom.
Here in this question an asymmetric alkene i.e there is one doubly bonded carbon that bears two methyl groups ($C{{H}_{3}}$) and the other carbon bears one methyl group and one hydrogen atom. So, treating with catalytic hydrogen gives an alkane after adding two hydrogen atoms across the double bond.
Now we have an alkane and we have to find whether it has optical isomers or not. There are certain conditions for optical isomerism are discussed below:
a. The compound must have a chiral center which means a carbon atom is bonded with four different groups or molecules.
b. compounds must have non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
c. Compounds should possess identical molecular formulas and also identical structural formulas.
d. They can rotate the plane of polarized light.
Here we can see the produced alkane has no chiral center and they are super impossible to each other.
Therefore no optical isomers are found in an alkane that is produced through catalytic hydrogenation.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Optical isomers are optically active when they have a chiral centre. Also, they possess a plane of symmetry and have non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Optical isomers have produced a mixture of compounds with $50:50$ ratio called a racemic mixture.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
In a hydrogenation process, alkenes react with hydrogen gas molecules in presence of a metal catalyst, thereby hydrogen molecules are added to the double bond of alkene in such a way that each carbon atom bonds with one hydrogen atom.
Here in this question an asymmetric alkene i.e there is one doubly bonded carbon that bears two methyl groups ($C{{H}_{3}}$) and the other carbon bears one methyl group and one hydrogen atom. So, treating with catalytic hydrogen gives an alkane after adding two hydrogen atoms across the double bond.
Now we have an alkane and we have to find whether it has optical isomers or not. There are certain conditions for optical isomerism are discussed below:
a. The compound must have a chiral center which means a carbon atom is bonded with four different groups or molecules.
b. compounds must have non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
c. Compounds should possess identical molecular formulas and also identical structural formulas.
d. They can rotate the plane of polarized light.
Here we can see the produced alkane has no chiral center and they are super impossible to each other.
Therefore no optical isomers are found in an alkane that is produced through catalytic hydrogenation.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Optical isomers are optically active when they have a chiral centre. Also, they possess a plane of symmetry and have non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Optical isomers have produced a mixture of compounds with $50:50$ ratio called a racemic mixture.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE




