
One mole of a perfect monoatomic gas is put through a cycle consisting of the following three reversible steps:
(CA): Isothermal compression from 2 atm and 10 litres to 20 atm and 1 litre.
(AB): Isobaric expansion to return the gas to the original volume of 10 litres with T going from ${T_1}$to ${T_2}$.
(BC): Cooling at constant volume to bring the gas to the original pressure and temperature.
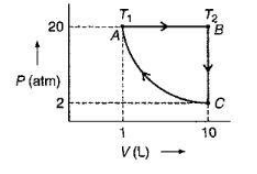
The steps are shown schematically in figure given above
(a) calculate ${T_1}$to ${T_2}$.
(b) Calculate $\Delta U,q$and$w$in calories, for each step and for the cycle.

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: For monoatomic gas, degrees of freedom is 3 $\therefore {C_v} = \dfrac{3}{2}R.$ We can use Ideal gas equation and the laws of thermodynamics to solve the given question.
Complete step by step answer:
Ideal gas equation, $PV = nRT$
First law of thermodynamics: $\Delta U = q + w$
We have $PV = nRT$
Where, P is pressure of ideal gas
V is volume of ideal gas
n is number of molecules
T is temperature
R is the ideal gas constant.
It is given that $n = 1$mole
In step CA:
Let us say, ${P_1}{V_1} = nR{T_1}$ . . . (1)
\[{P_1} = 2\] atm
${V_1} = 10$litres
$\therefore 2 \times 10 = 1 \times 0.821 \times {T_1}$
$\therefore {T_1} = 243.60K$
In step BC:
Volume is constant
$ \Rightarrow {P_2}{V_1} = 1R{T_2}$ …. (2)
Divide equation (1) by equation (2)
$\dfrac{{{P_1}{V_1}}}{{{P_2}{V_1}}} = \dfrac{{R{T_1}}}{{R{T_2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}} = \dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}}$
$\dfrac{2}{{20}} = \dfrac{{243.60}}{{{T_2}}}$
${T_2} = 10 \times 243.6$
$ = 2436K$
Now we have to find $\Delta U$i.e. change in energy
1) From A to B
${\left( {\Delta U} \right)_{AB}} = n{C_v}\Delta T$
$ = 1 \times \dfrac{3}{2}R({T_2} - {T_1})$
$ = 1 \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times 2 \times (246 - 243.6)$$\because R = 2$
$ = 6577.2cal$
2) From B to C
${\left( {\Delta U} \right)_{BC}} = n{C_v}R({T_1} - {T_2})$
$ = 1 \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times 2 \times (243.6 - 2436)$
$ = - 3577.2cal$
3) Process C to A is isothermal process
$\therefore {\left( {\Delta U} \right)_{CA}} = n{C_v}({T_1} - {T_1})$ (As there is no change in temperature.)
$ = 0$
Now the $\Delta U$of cycle is
\[\Delta U = {\left( {\Delta U} \right)_{AB}} + {(\Delta U)_{BC}} + {(\Delta U)_{CA}}\]
$ = 6577.2 - 6577.2 + 0$
$ = 0$
$\therefore $Net internal energy of cycle is zero
Now calculating the work done
1) A to B is isobaric process, so work done is
${\left( W \right)_{AB}} = - P\Delta V$
$ = - P({V_B} - {V_A})$
$ = - 20(10 - 1)$
$ = 180L$ atm
$ = - 180 \times \dfrac{2}{{0.0821}}cal$
$ = - 4384.9cal$
2) Volume is constant from B to C.
