
One way to reduce chromatic aberration is by:
A. using multiple lens
B. cutting the lens in half
C. praying to the lens to stop behaving erratically
D. all of the above
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must know the definition of Chromatic aberration. It is a defect in which the lens is unable to focus all the colours at the same time to one point.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The white light or the visible part of spectrum consists of seven colours also, called VIBGYOR i.e. Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red.
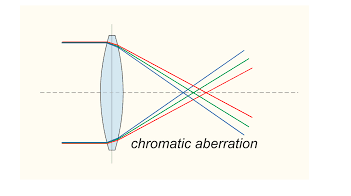
All these 7 different colours have different wavelengths. Due to the difference in wavelengths of these colours, it is not possible for the lens to converge all of the colours at the same point. Hence, we see the colours splitting near the edge of the lens as shown in the above picture.
This happens when the refractive index of the lens decreases due to higher wavelengths and thus, the colours of higher wavelengths (basically, the red part) undergo large deviation than the colours with lesser wavelengths (the blue part)
Refractive index, $n \propto \dfrac{1}{\lambda }$
Hence, by changing the refractive index of the lens to a correct value, we can avoid this defect.
So, now the question is about changing the refractive index.
The focal length of the lens is a property of the lens. The focal length of a lens is calculated by the Lens maker’s formula –
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {{n_{21}} - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$
where,
$f$= focal length of the lens ${n_{21}}$= refractive index of the lens material relative to the medium ${R_1}\& {R_2}$are the radii of curvature of the two sides of the lens.
Here, we see that there is a relationship between the focal length and refractive index of the lens.
Thus, to change the refractive index of the lens, we need to vary the focal length.
Focal length cannot be varied by cutting the lens into any pieces. But it can be changed by adding multiple lenses because when we add more lenses, the combined power (inverse of focal length) becomes the algebraic sum of the powers of the individual lens.
$P = \dfrac{1}{f}$
When we add multiple lens, the combined power –
$P = {P_1} + {P_2} + {P_3}....$
Hence, the correct option is Option A.
Note: In a lens, the edges of the lens deviate the ray of light more, compared to the centre. Thus, the edges of the lens act like a prism, thereby causing dispersion of light. Dispersion of light is a phenomenon where the white light splits into its constituent colours when it passes through a prism. This is the main reason for the chromatic aberration.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The white light or the visible part of spectrum consists of seven colours also, called VIBGYOR i.e. Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red.

All these 7 different colours have different wavelengths. Due to the difference in wavelengths of these colours, it is not possible for the lens to converge all of the colours at the same point. Hence, we see the colours splitting near the edge of the lens as shown in the above picture.
This happens when the refractive index of the lens decreases due to higher wavelengths and thus, the colours of higher wavelengths (basically, the red part) undergo large deviation than the colours with lesser wavelengths (the blue part)
Refractive index, $n \propto \dfrac{1}{\lambda }$
Hence, by changing the refractive index of the lens to a correct value, we can avoid this defect.
So, now the question is about changing the refractive index.
The focal length of the lens is a property of the lens. The focal length of a lens is calculated by the Lens maker’s formula –
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \left( {{n_{21}} - 1} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} - \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}} \right)$
where,
$f$= focal length of the lens ${n_{21}}$= refractive index of the lens material relative to the medium ${R_1}\& {R_2}$are the radii of curvature of the two sides of the lens.
Here, we see that there is a relationship between the focal length and refractive index of the lens.
Thus, to change the refractive index of the lens, we need to vary the focal length.
Focal length cannot be varied by cutting the lens into any pieces. But it can be changed by adding multiple lenses because when we add more lenses, the combined power (inverse of focal length) becomes the algebraic sum of the powers of the individual lens.
$P = \dfrac{1}{f}$
When we add multiple lens, the combined power –
$P = {P_1} + {P_2} + {P_3}....$
Hence, the correct option is Option A.
Note: In a lens, the edges of the lens deviate the ray of light more, compared to the centre. Thus, the edges of the lens act like a prism, thereby causing dispersion of light. Dispersion of light is a phenomenon where the white light splits into its constituent colours when it passes through a prism. This is the main reason for the chromatic aberration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




