
One side of a road, there is a tower and on the other side, a house is situated. The angle of depression from the top of a tower to the top and bottom of a house are ${45^ \circ }$and ${60^ \circ }$ respectively. Find the height of the tower.
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Here in this question we can use trigonometric triangle relations to find out the height of the tower. Some of the identities are as follows:
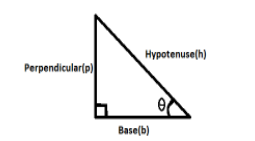
$\sin \theta = \dfrac{p}{h}$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{p}{b}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{b}{h}$
These are the three formulas which we will be using in this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
With the help of a diagram we will solve this question below is the figure.
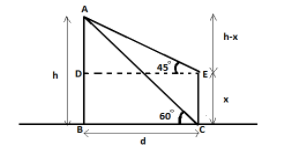
Where h= height of tower
x= height of house
d=distance between tower and house
Angle from top of the tower to top of the house =${45^ \circ }$
Angle from top of the tower to bottom of the house =${60^ \circ }$
In triangle ABC, $\angle ABC = {90^ \circ }$so we can apply trigonometric triangle relations.
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{p}{b} = \dfrac{h}{d}$ (Applying trigonometric relation)
$\tan {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{h}{d}$
$\dfrac{h}{d} = \sqrt 3 $ ($\tan {60^ \circ } = \sqrt 3 $)
$d = \dfrac{h}{{\sqrt 3 }}..............................(i)$
In triangle ADE, $\angle ADE = {90^ \circ }$so we can apply trigonometric triangle relations.
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{p}{b} = \dfrac{{h - x}}{d}$ (From the above figure we can easily find perpendicular and base side)$\tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{{h - x}}{d}$
$\dfrac{{h - x}}{d} = 1$ ($\tan {45^ \circ } = 1$)
$d = h - x............................(ii)$
Equating both equations$(i)$and$(ii)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{{\sqrt 3 }} = h - x$
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt 3 (h - x)$ (Cross multiplying)
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt 3 h - \sqrt 3 x$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 x = h(\sqrt 3 - 1)$
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 x}}{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}$
\[h = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 x}}{{\sqrt 3 - 1}} \times \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 + 1)}}{{(\sqrt 3 + 1)}}\] (Rationalising by multiplying numerator and denominator by \[\sqrt 3 + 1\])
\[h = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 x(\sqrt 3 + 1)}}{{[{{(\sqrt 3 )}^2} - {{(1)}^2}]}}\] (Appling identity \[{a^2} - {b^2} = (a - b)(a + b)\])
\[h = \dfrac{{x(3 + \sqrt 3 )}}{{3 - 1}}\]
\[\therefore h = \dfrac{{x(3 + \sqrt 3 )}}{2}\]
So the height of tower will be height of house multiplied by the factor of \[\dfrac{{x(3 + \sqrt 3 )}}{2}\]
Note: When you are applying a trigonometric triangle be cautious about base and perpendicular. Base is that side which contains two right angles and one more angle while the perpendicular side consists of only one angle i.e. ninety degrees. However this question can also be solved by using cosine and sin formula but it would be unnecessary time consuming and will have to eliminate one more variable i.e. d which is distance between tower and house so above method is efficient.

$\sin \theta = \dfrac{p}{h}$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{p}{b}$
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{b}{h}$
These are the three formulas which we will be using in this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
With the help of a diagram we will solve this question below is the figure.

Where h= height of tower
x= height of house
d=distance between tower and house
Angle from top of the tower to top of the house =${45^ \circ }$
Angle from top of the tower to bottom of the house =${60^ \circ }$
In triangle ABC, $\angle ABC = {90^ \circ }$so we can apply trigonometric triangle relations.
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{p}{b} = \dfrac{h}{d}$ (Applying trigonometric relation)
$\tan {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{h}{d}$
$\dfrac{h}{d} = \sqrt 3 $ ($\tan {60^ \circ } = \sqrt 3 $)
$d = \dfrac{h}{{\sqrt 3 }}..............................(i)$
In triangle ADE, $\angle ADE = {90^ \circ }$so we can apply trigonometric triangle relations.
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{p}{b} = \dfrac{{h - x}}{d}$ (From the above figure we can easily find perpendicular and base side)$\tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{{h - x}}{d}$
$\dfrac{{h - x}}{d} = 1$ ($\tan {45^ \circ } = 1$)
$d = h - x............................(ii)$
Equating both equations$(i)$and$(ii)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{{\sqrt 3 }} = h - x$
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt 3 (h - x)$ (Cross multiplying)
$ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt 3 h - \sqrt 3 x$
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 x = h(\sqrt 3 - 1)$
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 x}}{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}$
\[h = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 x}}{{\sqrt 3 - 1}} \times \dfrac{{(\sqrt 3 + 1)}}{{(\sqrt 3 + 1)}}\] (Rationalising by multiplying numerator and denominator by \[\sqrt 3 + 1\])
\[h = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 x(\sqrt 3 + 1)}}{{[{{(\sqrt 3 )}^2} - {{(1)}^2}]}}\] (Appling identity \[{a^2} - {b^2} = (a - b)(a + b)\])
\[h = \dfrac{{x(3 + \sqrt 3 )}}{{3 - 1}}\]
\[\therefore h = \dfrac{{x(3 + \sqrt 3 )}}{2}\]
So the height of tower will be height of house multiplied by the factor of \[\dfrac{{x(3 + \sqrt 3 )}}{2}\]
Note: When you are applying a trigonometric triangle be cautious about base and perpendicular. Base is that side which contains two right angles and one more angle while the perpendicular side consists of only one angle i.e. ninety degrees. However this question can also be solved by using cosine and sin formula but it would be unnecessary time consuming and will have to eliminate one more variable i.e. d which is distance between tower and house so above method is efficient.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