$\therefore \Delta V = 0$i.e. change in volume is zero.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{BC}} = 0$
Now, for finding $q$we use, the ${1^{st}}$law of thermodynamics
$\Delta U = q + w$
$q = \Delta U - w$
1) For A to B
${q_{AB}} = \Delta {U_{AB}} - {W_{AB}}$
$ = 6577.2 - ( - 4384.9)$
$ = 10962.1cal$
2) For B to C
${q_{BC}} = \Delta {U_{BC}} - {W_{BC}}$
$ = - 6577.2 - 0$
$ = - 6577.2cal$
3) For C to a
${q_{CA}} = \Delta {U_{CA}} - {W_{CA}}$
$ = 0 - 1122$
$ = - 1122cal$
$\therefore $For total cycle
${q_{cycle}} = {q_{AB}} + {q_{BC}} + {q_{CA}}$
$ = 10962.1 - 6577.2 - 1122$
$ = 3262.9cal$
Note: Positive sign indicates increase in energy and negative sign indicates the decrease in energy. To solve such types of questions, we need to have a clear idea about in which process temperature is constant and in which process volume is constant etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Ideal gas equation, $PV = nRT$
First law of thermodynamics: $\Delta U = q + w$
We have $PV = nRT$
Where, P is pressure of ideal gas
V is volume of ideal gas
n is number of molecules
T is temperature
R is the ideal gas constant.
It is given that $n = 1$mole
In step CA:
Let us say, ${P_1}{V_1} = nR{T_1}$ . . . (1)
\[{P_1} = 2\] atm
${V_1} = 10$litres
$\therefore 2 \times 10 = 1 \times 0.821 \times {T_1}$
$\therefore {T_1} = 243.60K$
In step BC:
Volume is constant
$ \Rightarrow {P_2}{V_1} = 1R{T_2}$ …. (2)
Divide equation (1) by equation (2)
$\dfrac{{{P_1}{V_1}}}{{{P_2}{V_1}}} = \dfrac{{R{T_1}}}{{R{T_2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}} = \dfrac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_2}}}$
$\dfrac{2}{{20}} = \dfrac{{243.60}}{{{T_2}}}$
${T_2} = 10 \times 243.6$
$ = 2436K$
Now we have to find $\Delta U$i.e. change in energy
1) From A to B
${\left( {\Delta U} \right)_{AB}} = n{C_v}\Delta T$
$ = 1 \times \dfrac{3}{2}R({T_2} - {T_1})$
$ = 1 \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times 2 \times (246 - 243.6)$$\because R = 2$
$ = 6577.2cal$
2) From B to C
${\left( {\Delta U} \right)_{BC}} = n{C_v}R({T_1} - {T_2})$
$ = 1 \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times 2 \times (243.6 - 2436)$
$ = - 3577.2cal$
3) Process C to A is isothermal process
$\therefore {\left( {\Delta U} \right)_{CA}} = n{C_v}({T_1} - {T_1})$ (As there is no change in temperature.)
$ = 0$
Now the $\Delta U$of cycle is
\[\Delta U = {\left( {\Delta U} \right)_{AB}} + {(\Delta U)_{BC}} + {(\Delta U)_{CA}}\]
$ = 6577.2 - 6577.2 + 0$
$ = 0$
$\therefore $Net internal energy of cycle is zero
Now calculating the work done
1) A to B is isobaric process, so work done is
${\left( W \right)_{AB}} = - P\Delta V$
$ = - P({V_B} - {V_A})$
$ = - 20(10 - 1)$
$ = 180L$ atm
$ = - 180 \times \dfrac{2}{{0.0821}}cal$
$ = - 4384.9cal$
2) Volume is constant from B to C.
$\therefore \Delta V = 0$i.e. change in volume is zero.
$ \Rightarrow {W_{BC}} = 0$
Now, for finding $q$we use, the ${1^{st}}$law of thermodynamics
$\Delta U = q + w$
$q = \Delta U - w$
1) For A to B
${q_{AB}} = \Delta {U_{AB}} - {W_{AB}}$
$ = 6577.2 - ( - 4384.9)$
$ = 10962.1cal$
2) For B to C
${q_{BC}} = \Delta {U_{BC}} - {W_{BC}}$
$ = - 6577.2 - 0$
$ = - 6577.2cal$
3) For C to a
${q_{CA}} = \Delta {U_{CA}} - {W_{CA}}$
$ = 0 - 1122$
$ = - 1122cal$
$\therefore $For total cycle
${q_{cycle}} = {q_{AB}} + {q_{BC}} + {q_{CA}}$
$ = 10962.1 - 6577.2 - 1122$
$ = 3262.9cal$
Note: Positive sign indicates increase in energy and negative sign indicates the decrease in energy. To solve such types of questions, we need to have a clear idea about in which process temperature is constant and in which process volume is constant etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




