
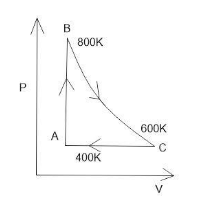
One molecule of diatomic ideal gas undergoes a cyclic process ABC as shown in figure. The process BC is adiabatic. The temperature at A, B and C are $400K,$$800K$ and $600K$respectively. Choose the correct statement.
A. The change in internal energy in the process AB is $ - 350R$.
B. The change in internal energy in the process BC is $ - 500R.$
C. The change in internal energy in whole cyclic process is $250R.$
D. The change in internal energy in the process is $700R.$

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Ideal gas is hypothetical gas composed of molecules which do not attract or repel each other.Diatomic means the molecule that contains two atoms that are chemically bonded. Adiabatic process occurs without transferring heat or mass between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings.
Formulae used:
$\Delta U = \dfrac{5}{2}nR\Delta T$
$\Delta {U_{BA}} = n{C_v}({T_B} - {T_A})$
Complete step by step answer:
The diatomic ideal gas is a total of three translational kinetic energy modes and two rotational energy modes and the equation for the diatomic gas is,
$\Delta U = \dfrac{5}{2}nR\Delta T$.
$\Delta U$ indicates the change in internal energy
$R$ indicates Rate constant
$\Delta T$ indicates change in temperature
$n$ is the number of moles
$\dfrac{5}{2}$ is a total of three translational kinetic energy modes and two rotational energy modes.
Cyclic processes a process in which the system is in the same initial and final thermodynamic state. The graph of the thermodynamic process forms a complete loop in any shape. The graph is drawn by joining the points $(V,P),$$(T,P),$$(V,T)$
In the cyclic process there is no change in internal energy.
For diatomic gas we know, ${C_v} = \dfrac{5}{2}.R$
We know that, $\Delta {U_{BA}} = n{C_v}({T_B} - {T_A})$ . . . (1)
We have, $n = 1$
${T_B} = 800K$
${T_A} = 400K$
$\therefore \Delta {U_{BA}} = 1 \times \dfrac{{5R}}{2}(800 - 400)$
$ = \dfrac{{5R}}{2}(400)$
$ = 5R(200)$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta {U_{BA}} = 1000R.$
Change in internal energy for BA is $1000R.$
We know that $\Delta {U_{AC}} = \Delta {Q_{AC}} - {W_{AC}}$
$ = n{C_p}({T_A} - {T_C}) - nR({T_A} - {T_C})$ . . . (2)
Where $\Delta {U_{AC}}$ is change in internal energy for $AC$
${W_{AC}}$is Work done to move from A to C
${T_B}$ is Temperature at $B$
${T_C}$ is Temperature at $C$
By substituting the values in equation (2) we get
$\Delta {U_{AC}} = 1 \times \dfrac{{5R}}{2}(400 - 600)$
$ = \dfrac{{5R}}{2}( - 200)$
$ = 5R( - 100)$
$\Delta {U_{AC}} = - 500R$
Change in internal energy for $AC(\Delta {U_{AC}})$is $ - 500R$
Thus adding up the change in internal energy in both processes we get change in internal energy from $B$to$C$as $ - 500R$. As the change in internal energy is a point function.
Thus get ${U_{BC}} = - 500R$
Thus option B $ - 500R$is correct
Note: In cyclic process graph is plotted along X and Y axis with volume$(V)$, temperature$(T)$ and pressure$(P).$ We have to remember that in the cyclic process the net change in internal energy is zero.
Formulae used:
$\Delta U = \dfrac{5}{2}nR\Delta T$
$\Delta {U_{BA}} = n{C_v}({T_B} - {T_A})$
Complete step by step answer:
The diatomic ideal gas is a total of three translational kinetic energy modes and two rotational energy modes and the equation for the diatomic gas is,
$\Delta U = \dfrac{5}{2}nR\Delta T$.
$\Delta U$ indicates the change in internal energy
$R$ indicates Rate constant
$\Delta T$ indicates change in temperature
$n$ is the number of moles
$\dfrac{5}{2}$ is a total of three translational kinetic energy modes and two rotational energy modes.
Cyclic processes a process in which the system is in the same initial and final thermodynamic state. The graph of the thermodynamic process forms a complete loop in any shape. The graph is drawn by joining the points $(V,P),$$(T,P),$$(V,T)$
In the cyclic process there is no change in internal energy.
For diatomic gas we know, ${C_v} = \dfrac{5}{2}.R$
We know that, $\Delta {U_{BA}} = n{C_v}({T_B} - {T_A})$ . . . (1)
We have, $n = 1$
${T_B} = 800K$
${T_A} = 400K$
$\therefore \Delta {U_{BA}} = 1 \times \dfrac{{5R}}{2}(800 - 400)$
$ = \dfrac{{5R}}{2}(400)$
$ = 5R(200)$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta {U_{BA}} = 1000R.$
Change in internal energy for BA is $1000R.$
We know that $\Delta {U_{AC}} = \Delta {Q_{AC}} - {W_{AC}}$
$ = n{C_p}({T_A} - {T_C}) - nR({T_A} - {T_C})$ . . . (2)
Where $\Delta {U_{AC}}$ is change in internal energy for $AC$
${W_{AC}}$is Work done to move from A to C
${T_B}$ is Temperature at $B$
${T_C}$ is Temperature at $C$
By substituting the values in equation (2) we get
$\Delta {U_{AC}} = 1 \times \dfrac{{5R}}{2}(400 - 600)$
$ = \dfrac{{5R}}{2}( - 200)$
$ = 5R( - 100)$
$\Delta {U_{AC}} = - 500R$
Change in internal energy for $AC(\Delta {U_{AC}})$is $ - 500R$
Thus adding up the change in internal energy in both processes we get change in internal energy from $B$to$C$as $ - 500R$. As the change in internal energy is a point function.
Thus get ${U_{BC}} = - 500R$
Thus option B $ - 500R$is correct
Note: In cyclic process graph is plotted along X and Y axis with volume$(V)$, temperature$(T)$ and pressure$(P).$ We have to remember that in the cyclic process the net change in internal energy is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




