
How open vascular bundles differ from closed vascular bundles?
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: The major difference between open vascular bundles and closed vascular bundles is the layer which helps in the secondary growth of the plants. Secondary growth mostly takes place in the dicots plants, not in monocot plants.
Complete answer:
The main and very basic difference between open and closed vascular bundles is that of the strip of cambium.
-Open Vascular Bundles- In open vascular bundles, the cambium is present between the xylem and phloem and due to this, the xylem and phloem are not in direct contact with each other.
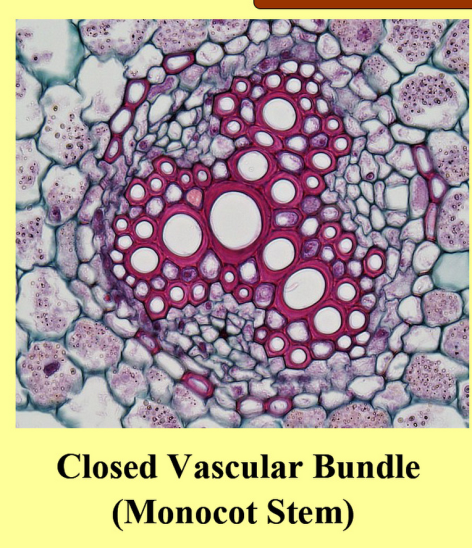
-Closed vascular bundles- In closed vascular bundles, the cambium is absent between xylem and phloem, and due to this, the xylem and phloem are in direct contact with each other.
Additional Information: A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport cells present in plant vascular tissue exist in two forms: xylem and phloem. These tissues play an important role in protection and support. The xylem typically lies adaxial with phloem which is positioned abaxial. When we consider a stem or root this suggests that the xylem is closer to the center of the stem or root while the phloem is closer to the outside. In a leaf, the adaxial surface of the leaf will usually be the top, with the abaxial surface the lower side.
Note: The term open in the open vascular bundle itself means that these types of plants are open for secondary growth i.e secondary growth will take place and in closed vascular bundles, close means that the plant is closed for secondary growth i.e secondary growth will not take place.
Complete answer:
The main and very basic difference between open and closed vascular bundles is that of the strip of cambium.
-Open Vascular Bundles- In open vascular bundles, the cambium is present between the xylem and phloem and due to this, the xylem and phloem are not in direct contact with each other.
-Closed vascular bundles- In closed vascular bundles, the cambium is absent between xylem and phloem, and due to this, the xylem and phloem are in direct contact with each other.
| S.NO | OPEN VASCULAR BUNDLE | CLOSED VASCULAR BUNDLE |
| 1 | It is capable of Secondary growth | It is not capable of Secondary growth |
| 2 | Cambium is present | Cambium is absent. |
| 3 | They are in dicotyledon plants. | They are in monocotyledon plants. |
| 4 | 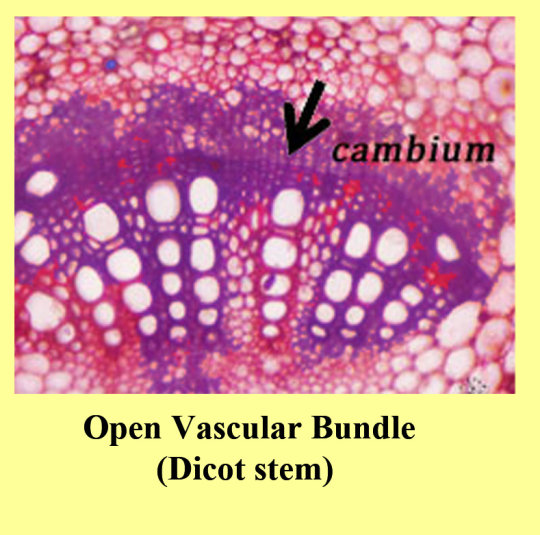
| 
|
Additional Information: A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport cells present in plant vascular tissue exist in two forms: xylem and phloem. These tissues play an important role in protection and support. The xylem typically lies adaxial with phloem which is positioned abaxial. When we consider a stem or root this suggests that the xylem is closer to the center of the stem or root while the phloem is closer to the outside. In a leaf, the adaxial surface of the leaf will usually be the top, with the abaxial surface the lower side.
Note: The term open in the open vascular bundle itself means that these types of plants are open for secondary growth i.e secondary growth will take place and in closed vascular bundles, close means that the plant is closed for secondary growth i.e secondary growth will not take place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




