
How can one identify benzylic carbons?
Answer
547.2k+ views
Hint: To identify a benzylic carbon, first we should know about the benzylic position and benzylic position is that position which is present exactly next or to the first position of the benzene ring.
Complete answer:
As we know that benzylic position is the adjacent next attached position after a benzene ring, so benzylic carbon is that saturated carbon which is directly attached to the benzene ring by occupying first position. Some examples if benzylic carbons are as follow:
-In the ethyl benzene, benzylic carbon is shown as follow:
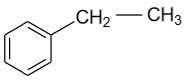
In the above diagram carbon which is present in ${\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ group is a benzylic carbon, because it is saturated in nature as well as attach to the benzene ring directly.
-In 1-ethyl-2-methyl Benzene, benzylic carbon is shown as follow:
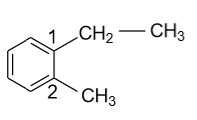
In the above diagram two benzylic carbons are present on the first as well as on the second position of the benzene ring. Carbon of ${\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ of ethyl group on the first position & carbon of ${\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$ group on the second position are saturated in nature and directly attached to the benzene ring, that’s why they are benzylic carbon of the above compound.
Note:
Here some of you may get confused by hearing the name benzylic carbon & may think that carbons of the benzene ring are termed as benzylic carbon, but that assumption will be wrong and you will never identify correct benzylic carbon.
Complete answer:
As we know that benzylic position is the adjacent next attached position after a benzene ring, so benzylic carbon is that saturated carbon which is directly attached to the benzene ring by occupying first position. Some examples if benzylic carbons are as follow:
-In the ethyl benzene, benzylic carbon is shown as follow:

In the above diagram carbon which is present in ${\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ group is a benzylic carbon, because it is saturated in nature as well as attach to the benzene ring directly.
-In 1-ethyl-2-methyl Benzene, benzylic carbon is shown as follow:

In the above diagram two benzylic carbons are present on the first as well as on the second position of the benzene ring. Carbon of ${\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ of ethyl group on the first position & carbon of ${\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$ group on the second position are saturated in nature and directly attached to the benzene ring, that’s why they are benzylic carbon of the above compound.
Note:
Here some of you may get confused by hearing the name benzylic carbon & may think that carbons of the benzene ring are termed as benzylic carbon, but that assumption will be wrong and you will never identify correct benzylic carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




