
One of the following having square planar structure is:
$\mathrm{A}) \mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}$
$B) B F_{4}^{-}$
$\mathrm{C}) \mathrm{XeF}_{4}$
$\mathrm{D}) \mathrm{SCl}_{4}$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: In order to find out the geometry, we first have to find out the hybridisation of the given compounds. In order to find the hybridisation, let's find out the lone pairs on each compound given.
Complete step-by-step answer:
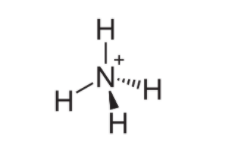
$\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}$ is ammonium cation ,the lone pair on the nitrogen atom (N) in ammonia, represented as a line above the N, forms the bond with a proton (H $^{+}$ ). Thereafter, all four $\mathrm{N}-\mathrm{H}$ bonds are equivalent, being polar covalent bonds.The ion has a tetrahedral structure and is isoelectronic with methane and borohydride.
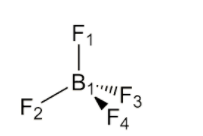
Boron has 3 valence electrons, and each of the four fluorides contributes one electron to each covalent bond. The overall negative charge of the molecule contributes another electron, so overall we have 3 + 4 + 1 = 8 valence electrons which form 4 electron pairs.
The pairs arrange themselves in space to maximise the distance between them, thereby reducing the electronic repulsion between them to a minimum. Thus it would be tetrahedral geometry.
$\mathrm{SCl}_{4}$ has seesaw molecular geometry because you must take into account the effect that the lone pair on S has on the shape. If no lone pair was there on S, then it would have been tetrahedral. But it has a seesaw geometry.
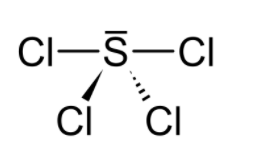
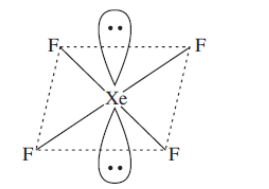
Now, in $\mathrm{XeF}_{4}$ the hybridisation is $\mathrm{sp}^{2} \mathrm{d}^{2} .$ Thus it gives us a square planar structure. The central atom has 6 electron groups out of which 2 pairs are lone pairs.
The answer is C)
Note: The hybridisation is the key factor in deciding the shape and geometry of the compound. Another factor is the distribution of the lone pairs in the compound.
Complete step-by-step answer:
$\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}$ is ammonium cation ,the lone pair on the nitrogen atom (N) in ammonia, represented as a line above the N, forms the bond with a proton (H $^{+}$ ). Thereafter, all four $\mathrm{N}-\mathrm{H}$ bonds are equivalent, being polar covalent bonds.The ion has a tetrahedral structure and is isoelectronic with methane and borohydride.

Boron has 3 valence electrons, and each of the four fluorides contributes one electron to each covalent bond. The overall negative charge of the molecule contributes another electron, so overall we have 3 + 4 + 1 = 8 valence electrons which form 4 electron pairs.
The pairs arrange themselves in space to maximise the distance between them, thereby reducing the electronic repulsion between them to a minimum. Thus it would be tetrahedral geometry.

$\mathrm{SCl}_{4}$ has seesaw molecular geometry because you must take into account the effect that the lone pair on S has on the shape. If no lone pair was there on S, then it would have been tetrahedral. But it has a seesaw geometry.
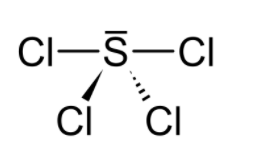
Now, in $\mathrm{XeF}_{4}$ the hybridisation is $\mathrm{sp}^{2} \mathrm{d}^{2} .$ Thus it gives us a square planar structure. The central atom has 6 electron groups out of which 2 pairs are lone pairs.

The answer is C)
Note: The hybridisation is the key factor in deciding the shape and geometry of the compound. Another factor is the distribution of the lone pairs in the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




